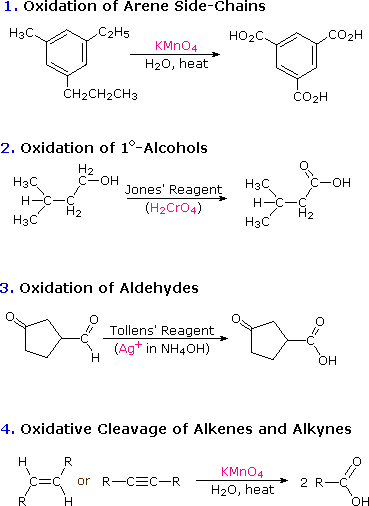
What happens when an acid reacts with a carboxylic acid?
Carboxylic acids are weak acids, so the reaction may be slow, but it will occur. With metal carbonates. A metal carbonate reacts with an acid to produce a salt, carbon dioxide, and water. For example, acetic acid reacts with sodium carbonate according to the equation.
Why do acids react with carbonates?
Acids react with carbonates because acids produce hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions (H+) are electron-deficient, while the carbonate ion (CO3–2) is electron-rich;- The hydrogen ion is attracted to the carbonate ion and first reacts with one of the negatively charged oxygen atoms which make up the carbonate ion, to form an H-O bond.
What happens when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate?
For example in the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium carbonate: The equation above is unbalanced but shows the hydrogen (blue) in the hydroxyl part of the carboxylic group is lost and replaced by the sodium (red).
Are carboxylic acids acids?
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AS ACIDS This page looks at the simple reactions of carboxylic acids as acids, including their reactions with metals, metal hydroxides, carbonates and hydrogencarbonates, ammonia and amines.
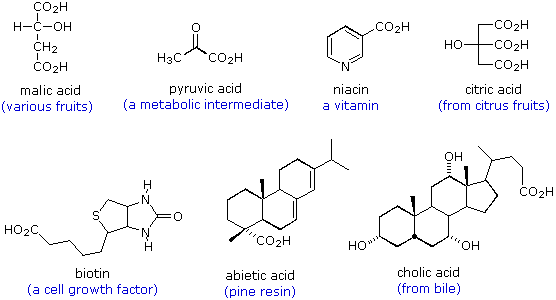
How do carboxylic acids react with carbonates?
Carboxylic acids react with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to form a salt, carbon dioxide and water.
What happens when carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates?
When carboxylic acid reacts with metal carbonates, the products formed are metal carboxylate, carbon dioxide and water. The metal carbonate used in the reaction is sodium carbonate and the acid used is acetic acid.
Do carboxylic acids react with sodium carbonate?
Reaction of carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate produces carbon dioxide.
What gas is produced when carboxylic acids react with carbonates?
carbon dioxideCarboxylic acids react with carbonates to produce a carboxylate salt, water and carbon dioxide.
Why do carboxylic acids react with metals?
Reactions of carboxylic acids with metals Carboxylic acids react with the more reactive metals to produce a salt and hydrogen. The reactions are just the same as with acids like hydrochloric acid, except they tend to be rather slower. For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium.
What makes a carboxylic acid more acidic?
The presence of groups near the -COOH group of a carboxylic acid has an effect on acidity. Generally, electron-withdrawing groups increase acidity by increasing the stability of the carboxylate ion. The presence of, electron-donating groups decrease acidity by destabilizing the carboxylate ion.
Why does ethanoic acid react with sodium carbonate?
Theory: The ethanoic acid reacts with the sodium hydrogen carbonate to form carbon dioxide gas and water. The carbon dioxide gas produced rushes away from the solution. This is seen as bubbles.
What neutralizes carboxylic acid?
Being an acid, carboxylic acids can undergo neutralization reactions with bases, forming water and a salt of a weak acid.
What happens when carboxylic acid reacts with sodium?
Carboxylic acids react to metals such as sodium, potassium, and provide salt and hydrogen(H2).
Why carboxylic acids are weak acids?
Carboxylic acids are weak acids because they only partially ionise in solution. Their solutions do not contain many hydrogen ions compared to a solution of a strong acid at the same concentration. A weak acid's pH will be higher than a strong acid's pH at the same concentration.
Why carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols?
Solution: Due to the resonance in carboxylic acids, the negative charge is at the more electronegative oxygen whereas, in alcohols or phenols, the negative charge is on a less electronegative atom. Thus, carboxylic acids can release proton easier than alcohols or phenols.
What happens when a carboxylic acid is added to water?
When added to water the carboxylic acids do not form dimers. Rather, hydrogen bonds are formed between the individual molecules of the acid and water molecules. It is because of these interactions that carboxylic acids can dissolve in water to form acidic solutions.
What type of reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a metal carbonate?
1:063:00Acid + Metal Carbonate | Acids,Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf fizzing is seen then the rock is a carbonate. In neutralization you might recall the generalMoreIf fizzing is seen then the rock is a carbonate. In neutralization you might recall the general equation acid plus base equals salt plus water only most metal carbonates are almost insoluble in water
What are the products when an acid and metal carbonate react?
It is said that acids react with metal carbonate to form salt carbon dioxide and water.
Do carboxylic acids react with metal oxides?
Abstract. Carboxylic acids are found to react with aluminium oxides via a topotactic reaction such that the carboxylate acts as a bridging ligand. This reaction allows for carboxylate-functionalized alumina nanoparticles to be prepared directly from boehmite (AlOOH).
What are the reactions of carboxylic acids?
Reactions of carboxylic acids with metals. Carboxylic acids react with the more reactive metals to produce a salt and hydrogen. The reactions are just the same as with acids like hydrochloric acid, except they tend to be rather slower. For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium. The magnesium reacts to produce a colorless solution ...
Why are carboxylic acids acidic?
Using the definition of an acid as a "substance which donates protons (hydrogen ions) to other things", the carboxylic acids are acidic because of the hydrogen in the -COOH group. In solution in water, a hydrogen ion is transferred from the -COOH group to a water molecule.
What reacts with methylamine?
That means that they will react with acids (including carboxylic acids) in just the same way as ammonia does. For example, ethanoic acid reacts with methylamine to produce a colorless solution of the salt methylammonium ethanoate.
What is the reaction between carboxylic acids and amines?
Reactions of carboxylic acids with amines. Amines are compounds in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in an ammonia molecule have been replaced by a hydrocarbon group such as an alkyl group. For simplicity, we'll just look at compounds where only one of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced.
What happens if you pour ethanoic acid on white carbonate?
If you pour some dilute ethanoic acid onto some white sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogencarbonate crystals, there is an immediate fizzing as carbon dioxide is produced. You end up with a colorless solution of sodium ethanoate.
What is the reaction of magnesium ribbon?
For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium. The magnesium reacts to produce a colorless solution of magnesium ethanoate, and hydrogen is given off. If you use magnesium ribbon, the reaction is less vigorous than the same reaction with hydrochloric acid, but with magnesium powder, both are so fast that you probably wouldn't notice much difference.
What are the reactions of carboxylic acids with metal hydroxides?
Reactions of carboxylic acids With metal hydroxides. These are simple neutralisation reactions and are just the same as any other reaction in which hydrogen ions from an acid react with hydroxide ions. They are most quickly and easily represented by the equation:
Why do acids react with carbonates?
Acids react with carbonates because acids produce hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions (H +) are electron-deficient, while the carbonate ion (CO 3 − 2) is electron-rich;-. The hydrogen ion is therefore attracted to the carbonate ion and first reacts with one of the negatively charged oxygen atoms which make up the carbonate ion, to form an H—O bond.
What happens when you treat calcium carbonate with carbonic acid?
When insoluble calcium carbonate is treated with carbonic acid, the former dissolves to give a colourless aqueous solution of calcium bicarbonate. The bicarbonate cannot be obtained in pure state. The aqueous solution on evaporation would decompose to give the insoluble carbonate back.
Why does carbonate drink produce gas?
But carbonic acid is highly unstable in normal atmospheric pressure, it decompose into water and carbon dioxide that’s why carbonate drinks produces gas when it is open. After that chloride ions reacts with the metal ions forming salts.
What is the difference between acid and carbonate?
An acid plus carbonate will produce water, carbon dioxide and a salt formed from the cation of the carbonate and the anion of the acid. For example, sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid will produce CO2 and H2O and NaCl. By the way; bicarbonates will do the same thing.
What is the acid test?
This is called the ‘acid test’. It means placing a drop of dilute (5% to 10%) hydrochloric acid (HCl) on a rock or mineral and watching for bubbles of carbon dioxide gas to be released. The bubbles signal the presence of carbonate minerals (like calcite).
What happens when limewater turns milky?
By bubbling the gas produced through limewater, a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide. If the limewater turns milky, i.e. produces a white precipitate, then carbon dioxide is produced. Hope your query is resolved and Best of luck. Related Answer.
Is copper a base or acid?
One is an acid and the other is a base. Copper (II) carbonate reacts with hydrochloric.acid to form copper (II) chloride, water and carbon dioxide. , I have taught high school and middle science for 38 years.
What are the reactions of carboxylic acids?
Reactions of the carboxylic acids. With metals. Carboxylic acids react with the more reactive metals to produce a salt and hydrogen. The reactions are just the same as with acids like hydrochloric acid, except they tend to be rather slower. For example, dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium. The magnesium reacts to produce a colourless ...
Why are carboxylic acids acidic?
Using the definition of an acid as a "substance which donates protons (hydrogen ions) to other things", the carboxylic acids are acidic because of the hydrogen in the -COOH group. In solution in water, a hydrogen ion is transferred from the -COOH group to a water molecule. For example, with ethanoic acid, you get an ethanoate ion formed together ...
What happens if you pour ethanoic acid on white carbonate?
If you pour some dilute ethanoic acid onto some white sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogencarbonate crystals, there is an immediate fizzing as carbon dioxide is produced. You end up with a colourless solution of sodium ethanoate.
What is the reaction of ethanoic acid and ammonia?
Ethanoic acid reacts with ammonia in exactly the same way as any other acid does. It transfers a hydrogen ion to the lone pair on the nitrogen of the ammonia and forms an ammonium ion.
How to tell if ethanoic acid is a change?
The only sign that a change has happened is that the temperature of the mixture will have increased.
What happens when you use magnesium ribbon?
The magnesium reacts to produce a colourless solution of magnesium ethanoate, and hydrogen is given off . If you use magnesium ribbon, the reaction is less vigorous than the same reaction with hydrochloric acid, but with magnesium powder, both are so fast that you probably wouldn't notice much difference. Warning!
Is ethanoic acid reversible?
This reaction is reversible and, in the case of ethanoic acid, no more than about 1% of the acid has reacted to form ions at any one time. (This is a rough-and-ready figure and varies with the concentration of the solution.)
What reacts with active metals to form hydrogen and metal carboxylates?
Carboxylic acids react with active metals to form hydrogen and metal carboxylates, and they react with metal carbonates to give metal carboxylates, carbon dioxide, and water.
What reacts with an acid to produce a salt and hydrogen?
An active metal reacts with an acid to produce a salt and hydrogen.
Is carboxylic acid a weak acid?
Carboxylic acids are weak acids, so the reaction may be slow, but it will occur.
What reacts with alkalies to yield their respective salts and water?
Carboxylic acids react with alkalies to yield their respective salts and water .
What group of acids give effervescence?
Test for COOH group : Carboxylic acids give effervescence due to evolution of CO 2 with saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate. Most of the phenols do not produce effervescence with aqueous solution of NaHCO 3; therefore, this reaction is used to distinguish phenols from carboxylic acids.