What are facts about smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle facts for kids. Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two subgroups; the single-unit (unitary) and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit cells, the whole bundle or sheet contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle cells are found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines ...
Is skelatal muscle involuntary?
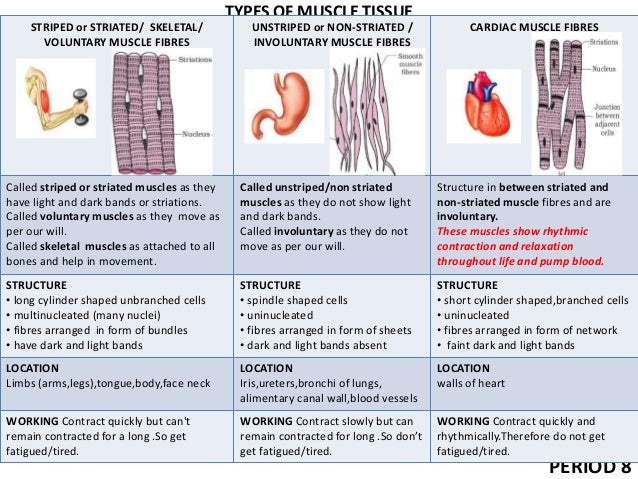
skeletal muscle – attached to the skeleton - this is voluntary Involuntary muscles are not under our conscious control which means we can't make them contract when we think about it. Voluntary...
Is muscle voluntary or involuntary?
Voluntary muscles are those whose movement can be controlled at will or conscious control, while involuntary muscles are those whose movement can not be controlled at will or without conscious control or that work involuntarily, i.e., automatic. Involuntary muscles include smooth muscles and cardiac muscles. What are the voluntary acts?
Is the nervous system voluntary or involuntary?
The voluntary nervous system (somatic nervous system) controls all the things that we are aware of and can consciously influence, such as moving our arms, legs and other parts of the body. The involuntary nervous system (vegetative or autonomic nervous system) regulates the processes in the body that we cannot consciously influence.

How do involuntary muscles differ from voluntary muscles?
From a histological point of view, involuntary muscles differ from voluntary muscles because the fibers from which they are composed do not consist of striations and thus, they are characterized by a structure almost completely uniform, defined as “smooth” musculature.The cells that make the involuntary muscles are crossed by thin filaments, called myofibrils, which are part contractile. Compared to striated muscles, smooth muscles contract and relax more slowly.
What is an example of an involuntary muscle?
Their contraction is regulated by the autonomic nervous system. An example of an involuntary muscle is the heart. When the involuntary muscles of the hollow organs (such as blood vessels and intestine) contract, it causes a reduction in the wall surfaces in which the muscle fibers themselves are found in. When the contraction phase follows ...
What function do involuntary muscles serve?
The main function of the muscular system is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that have the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. They also perform different functions such as: enable the body to maintain posture and body position (sitting or standing positions), stabilize and strengthen joints as well as produce heat to maintain normal body temperature.
What is the name of the muscle that is not affected by voluntary nerve activity?
Involuntary muscles, also known as “white muscles” or “smooth muscles”, are muscles in the human body whose contraction is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Involuntary muscles include all muscles whose activity is independent and not affected by voluntary nerve activity.
Which muscle contractes more slowly?
Compared to striated muscles, smooth muscles contract and relax more slowly. Involuntary muscles are present in the walls of the digestive system, blood vessels, bronchi, uterus and bladder.
What happens during contraction phase?
When the contraction phase follows distension, the surfaces of the walls of the organs return to their usual dimensions. The repetition of the mechanism is essential to allowing the regulation of blood vessel tone and giving rise to movements vital for the well being of the organism, such as intestinal peristalsis.
Why are smooth muscles called involuntary muscles?
smooth muscles are called involuntary muscles because they are not under our control and work at all the time .
What is voluntary muscle?
Voluntary muscles : Those muscles which can be controlled by us .
What is the involuntary muscle?
See Article History. Alternative Title: involuntary muscle. Smooth muscle, also called involuntary muscle, muscle that shows no cross stripes ...
What is a smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle, also called involuntary muscle, muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. It consists of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single, centrally located nucleus.
Where is smooth muscle located?
Because vertebrate smooth muscle is located in the walls of many hollow organs, the normal functioning of the cardiovascular, respiratory,... This article was most recently revised and updated by Richard Pallardy, Research Editor.
Why are smooth muscles called unstriated muscles?
Smooth muscles are called unstriated muscles because these muscles show no cross striations and look smooth . Therefore , are called non striated muscles or unstriped muscles.
Why aren't my muscles striated?
Dear reader, they are not striated because these muscles are not in the control of human or any animal such as the muscles of the intestine and the ones in hollow internal organs such as blood, pancreas etc. Their movement cannot be controlled unlike the hands and feet through the conscious mind but rather by the subconscious mind on which we consciously have no control and it is also supposed as a brain of its own.
What is a muscle that shows cross striations called?
In contrast to this , the muscle which shows cross striations are called striated muscles or striped muscles
What are the different types of muscles?
Muscles are classified into 3 types, cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles. Cardiac muscle is located in the heart, striated in appearance, and does involuntary contractions. Smooth muscles are located in internal organs, except in heart, non-striated in appearance, and do involuntary contractions. Skeletal muscles are located in bones, striated in appearance, and do voluntary contractions.
How to build muscle?
Muscle can be built by either bodybuilding style training or mixing powerlifting with some volume.
Why do people have a V-shaped torso?
In fact people who swim, for example, if from a young age, tend to have a v-shaped torso or “V-taper, already in development, from the work done by the back chest shoulders from swimming. Whether not those muscles are “ripped,” or less dense, those muscles have become substantial through developing the essential mind-muscle connections from the brain to those muscles, arguably (or compellingly) more important than the appearance of a muscle at a given time.
How do swimmers differ in their physique?
The differences in the appearance of their physiques can be accounted for by the resistance involved in the work being done. If it were possible to change the density of water or the viscosity (rate of flow) of the liquid in which they are doing their work, the muscles of swimmers would correspondingly develop in relation to the change in resistance involved and the forces required to propel oneself through that medium.