Why do amino acids have at least two pKa values? Because all amino acids have two groups that can be protonated, they have two pKa values. pKa1 is the pKa of carboxyl group. pka2 is the pKa of amino group.
How many pKas are in an amino acid?
An amino acid has at least two pKa’s, one for the amino group and one for the carboxyl group. The pKa for each group is the negative logarithm (base 10) of the equilibrium constant for its deprotonation. Put more simply, this works out to the pH at which the group is protonated (e.g. - N H 3 +, − C O O H) on half the molecules and deprotonated ( − N H 2, C O O −) on half. If the amino acid has an ionizable group in its side chain, it has a third pKa.
What does pka mean in math?
pKa, or simply pK, represents the tendency towards ionization for a given acidic/basic substance or group. However attention must be paid here, as we’re dealing with -log (Ka), have in mind that lower pK values indicate acidic species that easily ionize, while higher pK values indicate basic species, that do the exact opposite, to remain protonated. Making it simple, the lower the pK, the stronger the acid.
What is the net charge of aspartic acid at pH 3?
The pI is ~3. So at a pH of ~3 the net charge of aspartic acid is 0 . To understand why, one needs to think about what is happening to the alpha-amino and carboxylic groups and carboxyl side chain group. At pH 3, the alpha-amino group will be fully protonated given that the pKa is 9.9. So that contributes a charge of +1. So that means that at pH 3, the sum of the net charge on the alpha carboxylic group and carboxyl R group must add up to -1.
What is the total amount of the alpha carboxyl group at pH 3?
At pH 3, the fraction of the alpha carboxyl group existing as A- is 0.91 and the fraction of the R carboxyl group existing as A- is 0.09. The total amount of A- is 1.0 and contributes a total charge of -1. Adding in the +1 charge of the alpha amino group gives a net charge of 0.
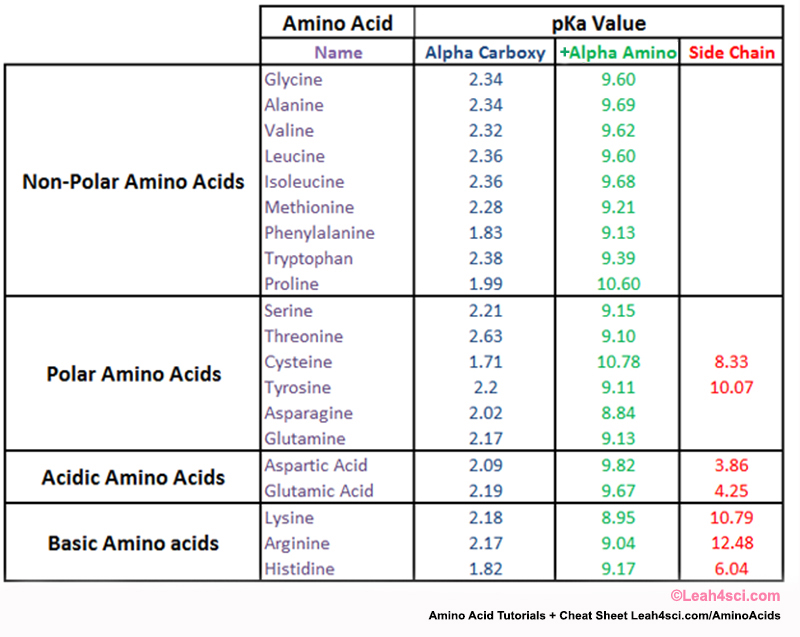
What is the pKa of glycine?
The pKa of glycine (H2N-CH2-COOH) is 2.34. So, if we add two F we can estimate the pKa of difluoroglycine to be
What is the pKa of trichloroacetic acid?
You can get below one with acids like trichloroacetic acid (Cl3COOH) and trifluoroacetic acid (F3COOH) with pKas of 0.7 and 0.23, respectively.
How to separate pKa?
One classic method is to do 2-D separation: chromatography in one dimension, electrophoresis or another chromatography in the other. Knowing the pKa in advance isn’t particularly a help, unless you think electrophoresing near its isoionic point will help separate it from other candidates.
Why are amino acids called amino acids?
Amino acids are so called because they all contain two common components. One is an amine, or a tetrahedral nitrogen attached to a carbon. The other is a carboxylic acid, which is a carbon that is double bonded to an oxygen and also attached to an OH or hydroxyl group. We have seen that carboxylic acids are moderately acidic.
Which amino acid has the least basic group?
There is a big difference in basicity between these three compounds. The difference can be seen by looking at the pKa's of the conjugate acids in each case. The higher the pKa of the conjugate acid, the more tightly the proton is held, and so the more basic the nitrogen atom. Arginine is by far the most basic and histidine is the least basic.
How are amino acids joined together?
Amino acids are joined together via "amide linkages" to form peptides and proteins. In these structures, the individual amino acids no longer have the same acidic carboxylic acid group; the carbonyl (or C=O) no longer has a hydroxyl group attached.
What are proteins used for?
Proteins, which are very large peptides, have a variety of uses. They form the key components of muscles, for instance, and they also form enzymes that carry out a multitude of chemical reactions necessary for life. Amino acids are so called because they all contain two common components.
Where are the acidic and basic sites found in amino acids?
However, peptides and proteins do have basic and acidic sites. These sites are found on the side chains of the amino acids, the part that varies from one amino acid to another.
Which compound holds the proton more tightly than the acid?
The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. The proton stays on the nitrogen. Amino acids are zwitterionic. A zwitterion is a compound that has no overall charge but that has charge separation within it. The zwitterionic nature of amino acids has an effect on their properties.
Which side chain is weakly acidic?
There are other side chains that are weakly acidic. For example, tyrosine is sometimes able to supply protons, and so is cysteine. The proton comes from the OH and SH groups, respectively, on these two compounds. However, neither of these compounds can supply protons as easily as aspartic acid or glutamic acid.