
What are facts about the Berlin Blockade?
Did You Know?
- Western Allies provided West Berlin with over 1.9 million tons of supplies.
- At least every 45 seconds, Allied aircraft would land in West Berlin with supplies.
- The Soviet Union unsuccessfully attempted to sabotage airlift attempts by shining searchlights at night to blind pilots.
- The Allies delivered as much as 6,000 tons of supplies each day.
What was the result of the Berlin Blockade?
Results of the Blockade Over the 15 months of the Berlin Airlift, the US delivered 1,783,573 tons and the UK 541,937 tons, totaling 2,326,406 tons. That’s over 2-billion kilograms (4.6 billion pounds) of goods, nearly two-thirds of which was coal.
How did the Berlin Blockade contribute to the Cold War?
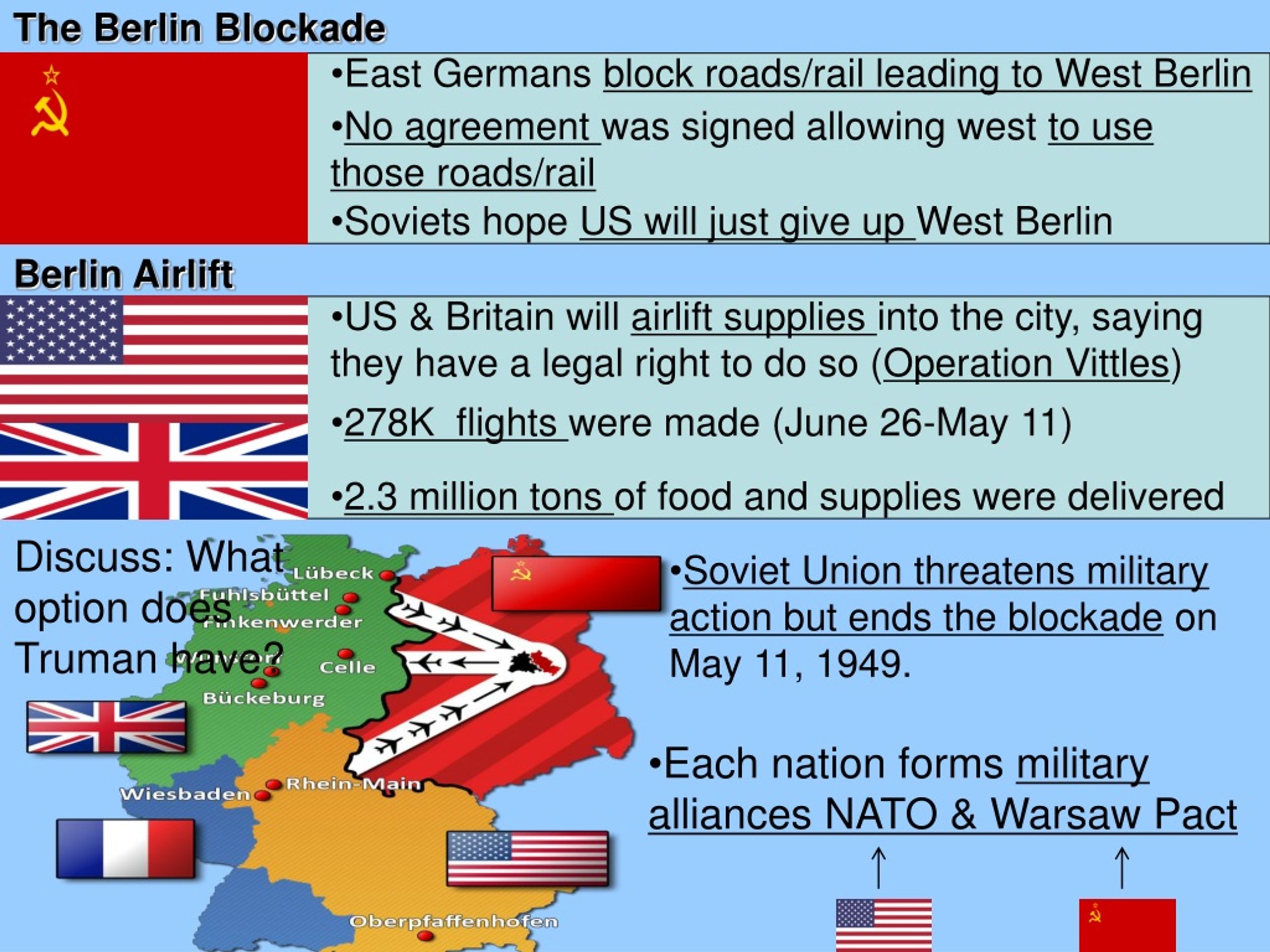
How did the Berlin Blockade contribute to the Cold War? Nearly 700 aircraft were used during the Berlin Airlift, more than 100 of which belonged to civilian operators. By May 1949, when the Soviets lifted the blockade, the crisis in Berlin had hardened the East/West division of Germany and all of Europe, ushering in the Cold War in earnest.
What were the effects of the Berlin Blockade?
What were the consequences of the Berlin Blockade?
- The Berlin Blockade demonstrated how stubborn each side could be – Stalin thought he should make a stand because the West was threatening him – the West thought he was ...
- Eventually Stalin was forced to back down and the blockade was lifted. ...
- NATO was formed. ...
- It was clear that Germany could not now form a united country. ...
When did the Berlin Blockade end and why?
The crisis ended on May 12, 1949, when Soviet forces lifted the blockade on land access to western Berlin. The crisis was a result of competing occupation policies and rising tensions between Western powers and the Soviet Union.
What ended the Berlin Blockade quizlet?
How/why did the Berlin Airlift end? When Soviet forces lifted the blockade on land access to western Berlin. On May 11, 1949, Moscow lifted the blockade of West Berlin. On August 24, 1949, the Western Allies created the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
Was the Berlin Blockade a success or failure?
The Berlin Airlift: The End of the Blockade By spring 1949, it was clear that the Soviet blockade of West Berlin had failed. It had not persuaded West Berliners to reject their allies in the West, nor had it prevented the creation of a unified West German state.
When did Berlin Airlift end?
June 24, 1948 – May 12, 1949Berlin Blockade / PeriodAir and ground crews of the U.S. Navy Squadron VR-6 at Rhein-Main celebrate the end of the Berlin Airlift, May 12, 1949.
What were the causes and results of the Berlin Blockade?
What caused the Berlin Blockade? Stalin wanted Germany to remain weak, as a strong Germany could represent a threat to the Soviet Union. The Western Allies disagreed and were encouraging Germany to rebuild in the Western sectors. This angered Stalin who decided to force the Allies out of Berlin.
How did the US respond to the Berlin Blockade?
In response to the Soviet blockade of land routes into West Berlin, the United States begins a massive airlift of food, water, and medicine to the citizens of the besieged city. For nearly a year, supplies from American planes sustained the over 2 million people in West Berlin.
Why do you think the Soviets ended the blockade?
The end to the blockade was brought about because of countermeasures imposed by the Allies on East German communications and, above all, because of the Western embargo placed on all strategic exports from the Eastern bloc.
Why did the Berlin Wall fall?
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 was a pivotal moment, not just in the Cold War but in the history of modern Europe. It was brought about by political reforms inside the Soviet bloc, escalating pressure from the people of eastern Europe and ultimately, confusion over an East German directive to open the border.
What was the impact of the Berlin Blockade?
Lasting Impact of the Blockade and the Allied Response With their blockade, the Soviets cut some 2.5 million civilians in the three western sectors of Berlin off from access to electricity, as well as food, coal and other crucial supplies.
What was the outcome of the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Airlift was a tremendous Cold War victory for the United States. Without firing a shot, the Americans foiled the Soviet plan to hold West Berlin hostage, while simultaneously demonstrating to the world the “Yankee ingenuity” for which their nation was famous.
What led to the Berlin Blockade quizlet?
What were the causes of the Berlin Blockade? stalin refused to allow marshall aid for communist controlled countries. in 1946, britain, france and the USA combine their zones of occupation in germany. in 1946, britain, france and the USA introduced a new currency.
What was the result of the Soviet blockade of West Berlin quizlet?
What was the result of the Berlin Blockade? Germany split up. In May 1949, America, Britain and France united their zones into the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany). In October 1949, Stalin set up the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) .
How did the United States respond to the Berlin Blockade quizlet?
How did the United States respond to the 1948 Soviet blockade of West Berlin? In response to the Soviet blockade of land routes into West Berlin, the United States begins a massive airlift of food, water, and medicine to the citizens of the besieged city.
What is one major event that happened after the Berlin Wall came down quizlet?
What is one major event that happened after the Berlin Wall came down? The USSR broke up into several nations.
What currency did the Soviets use?
Viewing this as a violation of their postwar agreements, the Soviets immediately issued their own currency, the Ostmark, into Berlin and eastern Germany.
What happened in Berlin in 1948?
In June 1948, the simmering tensions between the Soviet Union and its former allies in World War II, exploded into a full-blown crisis in the city of Berlin. Alarmed by the new U.S. policy of giving economic aid to Germany and other struggling European nations, as well as efforts by the Western Allies to introduce a single currency to ...
What was the Soviet decision to blockade Berlin?
Over the first half of 1948, representatives from the United States, Britain and France met in London to discuss the future of Germany. As a result, the United States and Britain agreed to combine their occupied zones to create Bizonia, with the ultimate goal being a single, unified West German state ...
What was the Berlin blockade?
The Berlin Blockade was an attempt in 1948 by the Soviet Union to limit the ability of the United States, Great Britain and France to travel to their sectors of Berlin, which lay within Russian-occupied East Germany.
What was the Truman doctrine?
Truman announced in a speech to Congress that the United States would henceforth “support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures,” by giving them military aid. This policy, which became known as the Truman Doctrine, introduced a new era of global engagement for the United States and helped articulate the growing divide between between Western democracies and the Soviet Union.
What was the first major conflict in the Cold War?
The Berlin Blockade, and the Allied response in the form of the Berlin Airlift, represented the first major conflict of the Cold War.
What was the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Blockade, and the Allied response in the form of the Berlin Airlift, represented the first major conflict of the Cold War. pinterest-pin-it. A 1948 map detailing the Berlin Blockade, ...
Why did the Berlin airlift continue?
The Berlin airlift continued until September 30, in an effort to build up a year’s supply of essential goods for West Berlin in the event of another Soviet blockade. Another blockade did not occur, but Cold War tensions over Berlin remained high, culminating in the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961. With the gradual waning of Soviet power in ...
What happened to East Germany in the 1980s?
With the gradual waning of Soviet power in the late 1980s, the Communist Party in East Germany began to lose its grip on power. Tens of thousands of East Germans began to flee the nation, and by late 1989 the Berlin Wall started to come down. Shortly thereafter, talks between East and West German officials, joined by officials from the United States, Great Britain, France, and the USSR, began to explore the possibility of reunification, which was achieved on October 3, 1990. Two months following reunification, all-German elections took place and Helmut Kohl became the first chancellor of the reunified Germany. Although this action came more than a year before the dissolution of the Soviet Union, for many observers the reunification of Germany effectively marked the end of the Cold War.
What did the Soviets say about Berlin?
The Soviets condemned this move as an attack on the East German currency and on June 24 began a blockade of all rail, road, and water communications between Berlin and the West. The four-power administration of Berlin had ceased with the unification of West Berlin, the Soviets said, and the Western powers no longer had a right to be there.
What was the name of the city in West Germany?
The three western sectors of Berlin were united as West Berlin, which was to be under the administration of West Germany. On June 20, as a major step toward the establishment of a West German government, the Western powers introduced a new Deutsche mark currency in West Germany and West Berlin.
What was the future of Germany and Berlin?
The future of Germany and Berlin was a major sticking point in postwar treaty talks, especially after the United States, Britain, and France sought to unite their occupation zones into a single economic zone. In March 1948, the Soviet Union quit the Allied Control Council governing occupied Germany over this issue.
What were the four major Allied powers at the end of World War II?
At the end of World War II, Germany was divided into four sectors administered by the four major Allied powers: the USSR, the United States, Britain, and France. Berlin, the German capital, was likewise divided into four sectors, even though it was located deep within the Soviet sector of eastern Germany. The future of Germany and Berlin was ...
When did the Cold War end?
On May 12, 1949, an early crisis of the Cold War comes to an end when the Soviet Union lifts its 11-month blockade against West Berlin. The blockade had been broken by a massive U.S.-British airlift of vital supplies to West Berlin’s two million citizens.
How many tons of coal did the Berlin Airlift deliver?
The US Air Force had delivered 1,783,573 tons (76.40% of total) and the RAF 541,937 tons (23.30% of total), totalling 2,334,374 tons, nearly two-thirds of which was coal, on 278,228 flights to Berlin.
How many tons of candy were dropped on Berlin?
Soon, major candy manufacturers joined in. In the end, over three tons of candy were dropped on Berlin and the "operation" became a major propaganda success. German children christened the candy-dropping aircraft " raisin bombers ".
What happened in 1945-1946?
After harsh treatment, forced emigration, political repression and the particularly hard winter of 1945–1946, Germans in the Soviet-controlled zone were hostile to Soviet endeavours. Local elections in 1946 resulted in a massive anti-communist protest vote, especially in the Soviet sector of Berlin. Berlin's citizens overwhelmingly elected non-Communist members to its city government.
How many air corridors were there in Berlin?
On 30 November 1945, it had been agreed in writing that there would be three twenty-mile-wide air corridors providing free access to Berlin. Additionally, unlike a force of tanks and trucks, the Soviets could not claim that cargo aircraft were a military threat.
What was the name of the city that the Allies divided into four zones?
These zones were located roughly around the then-current locations of the allied armies. Also divided into occupation zones, Berlin was located 100 miles (160 km) inside Soviet-controlled eastern Germany. The United States, United Kingdom, and France controlled western portions of the city, while Soviet troops controlled the eastern sector.
What was the Berlin blockade?
e. The Berlin Blockade (24 June 1948 – 12 May 1949) was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies ' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control.
Why did the Soviets celebrate the blockade?
General Clay felt that the Soviets were bluffing about Berlin since they would not want to be viewed as starting a Third World War.
What was the purpose of the Berlin Airlift?
He and the remaining Allies began the Berlin Airlift, an operation that carried food, fuel and other supplies into West Berlin by plane. The effort required a lot of careful planning and many resources, but the Airlift allowed the United States to keep a foothold in post-war Germany.
What did Truman do to help West Berlin?
Truman’s advisors suggested several options. They could evacuate the citizens of West Berlin, try to negotiate with the Soviet Union with the support of the newly-formed United Nations, figure out a way to get supplies into the city or simply abandon Berlin altogether. Their decision would determine exactly how involved the United States would be in Berlin - and in rebuilding post-war Europe.
Why did the Soviet Union blockade Berlin?
In June 1948 the Soviet Union, whose territory fully surrounded the capital, cut off all ground traffic into and out of West Berlin in an attempt to force the Allies to abandon the city. The blockade of Berlin had begun. President Truman suddenly faced a crisis.
How did World War 2 affect the world?
One of the most brutal conflicts in recent history, World War II devastated 113 countries from six continents. Beginning in 1939, the Allied forces — primarily Britain, Russia and the USA — sought to stop Nazi Germany in its conquest for European domination. In the six years that followed, Adolf Hitler’s Nazi party devastated Europe and wreaked violence against many social minority groups. By 1945, Western Europe had been ravaged, an entire race of people had come close to extinction and the dynamic of power in several affected countries had been forever changed. Hitler committed suicide in May 1945, and the Nazi regime collapsed. Japan surrendered in August. Even after peace was declared, the world felt the political and economic repercussions for decades.
What happened to Europe in 1945?
By 1945, Western Europe had been ravaged, an entire race of people had come close to extinction and the dynamic of power in several affected countries had been forever changed.
What happened to Japan after the war?
Japan surrendered in August. Even after peace was declared, the world felt the political and economic repercussions for decades. Following the war, a defeated Germany was divided into four sections, each of which was to be occupied by one of the Allied Powers.
Which country controlled Germany?
The Soviet Union took control of the eastern part of Germany, while France, Great Britain and the United States took control of the western part. The German capital of Berlin was also divided into four sections, even though Berlin itself was in the middle of the Soviet-controlled part of Germany.
Why did Stalin end the Berlin Blockade?
As far as I can tell, Joseph Stalin ended the Berlin Blockade due to it being too ineffective to actually work . The Western Allies already found a way to go around it, and there wasn’t really anything they could do about it other than provoke war, which Stalin and the USSR did not want.
Why did the Soviets want to blockade Berlin?
The Soviets feared the Western portions of occupied Germany might one day unite into a pro-Western German state (we now call this West Germany), and that fear was validated when representatives from the Western zones were meeting to formulate the groundwork of a post-war Germany. As a response to what seemed to be a move against their interests, the Soviets decided to strong-arm the West into moving in Russian terms, by stopping trains and boat traffic, effectively blockading Berlin.
What did the airlift do to the West?
Instead, the airlift changed the story and dramatically demonstrated for all the world that West Berlin didn't want Soviets rule, and allowed the Western powers to cast themselves as dashing heroes delivering much needed eggs and milk and potatoes to hungry children.
How does the literature distort the facts on the ground during the conflict?
The literature fundamentally distorts the facts on the ground during the conflict by portraying (as Allies did at the time) the situation in Berlin as creating a fully isolated city. As Stivers puts it and argues in detail in the article, “the Soviet blockade neither attempted nor achieved the isolation of West Berlin” [1:569]No effort was made, however – either at the beginning of the blockade or during the course of it – to seal off the Western sectors from either East Berlin or from the surrounding countryside. As a result, a flood of goods – roughly a half a million tons, to take the mean of various estimates – entered the Western sectors from Soviet area sources over the ten-and-a-half-month period of “restrictions.” [1:570]Many works, including the wikipedia entry note that there was food offered from the east but, "they do so chiefly to emphasize that the great majority of Western sector residents turned it down.” [1:571]
What was the purpose of the Berlin blockade?
The blockade was meant to win Berlin without firing a shot, the idea being that with Berlin starving, the people would demand the Western Allies withdraw and the Soviets could triumphantly say “See? The people of Berlin are hungry for the fruits of our socialist paradise!” And world opinion would be on their side for peacefully integrating Berlin into the Soviet empire.
What did the Soviets fear?
The Soviets feared the Western portions of occupied Germany might one day unite into a pro-Western German state (we now call this West Germany), and that fear was validated when representatives from the Weste
What did the Soviets want to do in Berlin?
The short story was that, the Soviets wanted to consolidate control over Berlin, and underline the West’s presence in Germany via their respective occupation zones- Germany at that time was divided into four zones, and Berlin itself was also divided into four zones, under British, American, French and Soviet authorities.
Why did the Soviets stop caring about the blockade?
So my explanation: Soviets stopped caring about the blockade mid-1949 because they have made the decision about the split. There was no more point to the blockade, since Germany would soon become two countries anyway, with real borders etc. And that's exactly what happened. Sources:
What happened in May 1949?
In May 1949, Stalin had little choice but to lift the blockade. Keeping the blockade could thus unite West more, which was not desired by Stalin. Please also note that in West Berlin there were not only civilians, but also military forces of USA, UK and France.
How does literature distort facts?
The literature fundamentally distorts the facts on the ground during the conflict by portraying (as Allies did at the time) the situation in Berlin as creating a fully isolated city. As Stivers puts it and argues in detail in the article, “the Soviet blockade neither attempted nor achieved the isolation of West Berlin” [1:569]
What does "help" mean in a sentence?
Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers.
Why did the USSR object to the separation of the three "western" zones from the "eastern" one?
USSR objected to that step because this resulted in clear economical separation of the three "western" zones from the " eastern" one which went (in Soviet opinion) against Potsdam agreement about collective sovereinghty of the four allied powers over Germany.
When did Germany split into FRG and GDR?
Result - split of Germany into FRG and GDR in October 1949. So my explanation: Soviets stopped caring about the blockade mid-1949 because they have made the decision about the split. There was no more point to the blockade, since Germany would soon become two countries anyway, with real borders etc. And that's exactly what happened.
When did West Berlin get blocked?
Between 24th June 1948 and 12th May 1949 land routes into West Berlin were blocked by Soviet forces and West Berliners were supplied entirely by air (the famous Berlin Airlift ).
How did the Berlin Airlift work?
It was a daunting task: supplying the daily wants and needs of so many civilians would require tons of food and other goods each and every day. On June 26, 1948, the Berlin Airlift began with U.S. pilots and planes carrying the lion’s share of the burden. During the next 15 months, 277,264 aircraft landed in West Berlin bringing over 2 million tons of supplies. On September 30, 1949, the last plane–an American C-54–landed in Berlin and unloaded over two tons of coal. Even though the Soviet blockade officially ended in May 1949, it took several more months for the West Berlin economy to recover and the necessary stockpiles of food, medicine, and fuel to be replenished.
How many tons of coal did the Berlin Airlift bring?
During the next 15 months, 277,264 aircraft landed in West Berlin bringing over 2 million tons of supplies. On September 30, 1949, the last plane–an American C-54–landed in Berlin and unloaded over two tons of coal.
What was the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Airlift was a tremendous Cold War victory for the United States. Without firing a shot, the Americans foiled the Soviet plan to hold West Berlin hostage, while simultaneously demonstrating to the world the “Yankee ingenuity” for which their nation was famous.
What was the Soviet Union's biggest logistical feat during the Cold War?
The airlift was one of the greatest logistical feats in modern history and was one of the crucial events of the early Cold War. In June 1948, the Soviet Union suddenly blocked all ground traffic into West Berlin, which was located entirely within the Russian zone of occupation in Germany.
What did George Washington write in his letter to his nephew?
In a letter to his nephew, Lund Washington, plantation manager of Mount Vernon, General George Washington writes on September 30, 1776, of his displeasure with the undisciplined conduct and poor battlefield performance of the American militia. Washington blamed the Patriot ...read more
Where was the first antiwar demonstration?
First large-scale antiwar demonstration staged at UC Berkeley. The first large-scale antiwar demonstration in the United States is staged at the University of California at Berkeley, by students and faculty opposed to the war.
Who built the first nuclear submarine?
The USS Nautilus, the world’s first nuclear submarine, is commissioned by the U.S. Navy. The Nautilus was constructed under the direction of U.S. Navy Captain Hyman G. Rickover, a brilliant Russian-born engineer who joined the U.S. atomic program in 1946. In 1947, he was put in ...read more

Overview
Postwar division of Germany
Political division
- On May 12, 1949, the Soviets abandoned the blockade, and the first British and American convoys drove though 110 miles of Soviet Germany to reach West Berlin. On May 23, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) was formally established. On October 7, the German Democratic Republic, a Communist state, was proclaimed in East Germany. The Berlin...
Start of the Berlin Airlift
The Berlin Blockade (24 June 1948 – 12 May 1949) was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. The Soviets offered to drop the blockade if the Western Allies withdrew the newly i…
Soviet responses
From 17 July to 2 August 1945, the victorious Allies reached the Potsdam Agreement on the fate of postwar Europe, calling for the division of defeated Germany, west of the Oder-Neisse line, into four temporary occupation zones each one controlled by one of the four occupying Allied powers: the United States, the United Kingdom, France and the Soviet Union (thus re-affirming pri…
Winter 1948 to spring 1949
The US had secretly decided that a unified and neutral Germany would inevitably fall under Soviet domination, with Ambassador Walter Bedell Smith telling General Eisenhower that "in spite of our announced position, we really do not want nor intend to accept German unification on any terms that the Russians might agree to, even though they seem to meet most of our requirements." American planners had privately decided during the war that it would need a strong, allied Germ…
End of the blockade
The day after the 18 June 1948 announcement of the new Deutsche Mark, Soviet guards halted all passenger trains and traffic on the autobahn to Berlin, delayed Western and German freight shipments and required that all water transport secure special Soviet permission. On 21 June, the day the Deutsche Mark was introduced, the Soviet military halted a United States military supply train to Be…
Subsequent events
The Soviets had an advantage in conventional military forces, but were preoccupied with rebuilding their war-torn economy and society. The US had a stronger navy and air force, and had nuclear weapons. Neither side wanted a war; the Soviets did not disrupt the airlift.
As the tempo of the airlift grew, it became apparent that the Western powers might be able to pull off the impossible: indefinitely supplying an entire city by air alone. In response, starting on 1 Au…