- to understand the compaction characteristic of different soil with the change in the moisture content.
- to determine the optimum moisture content at which the given soil become most dense and has maximum dry density
How much is a compaction test?
Soil Compaction Test Cost. Soil compaction tests cost $75 to $150 each plus $200 to $500 for an onsite technician if it’s required by local regulations. This investigates the density after compaction. You’ll find it used most often under foundations and for roads. Perc Test. Perc tests cost $150 to $3,000.
Why is compaction test done?
- An increase in strength of soils
- A decrease in compressibility of soils
- A decrease in permeability of soils
What is the compaction test?
Definition of compaction test. A laboratory compacting procedure to determine the optimum water content at which a soil can be compacted so as to yield the maximum density (dry unit weight). The method involves placing (in a specified manner) a soil sample at a known water content in a mold of given dimensions, subjecting it to a compactive effort of controlled magnitude, and determining the resulting unit weight (ASCE, 1958, term 74).
How do you do a soil compaction test?
How do you do a soil compaction test? The procedure of the Proctor Compaction Test consists of the following steps: Obtain about 3 kg of soil. Pass the soil through the No. Weight the soil mass and the mold without the collar (Wm). Place the soil in the mixer and gradually add water to reach the desired moisture content (w).

What is the purpose of compaction?
Compaction is a process of increasing soil density and removing air, usually by mechanical means. The size of the individual soil particles does not change, neither is water removed. Purposeful compaction is intended to improve the strength and stiffness of soil.
Why is soil compaction done in laboratory?
Within the framework of engineering applications, compaction is particularly useful as it results in: An increase in strength of soils. A decrease in compressibility of soils. A decrease in permeability of soils.
Why we do Proctor compaction test?
The Proctor Compaction Test establishes the maximum unit weight that a particular type of soil can be compacted to using a controlled compactive force at an optimum water content.
What are the benefits of soil compaction?
The benefits of compaction are:Increased soil strength.Increased load-bearing capacity.Reduction in settlement (lower compressibility).Reduction in the fl ow of water (water seepage).Reduction in soil swelling (expansion) and collapse (soil contraction).Increased soil stability.Reduction in frost damage.
What is standard compaction test?
Standard Compaction Test Proctor compaction test measures the maximum unit load that a particular type of soil can be compacted to use a controlled compact force at an optimal water content.
What does 95% Proctor density mean?
For example, specifications often require compaction to be 95 percent of Standard Proctor. This means the on-site soil density must be equal to 95% of the maximum achievable compaction.
How many compaction tests are required?
Not less than 2 tests per day; One test per 500 sq. m.
What is compaction factor of soil?
Compaction factor is defined as the ratio of Loose thickness divided by the designed thickness when the field trials are being conducted. Similarly in laboratory condition the compaction factor is defined as Weight of soil required at defined compaction divided by the weight of loose soil for the same volume.
Where is soil compaction used?
In construction. Soil compaction is a vital part of the construction process. It is used for support of structural entities such as building foundations, roadways, walkways, and earth retaining structures to name a few.
What are the two aims of compaction?
The principal reason for compacting soil is to reduce subsequent settlement under working loads. Other purposes of soil compaction are: Compaction of soil increases the shear strength and load bearing capacity of the soil.
How do you test soil for compaction?
A lab technician will start by sifting and moisture conditioning of the soil. Once the soil is prepped the soil will go into a cylindrical mold to be compacted at various moisture contents and weighted. The test is to see how much of the material can be compacted into the same volume at the various amounts of moisture.
What types of equipment are used for soil compaction?
Compaction EquipmentVibrating Plates. Hand-guided equipment, including one-way and reversible types.Pedestrian Rollers. ... Trench Compactors. ... Tandem Rollers. ... Self-Propelled Rollers. ... Pneumatic-Tyred Rollers (PTRS) ... Combination Rollers. ... Towed Rollers.More items...
How to do a compaction test?
The procedure of the Proctor Compaction Test consists of the following steps: 1 Obtain about 3 kg of soil. 2 Pass the soil through the No. 4 sieve. 3 Weight the soil mass and the mold without the collar (W m ). 4 Place the soil in the mixer and gradually add water to reach the desired moisture content (w). 5 Apply lubricant to the collar. 6 Remove the soil from the mixer and place it in the mold in 3 layers or 5 layers depending on the method utilized (Standard Proctor or Modified Proctor). For each layer, initiate the compaction process with 25 blows per layer. The drops are applied manually or mechanically at a steady rate. The soil mass should fill the mold and extend into the collar but not more than ~1 centimeter. 7 Carefully remove the collar and trim the soil that extends above the mold with a sharpened straight edge. 8 Weight the mold and the containing soil (W). 9 Extrude the soil from the mold using a metallic extruder, making sure that the extruder and the mold are in-line. 10 Measure the water content from the top, middle and bottom of the sample. 11 Place the soil again in the mixer and add water to achieve higher water content, w.
What is the most common test for soil compaction?
The most common laboratory test for soil compaction is the Proctor compaction test. The Proctor test was invented in the 1930s by R. R. Proctor, a field engineer for the Bureau of Waterworks and Supply, in Los Angeles, California. The process, which simulates the in-situ compaction processes typically performed during construction ...
What determines the degree of compaction of soil?
The degree of the compaction depends on the soil properties, the type and amount of energy provided by the compaction process and the soil’s water content. For every soil, there is an optimum amount of moisture for which it can experience its maximum compression.
What is the process of compaction of soils?
Compaction of soils is a procedure in which a soil sustains mechanical stress and is densified. Soil consists of solid particles and voids filled with water or/and air. A more detailed explanation of the three-phase nature of soils is provided in Soil as a three-phase System. When subjected to stress, soil particles are redistributed within ...
How many layers are in a Proctor test?
The standard Proctor test includes a 0.95-liter volume cylindrical mold in which the soil mass is placed and compacted in 3 layers. Each layer is compressed by dropping 25 times a 2,5 kg weight falling from an elevation of 30 centimeters.
When was the Proctor test invented?
The Proctor test was invented in the 1930s by R. R. Proctor, a field engineer for the Bureau of Waterworks and Supply, in Los Angeles, California. The process, which simulates the in-situ compaction processes typically performed during construction of earth dams or embankments, is the most common laboratory test conducted to derive the compressibility of soils.
Which sieve to pass soil through?
Pass the soil through the No. 4 sieve.
Why are foundation soils compacted?
Foundation soils are often compacted to improve their engineering properties.
How to make a soil compaction mold?
Measure the water and add it to the soil. Using a trowel, mix it thoroughly into the soil, until the soil becomes a uniform color. Attach the compaction mold to the base, place some soil in the mold and compact the soil into the number of equal layers specified by the type of compaction method employed.
How to determine the wet mass of soil?
Determine the wet mass of the soil by subtracting the weight of the mold and base. Remove the soil from the mold, using a mechanical extruder, and take soil moisture content samples from the top and bottom of the specimen. Fill the moisture cans with soil and determine the water content.
How to make a soil sample with water?
Fill the moisture cans with soil and determine the water content. Place the soil specimen in the large tray and break up the soil until it appears that it will pass through the #4 sieve. Add 2 percent more water, based on the original sample mass, and re-mix as in step 4.
What is the purpose of balance in soil?
Use the balance to determine the weight of the soil samples and compaction molds and bases (without the collar), and record the weights.
What is the purpose of a modified Proctor compaction test?
For soil with higher densities, a Modified Proctor Compaction Test which uses higher values will be necessary.
What is the purpose of soil compaction?
In the construction of high load structures such as dams, paved roadways, and construction projects that rely on the stability of embankments; soil compaction is used to increase soil strength.
What is the process of compaction of soils?
Introduction Compaction of soils is a procedure in which a soil sustains mechanical stress and is densified.
How to find the density of compacted soil?
The dry weight of the soil removed is divided by the volume of dry sand needed to fill the hole, which gives us the density of the compacted soil in lbs. per cubic ft. This can be compared to the maximum Proctor density determined earlier to get the relative density of the compacted soil.
What is the purpose of a dry density test?
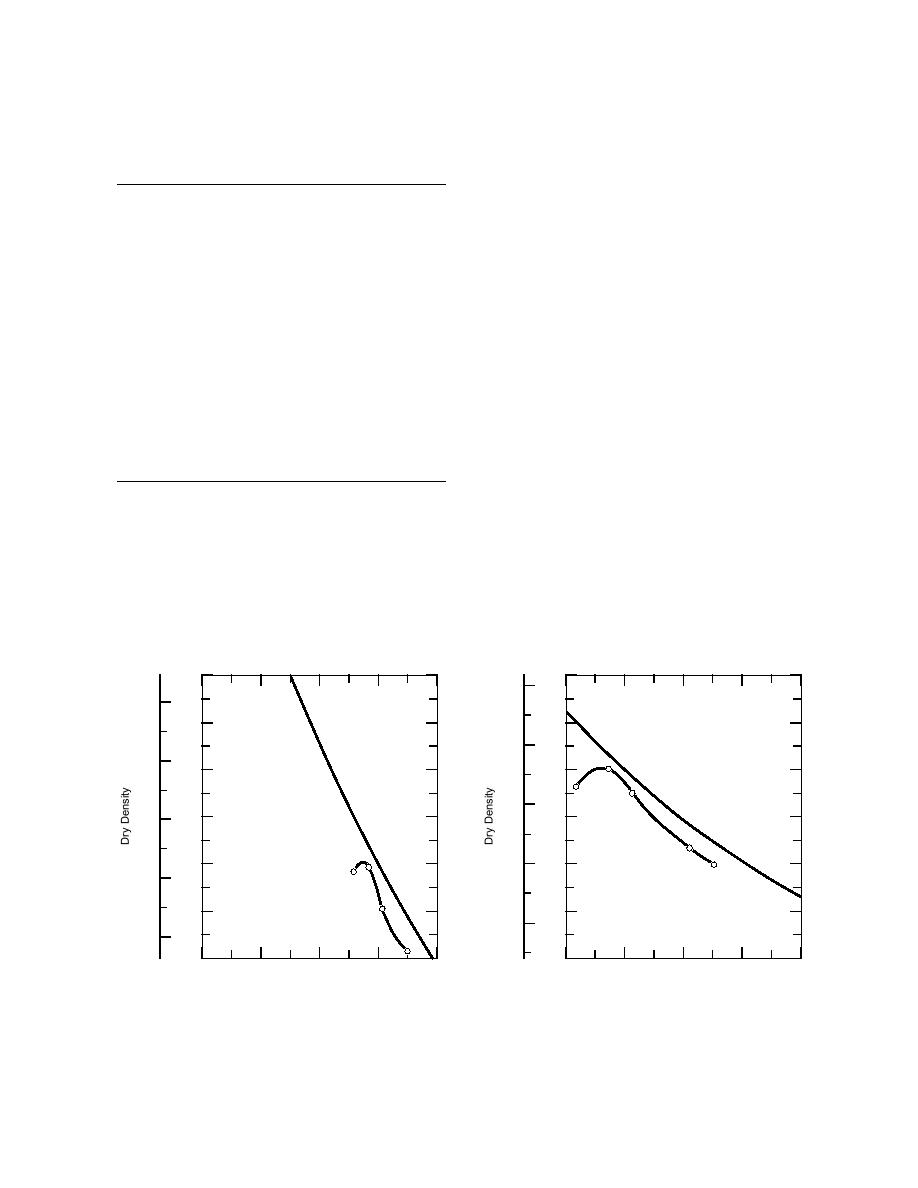
The test aims to establish the maximum dry density that may be attained for a given soil with a standard amount of compaction effort. When a series of soil samples are compacted at different water content, the plot usually shows a peak.
How can loose soil be compacted?
Loose soil can be compacted by using mechanical equipment to remove air-voids, thereby densifying the soil and increasing its dry unit weight.
How accurate is a nuclear test?
A Nuclear Test is a quick and fairly accurate way to measure the density and moisture content of the compacted soil. This test utilizes a radioactive isotope source at either the surface of the soil or from a probe placed in the soil (called direct transmission).
Why is compaction testing important?
Why Compaction Testing is Important. There is a very good reason for all the necessity. Basically, if soil tests are not conducted you risk shifting, cracking, and even the collapse of your building . Roadways could also result in disaster by cracking, sagging, potholes, or even sinkholes. In the end, it’s vital for the success ...
What is soil compaction testing?
Soil Compaction Testing is a crucial step in the construction process. Ground that has not been properly compacted can be detrimental to the structural integrity of buildings, retaining structures, roads and pavements, just to name a few. Essentially, proper soil integrity could make or break your structure. Since soils are so critical to a structures reliability you will find that soil compaction testing is required most cases. For instance, most regulatory agencies such as, the Department of Transportation and American Society for Testing and Materials all require laboratory testing. Additionally, you will find that the California and Uniform Building Codes, the geotechnical engineer, and structural engineers will also require soil compaction testing.
Which agencies require soil compaction testing?
Additionally, you will find that the California and Uniform Building Codes, the geotechnical engineer, and structural engineers will also require soil compaction testing.
Why do you take a sample from a stockpile?
This is usually done if the technician notices that the stockpile soil has different properties than the other site soil, or because several soil types are being blended together.
What is the basic concept of compaction?
The basic concept for compaction is to ‘work’ the material to remove effectively remove air voids resulting from the loosely placed material until achieving a nominated level of compaction.
What happens if compaction is not achieved?
If this level of compaction cannot be achieved, it can pose significant risk to short term and long term performance on the basis of the following: Increased permeability – A lack of compaction can accelerate the pavement deterioration on the basis of increased permeability from moisture ingress.
What is sand replacement test?
Sand Replacement Test – the removal of a test specimen from the compacted area followed by the replacement of fine grained sand. Effectively calculating the volume of sand replaced. The mass of the sample is then weighed in a laboratory environment to calculate the density. The level of compaction is subsequently measured from the ratio of the insitu density to the maximum dry density of the material – typically only used on granular material and soils.
Why is soil testing important?
Reasons why soil testing is important before any construction. Soil test is critical for anyone wishing to construct a building. You see, the most important part of any building is in fact the part you cannot see, the bit under the ground – the foundations. The larger the building, the more important this is.
What is moisture content test?
1. Moisture Content Test: Moisture content test gives all information about moisture or water content of the soil. The information about water table will provides detailed impact of humidity on the foundation.
What is dry density test?
Dry Density of Soil: Dry density test gives the weight of soil in a given volume of sample, enabling to categorise the soil into loose, medium dense and dense classifications.
Why does soil liquefaction happen?
Soil liquefaction is a phenomenon in which a saturated soil deposit loses its strength and stiffness due to the ground shaking, mainly during earthquake, which generates excess pore water pressure. So the foundations may fail during the earthquake, and it may be the reason for the partial or total collapse of the building.

Introduction
Practical Application
- The most common laboratory test for soil compaction is the Proctor compaction test. The Proctor test was invented in the 1930s by R. R. Proctor, a field engineer for the Bureau of Waterworks and Supply, in Los Angeles, California. The process, which simulates the in-situ compaction processes typically performed during construction of earth dams or ...
Objective
Equipment
Standard Reference
- Soil placed as engineering fill (embankments, foundation pads, road bases) is compacted to a dense state to obtain satisfactory engineering properties such as, shear strength, compressibility, or p...
- Foundation soils are often compacted to improve their engineering properties.
- Laboratory compaction tests provide the basis for determining the percent of compaction an…
- Soil placed as engineering fill (embankments, foundation pads, road bases) is compacted to a dense state to obtain satisfactory engineering properties such as, shear strength, compressibility, or p...
- Foundation soils are often compacted to improve their engineering properties.
- Laboratory compaction tests provide the basis for determining the percent of compaction and water content needed to achieve the required engineering properties, and for controlling construction to...
Method
- The objective of this experiment is: 1. To evaluate the maximum dry unit weight, γd(max) and optimum moisture content, wopt, of compaction.
Data Analysis
- Molds, manual rammer
- Extruder, Balance
- Drying oven
- Mixing pan
Video Materials
- ASTM D698: Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort
Results and Discussions
- Put air-dried soil into a large mixing pan (10 lbs. of soil for a 4-inch mold, and 15 lbs. for a 6-inch mold). Pulverize the soil and run it through a \# 4 sieve.
- Use the balance to determine the weight of the soil samples and compaction molds and bases (without the collar), and record the weights.
- Compute the amount of water to add, using the following methods:
- Put air-dried soil into a large mixing pan (10 lbs. of soil for a 4-inch mold, and 15 lbs. for a 6-inch mold). Pulverize the soil and run it through a \# 4 sieve.
- Use the balance to determine the weight of the soil samples and compaction molds and bases (without the collar), and record the weights.
- Compute the amount of water to add, using the following methods:
- Assume the water content for the first test to be 8 percent.
Report
- Calculate the moisture content of each compacted soil specimen by using the average of the two water contents.
- Compute the wet density in grams per $cm^3$ of the compacted soil sample by dividing the wet mass by the volume of the mold that was used.
- Compute the dry density using the wet density and the water content determined in step 1, e…
- Calculate the moisture content of each compacted soil specimen by using the average of the two water contents.
- Compute the wet density in grams per $cm^3$ of the compacted soil sample by dividing the wet mass by the volume of the mold that was used.
- Compute the dry density using the wet density and the water content determined in step 1, employing the following formula:where, w = moisture content in percent divided by 100, and ρ = wet density...
- Plot the dry density values on the y-axis and the moisture contents on the x-axis. Draw a smooth curve connecting the plotted points.