
Why is saving always equal to actual investment?
Why is saving always equal to actual investment? (a) Equilibrium in the economy occurs only when planned investment and planned savings are equal. Such equilibrium is rare because savers and investors are different people who save and invest with different motives. (Mind, actual savings and actual investments are always equal at all levels of ...
Why stock dividends may be a good investment option?
Five of the primary reasons why dividends matter for investors include the fact they substantially increase stock investing profits, provide an extra metric for fundamental analysis, reduce overall portfolio risk, offer tax advantages, and help to preserve the purchasing power of capital.
Why dividend investors should know about high yield?
When stocks sell off, the dividend yield naturally increases. So, you can assume that higher yield stocks are cheaper, and they are often cheap for a reason. Just because the market views them as higher risk doesn’t mean they aren’t worth an investment, though.
Why investment in mutual fund is risk less?
These mutual funds invest in different securities, based on the previous performance and credit ratings. Usually, the funds are invested in high credit quality instruments to generate assured returns. It also ensures that the investment stays in less volatile sector compared to equity funds.
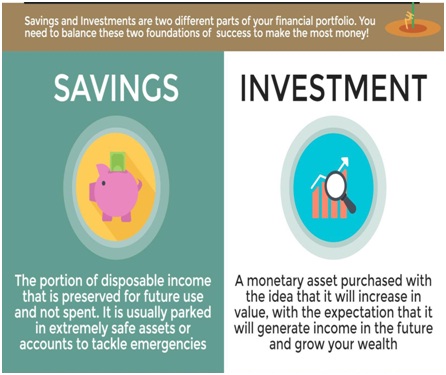
Are savings equal to investment?
Saving and Investment Equality # Saving Always Equals Investment (Accounting Equality): Keynes defined saving and investment in such a way that in his theory, saving always equals investment. This is called accounting equality. Accounting equality between saving and investment is also called logical identity.
Why saving and investment are equal in closed economy?
In the basic, closed economy model, you are right that Savings=Investment. The reason for this is because, in this model, growing capital stock is not the only item taken into account in Investment. The other item is inventory accumulation.
How are investment and savings related?
The biggest difference between saving and investing is the level of risk taken. Saving typically results in you earning a lower return but with virtually no risk. In contrast, investing allows you the opportunity to earn a higher return, but you take on the risk of loss in order to do so.
How are savings and investment related quizlet?
Saving your money is staying at the same amount and it is there when you need it. Investing is when you make money off of the money you put in and not all investments are easy to get money out of when you need it.
Which flexibility brings equality between saving and investment?
Interest flexibility brings equality between saving and investment.
What is savings and investment answer?
Savings represent that part of the person's income which is not used for consumption. Investment refers to the process of investing funds in capital assets, with a view to generate returns. Savings are made to fulfill short-term or urgent requirements.
What is investment in economics?
In macroeconomics, investment is the amount of goods (consumer goods or capital goods) produced or purchased per unit time which are not consumed at the present time. In other words, "investment" is the amount of goods saved for future use which is by definition "Savings".
Is saving equal to investment?
Now, if the word "Investment" means amount of capital goods produced or purchased per unit time which are not consumed at the present time and the word "Saving" means amount of consumer goods produced or purchased per unit time which are not consumed at the present time, "Saving" is not necessarily equal to "Investment".
Does Joe have to earn money to dissave?
However, Joe has to either earn an income (and therefore, produce something himself) or he has to dissave. In the first case, Joe has produced 500 output and earned an income of 500. He spends his income on a car, but Amanda saves the money.
When investment exceeds saving, does the rate of interest rise?
ADVERTISEMENTS: Similarly, when investment exceeds saving, rate of interest rises to discourage investment to increase saving. Thus, the disequilibrium between savings and investment is corrected by changes the rate of interest.
How does Keynes explain the equality between saving and investment?
Keynes made it known clearly that the equality between saving and investment is brought about by the changes in the national income (and not by the rate of interest as stressed by the classicals). Let us see what happens when investment exceeds saving (by Rs. 20 crores) at a certain level of income (say Rs. 100 crores). This will increase national income through multiplier to such an extent that savings out of the increased income would be equal to the investment (or the excess of investment, i.e., Rs. 20 crores).
What is Keynes's theory of saving and investment?
Keynes defined saving and investment in such a way that in his theory, saving always equals investment. This is called accounting equality. Accounting equality between saving and investment is also called logical identity. The logic behind this equality is as under.
What is income change?
Thus, income change is the mechanism through which the equality between saving and investment is established. Further, the novelty of Keynes’s approach to saving and investment equality lies in the belief that they can be equal at less than full employment.
What is the difference between classical and classical economists?
There are, however, important differences between classical and Keynes. Firstly, classical believed that saving and investment equality is brought about by the rate of interest. When saving tends to exceed investments, the rate of interest falls to discourage savings on the one hand and encourage investment on the other.
Is saving and investment in equilibrium?
If the economy is in motion and the variables are always in a normal functional relationship to each other, then saving and investment are not only equal but may also be in equilibrium. But if the process of change involves lagged adjustment of certain variables, this will not be the case.
Does Keynes say saving always equals investment?
At some places, in his ‘General Theory’, Keynes says that saving always equals investment. At other places, he writes that saving equals investment only in equilibrium. This double meaning and dual approach to equality between saving and investment has been a source of great confusion for many writers and readers.
Why are savings and investment not equal?
This is firstly because saving and investment are made by two different classes of people. While investment is undertaken by entrepreneurial class of the society, saving is done by the general public.
What is the sense in which savings and investment are always equal?
The sense in which savings and investment are always equal refers to the actual savings and actual investment made in the economy during a year. They are also called ex-post saving and ex-post investment.
What is the relationship between saving and investment?
Many economists before J.M. Keynes were generally of the view that saving and investment are generally not equal; they are equal only under condition of equilibrium.
What is the second sense of saving and investment?
ADVERTISEMENTS: The second sense in which saving and investment words are used is that in a certain year how much saving or how much investment people of the country desire or intend to do. Therefore, saving and investment in this sense are known as desired, intended or planned savings and investment.
What did Keynes think about equality?
Besides, they thought that equality between saving and investment is brought about by changes in the rate of interest. Keynes in his famous work “General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money” put forward the view that saving and investment are always equal.
What happens if savings declines?
On the other hand, if in any year saving declines, it will result in the unplanned decline in the inventories of consumer goods with the traders and manufacturers. This unintended decline in inventories will mean the fall in actual investment. In this way, investment will decline to become equal to the lower savings.
Why are ex post and ex post investments always equal?
For instance, when more investment is undertaken by the entrepreneurs how actual saving becomes equal to this larger investment and if the saving falls how investment will become equal to smaller savings.
What is investment in accounting?
Investment is the process of capital formation plus addition to stocks and therefore is an addition to the income flow. The main reason for the apparent paradox in the above two statements is that both terms, savings and investment, are defined differently in each statement.
When any discrepancy between the plans to save and invest occurs a change in the level of income?
When any discrepancy between the plans to save and invest occurs a change in the level of income brings about a state of disequilibrium, and as income continues to change so do these plans get readjusted until a level of income is reached where planned saving and investment are once more equal to each other.
What is consumption function?
The table gives a consumption function, from which saving plans can be obtained. Assuming that planned investment is autonomous and that all household plans are realised, an equilibrium level of income can be calculated.
Why is the desired investment function horizontal?
The desired investment function is horizontal because in Keynes’ model all investment is autonomous, i.e., is assumed to be independent of national income. National income equilibrium occurs at point E where the desired saving function intersects the desired investment function.
Why do businesses hold inventories?
Some of the inventories business firms hold is planned (desired), because businesses require inventories to survive (i.e., because production and sales do not coincide). Some of it is unplanned (undesired) — business may be surprised by a brief recession that spoils their sales forecasts.
What is the equation for aggregate output and income?
As aggregate output and income are always equal and consumption is identical in both places, the rest of the equation must also be equal or Y = C + I and Q = GNP = C + S and if Y = Q, C + S = C + I or S = I.
Is actual saving equal to actual investment?
Therefore, we observe that actual (ex-post) saving is always equal to actual (ex-post) investment. But planned or desired (ex-ante) saving is equal to planned or desired (ex-ante) investment only when national income is in equilibrium.
Why is it assumed that the level of saving will equal the level of investment?
This is because investment is determined by available savings in the economy. If there is an increase in savings, then banks can lend more to firms to finance investment projects.
How does savings affect interest rates?
Levels of savings are influenced by 1 Interest rates – higher interest rates make it more attractive to save 2 Confidence – low confidence can encourage households to save more
What is savings ratio?
Typically surplus income is saved in a bank account. But, it could be saved as cash (cash under the bed e.t.c) The Savings Ratio is the % of income that is saved.
What is investment in economics?
Investment in economics is defined as an addition to the capital stock. ( Gross fixed capital formation) For example, investment can involve spending on factories or new capital. Investment can also involve spending on human capital such as investment in training and education. Levels of investment are affected by.
Why are interest rates higher?
Interest rates – higher interest rates make investment more expensive (cost of borrowing goes up) Confidence – if firms are confident, they are more willing to invest. Economic growth – An increase in the rate of economic growth will encourage firms to invest to meet future demand.
What is the equality between saving and investment?
Equality between saving and investment is regarded as an essential condition of equilibrium level of income, output and employment by Keynes as well as classical economists. ADVERTISEMENTS: But, their approach and views regarding the phenomenon are altogether different and controversial.
What is the meaning of saving and investment equality?
According to Keynes, the saving-investment equality is a condition of equilibrium at any level of employment, and not necessarily always the full employment level. More realistically, it is usually at less than full employment level. Again, savings and investment are brought into equality by income changes.
What is the classical view of economics?
The Classical View: The classical economists believed in the economy’s equilibrium at full employment level. In their view, saving- investment equality is brought about by the mechanism of the rate of interest. Rate of interest, thus, is regarded as a strategic variable. The classicists held that if saving and investment are equal at a time, ...
What does Keynes mean by "saving" and "investment"?
Keynes states that “saving” and “investment” are not only equal but also identical. He defined saving as the excess of income over consumption. He defined investment as the increment of capital equipment or in other words, the addition which is made to the stock of real capital.
What is the classical notion of monetary equilibrium?
Thus, the classical notion of monetary equilibrium is one in which savings flow automatically into an equal amount of investment via changes in the interest rate to give full-employment level of income.
What is income in Keynes's theory?
To Keynes, income is equal to the value of current output. Since investment causes an increment in capital equipment, which, in other words, is an addition made to the stock of real capital, this addition represents the unconsumed output in a given period. In other words, it is known as current investment.
When will income continue to fall?
Income will continue to fall until the saving out of the lower income is equal to the reduced investment. Similarly, if investment increases, saving remaining constant (thus, investment exceeding saving), income will rise until the saving out of the higher income is equal to the increased investment.
