Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of i…
Why is ATP important to all living things?
Reasons Why Photosynthesis Is Important
- It is the number one source of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- It contributes to the carbon cycle between the earth, the oceans, plants and animals.
- It contributes to the symbiotic relationship between plants, humans and animals.
- It directly or indirectly affects most life on Earth.
- It serves as the primary energy process for most trees and plants.
What are the roles of ATP?
Some Pros and Cons of ATP Supplements
- Improves muscle function, including muscle mass
- Enhances blood circulation and oxygen flow
- Reduces fatigue
- Accelerates recovery period
- Most are affordable
- Most have natural ingredients
- Most are vegan
What makes the most ATP?
Which yields the most ATP?
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP.
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain/Chemiosmosis): 28 ATP.
- Fermentation: 2 ATP.
What causes low ATP levels?
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or softening of the bones.. Causes include alcohol use disorder, refeeding in those with malnutrition, diabetic ketoacidosis, burns, hyperventilation, and certain ...

Why is ATP important?
Image Credit: aerogondo/iStock/Getty Images. ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate, a crucial chemical in human metabolism that has been called "chemical currency" because the cells use it as a direct source of energy. You make ATP when you burn sugars and other nutrients, and your cells consume ATP when they engage in activities like building ...
Why do cells use ATP?
For instance, since your cells can either burn nutrients immediately or store them for later use, the cells use ATP to help them determine which they should do. If a cell has plenty of ATP, the ATP signals the cell to store nutrients rather than burning them. If a cell is low on ATP, however, that signal indicates that the cell should burn ...
How much ATP can a human body make?
Even though human cells can make about 30 ATP per glucose molecule -- and can also make large and varying amounts of ATP from burning protein and fat -- not all glucose metabolism results in the production of that much ATP. You can only make two ATP molecules per glucose if you're burning sugar without oxygen, a process called anaerobic metabolism.
How many molecules of ATP are produced by the cells that break down glucose?
They use the energy liberated from breaking down a single molecule of glucose to make approximately 30 molecules of ATP.
What is the chemistry of ATP?
ATP Chemistry. ATP is a relatively small molecule that serves as an "energy intermediate" in human metabolism. In essence, your cells extract the chemical energy from various nutrient molecules like proteins, carbohydrates and proteins, and use the chemical energy to make ATP.
What is ATP short for?
A woman performing high energy jumping jacks in a gym studio. ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate, a crucial chemical in human metabolism that has been called "chemical currency" ...
Why do cells need energy?
Cells need energy to make large molecules, like hormones. Muscle cells use ATP to produce movement. As a cell makes a hormone molecule, it breaks down molecules of ATP and uses the energy to make new bonds between smaller molecules in order to produce a larger one, explain Drs. Garrett and Grisham. When a muscle cell contracts, it uses large ...
What is the role of ATP in the cell?
Not only does it provide us energy, ATP is responsible for an array of other vital functions, like transporting macromolecules in and out of the cell and through the cell membrane, and being an extracellular and intracellular signaling molecule (an important function in both the central and peripheral nervous system).
How Does ATP Give Energy?
To understand energy synthesis in our metabolism, understanding three key molecules — AMP, ADP, and ATP is essential.
How is energy synthesized in the body?
Energy in our body is synthesized from an exothermic reaction. Exothermic reaction = Reaction that releases energy. » An ATP molecule consists of three phosphate groups linked together. » Under certain conditions, this molecule can lose one or two phosphate groups. » The reaction wherein a phosphate bond is broken is an exothermic reaction.
What is the molecule that powers plants, animals, and every cell within them?
ATP is the one molecule that powers plants, animals, and every cell within them. This incredible source incessantly drives every thought and action of ours — every second of the day!
What is the name of the substance that is used as a currency of energy?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). Molecules of this essential substance are often referred to as “currency of energy.”. Though we have several sources of energy in our body, ATP is the only one that is directly usable by any part, muscle, or cell! ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. Empirical Formula. C 10 H 16 N 5 O 13 P 3.
What is the term for the use of all the oxygen in a muscle?
Anaerobic/Fast Glycolysis. » When a muscle is rigorously exerted, it uses up all the available oxygen. » Muscles are always stocked up on glucose, which is stored in the form of glycogen. (One molecule of glycogen has several molecules of glucose packed together.)
What are the parts of ATP?
Instead of looking at it like a big molecule, break it down into three smaller parts; that way, it’s easier understood and quicker learned! The pentagon-shaped structure in the molecular diagram, made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen is the core of an ATP molecule.
Why is ATP important for metab?
ATP is a metabolically important molecule because it is a kinetically stable molecule whose highly exergonic hydrolysis can be coupled to drive otherwise endergonic reactions to completion.
Why is ATP used in phosphorylation?
ATP is used in cells to drive anabolic reactions that require energy to accomplish. In phosphorylation, ATP is hydrolyzed and one or two phosphates are transferred to another molecule raising its energy and enabling it to participate in biochemical reactions favorable to the cell that would otherwise not occur.
How long does ATP last?
Once formed, an ATP molecule typically lasts only one minute or less before its third phosphate group splits off, energy is transferred to something else, and the ATP becomes ADP—ready to have another go. If ATP production ceases, we die within a few minutes because our metabolism shuts down.
Why is ATP called an energy rich molecule?
ATP (Adenosine triphospahte) is called an energy rich molecule because of the large negative free energy of its hydrolysis (And has nothing to do with high bond energy). 30.5 kilo Joules or 7.3 kilo calorie energy is liberated after hydrolysis of one ATP molecule to form ADP (Adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate.
How many molecules of ATP are needed for reduction?
But, for each turn of the cycle, reduction requires 2 molecules of ATP and 2 of NADPH. Regeneration - The intermediate product formed after reduction if phosphorylised, will form RuBP. To let the cycle continue, this is important. And thus, for the phosphorylation to 1 RuBP, 1 ATP molecule is required.
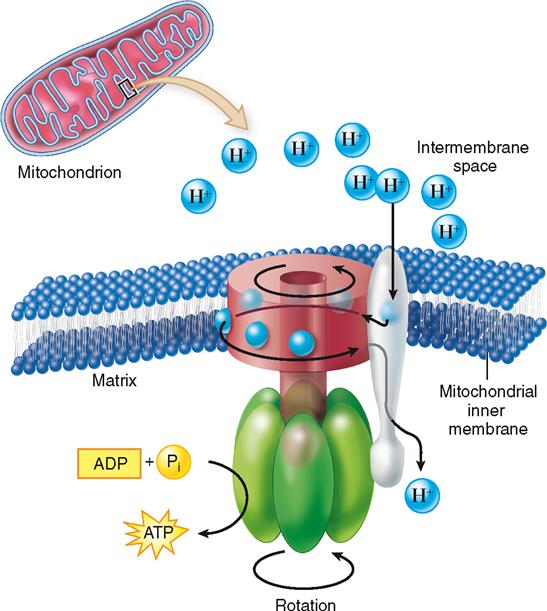
What is the function of the mitochondria in aerobic metabolism?
During aerobic metabolism, oxygen is pulled from the blood and into the cell with the glucose. The mitochondria uses the oxygen to burn the glucose into heat energy and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is then used to store or release the energy created, depending on the cell's needs. Related Answer. Venu Pandit.
What is the last product of glycolysis?
The last product of glycolysis, pyruvate or pyruvic acid, is reduced to lactate (lactic acid) by lactate dehydrogenase. And in this reaction is also NADH used, so some NAD+ ready for use in glycolysis is formed. Alcoholic fermentation has two steps when compared to one-step lactic acid fermentation.
Why is metabolism important for cells?
Metabolism is important for cells because the processes keep organisms alive and allow them to grow, reproduce or divide.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to make ATP?
There are actually multiple metabolism processes. Cellular respiration is a type of metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to make adenosine triphosphate, or ATP.
What Is Cell Metabolism Like in Different Types of Prokaryotes?
You can categorize prokaryotes into different groups based on their metabolism. The main types are heterotrophic, autotrophic, phototrophic and chemotrophic. However, all prokaryotes still need some type of energy or fuel to live.
What are the different types of metabolic pathways?
The basic types of metabolic pathways include heterotrophic, autotrophic, phototrophic and chemotrophic reactions. The type of metabolism that a prokaryote has can influence where it lives and how it interacts with the environment. Their metabolic pathways also play a role in ecology, human health and diseases.
What are the main steps of photosynthesis?
Plants, algae and cyanobacteria use photosynthesis. The main steps are the light-dependent reactions, and the Calvin cycle or light-independent reactions. The main reactants are light energy, carbon dioxide and water, while the main products are glucose and oxygen. Metabolism in prokaryotes can vary.
What is the term for the process of converting food into energy?
In cell biology and molecular biology, metabolism refers to the biochemical reactions that happen inside organisms to produce energy. The colloquial or nutritional use of metabolism refers to the chemical processes that happen in your body as you convert food into energy.
What is the process of cellular metabolism?
Cellular Metabolism. Cell metabolism is the series of processes that take place in living organisms to sustain those organisms. In cell biology and molecular biology, metabolism refers to the biochemical reactions that happen inside organisms to produce energy.
What is ATP in the cell?
Since 1929, when it was discovered that ATP is a substrate for muscle contraction, the knowledge about this purine nucleotide has been greatly expanded. Many aspects of cell metabolism revolve around ATP production and consumption. It is important to understand the concepts of glucose and oxygen consumption in aerobic and anaerobic life and to link bioenergetics with the vast amount of reactions occurring within cells. ATP is universally seen as the energy exchange factor that connects anabolism and catabolism but also fuels processes such as motile contraction, phosphorylations, and active transport. It is also a signalling molecule in the purinergic signalling mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss all the main mechanisms of ATP production linked to ADP phosphorylation as well the regulation of these mechanisms during stress conditions and in connection with calcium signalling events. Recent advances regarding ATP storage and its special significance for purinergic signalling will also be reviewed.
How many molecules of ATP are produced during the process of ATP?
During all these processes, only one molecule of ATP (or GTP) is produced, but three molecules of NADH and one of FADH2 (plus one molecule of NADH from pyruvate dehydrogenase), which provide electrons for respiratory chain, are also generated and subsequently result in the production of large amounts of ATP (discussed later).
What is the first phase of phosphorylation of glucose?
In the first phase, glucose is phosphorylated at the hydroxyl group on C-6 by hexokinase (HK) generating glucose 6-phosphate . This event is fundamental to “trap” the hexose within the cell. In fact, the existence of a transporter of phosphorylated hexose has not been reported in mammalian cells.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis . Glycolysis is a process by which glucose is partially converted through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions into two molecules of pyruvate. Some mammalian cell types (erythrocytes, sperm) and tissues (brain, renal medulla) are able to survive only (or mostly) on the energy derived from glycolysis.
How many molecules of ATP are in the second phase of glycolysis?
Thus, the second phase of glycolysis provides four molecules of ATP and two of NADH per molecule of glucose, paying the investment of the preparatory phase. The final balance of this process is then: two molecules of ATP, two of NADH (that could directly feed into the respiratory chain), and two of pyruvate.
What happens when glucose is converted to pyruvate?
In the first process, when glucose is converted into pyruvate, the amount of ATP produced is low. Subsequently, pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) which enters the TCA cycle, enabling the production of NADH.
What is the main energy source for cellular metabolism?
In general, the main energy source for cellular metabolism is glucose, which is catabolized in the three subsequent processes—glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA or Krebs cycle), and finally oxidative phosphorylation—to produce ATP. In the first process, when glucose is converted into pyruvate, the amount of ATP produced is low. Subsequently, pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) which enters the TCA cycle, enabling the production of NADH. Finally, NADH is used by the respiratory chain complexes to generate a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, necessary for the production of large amounts of ATP by mitochondrial ATP synthase. In addition, it should be mentioned that acetyl-CoA can be generated also by lipid and protein catabolism.