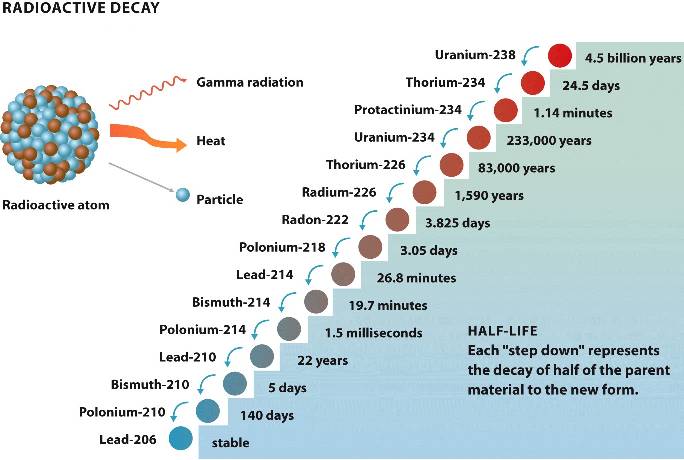
Explanation: Unstable nuclei cause nuclear decay. When an atom
Atom
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-milliont…
What do you mean by nucleus decay?
this emission is called nucleus decay. if nucleus emit Beta ray means a neutron is converted into proton. and if alpha arays is emitted it means helium nucleus (2 protons and 2 neutrons) simultaneously emitted from nucleus. heavier nuclei get to ground state by decay process and most of them eventually become Lead (Pb).
Why does ununoctium decay?
In a nutshell, atoms decay because they're unstable and radioactive. Ununoctium (or Oganesson) has an atomic number of 118. That means that there are 118 protons in the nucleus of one atom of Oganesson, and that isn't including the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
What causes an atom to decay?
Basically, there is too much energy inside the nucleus to hold all the nucleons together. The status of the electrons of an atom doesn't matter for decay, although they, too, have their own way of finding stability. If the nucleus of an atom is unstable, eventually it will break apart to lose at least some of the particles that make it unstable.
Why is radioactive decay so stable?
It's basically a matter of thermodynamics. Every atom seeks to be as stable as possible. In the case of radioactive decay, instability occurs when there is an imbalance in the number of protons and neutrons in the atomic nucleus. Basically, there is too much energy inside the nucleus to hold all the nucleons together.
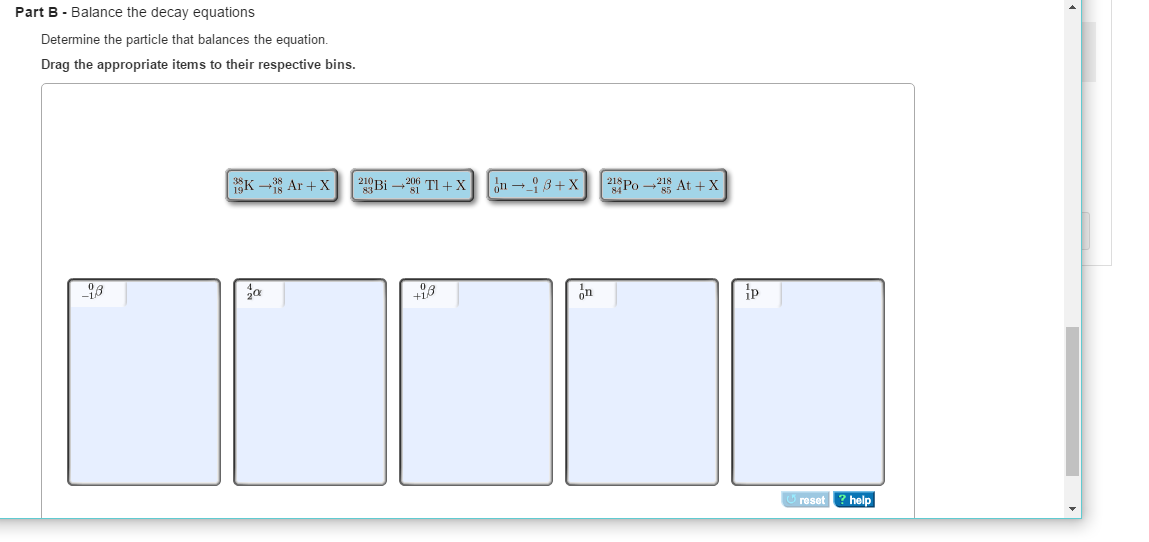
Why do nuclei become unstable?
When the atoms of an element have extra neutrons or protons it creates extra energy in the nucleus and causes the atom to become unbalanced or unstable. Whether radioactive elements can become stable and if so, how. The unstable nucleus of radioactive atoms emit radiation.
Why do some nuclei disintegrate?
Nuclei with too many, or too few, neutrons do exist naturally but are unstable and will disintegrate (or decay) by emitting radiation. This is called radioactive decay.
What is the decay of nuclei?
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive.
What causes radioactive decay to occur?
Radioactive decay involves the spontaneous transformation of one element into another. The only way that this can happen is by changing the number of protons in the nucleus (an element is defined by its number of protons). There are a number of ways that this can happen and when it does, the atom is forever changed.
Why do some elements decay?
Every atom seeks to be as stable as possible. In the case of radioactive decay, instability occurs when there is an imbalance in the number of protons and neutrons in the atomic nucleus. Basically, there is too much energy inside the nucleus to hold all the nucleons together.
Why do some atoms decay GCSE?
Nuclear decay refers to the changes in unstable isotopes as they change to other more stable isotopes with the release of particles and energy in the form of radiation. Beta decay happens to small nuclei with an unstable ratio of neutrons to protons.
Why does a neutron decay?
Outside of stable atomic nuclei, neutrons decay when one of their down quarks undergoes weak nuclear decay into an up quark, transforming the neutron into a positively charged proton and spitting out a negative electron and an antineutrino in compensation.
Why does beta decay happen?
Beta decay occurs when an atom has either too many protons or too many neutrons in its nucleus.
What happens radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the random process in which a nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This is usually in the form of alpha particles (Helium nuclei), beta particles (electrons or positrons), or gamma rays (high energy photons). The nucleus' energy reduces, making it more stable.
What are nuclei?
A nucleus, as related to genomics, is the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes. An array of holes, or pores, in the nuclear membrane allows for the selective passage of certain molecules (such as proteins and nucleic acids) into and out of the nucleus.
Why does radioactive decay occur quizlet?
What is radioactive decay? When unstable atoms break down by releasing energy and or particles until they reach a stable form. It is a random process that can be modeled by exponential decay.
What increases the rate of radioactive decay?
The rate of this kind of decay depends on the chance of an electron straying into the nucleus and getting absorbed. So increasing the density of electrons surrounding the atomic nucleus can speed up the decay.
What is the process of nucleosynthesis?
Nucleosynthesis is the creation of new atomic nuclei, the centers of atoms that are made up of protons and neutrons. Nucleosynthesis first occurred within a few minutes of the Big Bang. At that time, a quark-gluon plasma, a soup of particles known as quarks and gluons, condensed into protons and neutrons.
What is the term referred to the process by which light nuclei fuse together to form heavier nuclei?
nuclear fusion, process by which nuclear reactions between light elements form heavier elements (up to iron).
Can you replace one element into another element?
One element cannot be changed into another in this way. But it can be done by the methods of a new science called nuclear chemistry.
What is the product of nuclear decay?
Often, the products of nuclear decay reactions are formed in an excited state . Similar to the way an electron in an excited state will emit energy as it returns to the ground state, the daughter nuclei release a high-energy photon (a gamma ray) as it reaches its stable form.
What are the different types of nuclear decay?
Types of Nuclear Decay. There are six common types of nuclear decay. 1. Alpha decay produces a helium-4 nucleus, which is also known as an alpha particle. The daughter nucleus therefore contains two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent.
How long does it take for a radioactive element to decay?
The half-life of a radioactive element is the time that it takes for half the nuclei in the sample to decay in a first-order reaction. The half-life of a radioisotope can be fractions of a second or millions of years, depending on the element.
What is the term for a nucleus breaking completely?
Positron emission tomography (PET) is commonly used in medicine. PET image of a human brain [2] 6. Spontaneous fission occurs when a nucleus breaks completely, creating two separate pieces with different atomic numbers and atomic masses.
What is beta decay?
Beta decay is commonly observed in nuclei that have a large number of neutrons. A neutron is split into a proton and a high-energy electron (called the beta particle ), the latter of which is ejected from the nucleus. public domain image. Neutron to proton ratio Mass number Atomic number.
What is the opposite of beta decay?
Positron emission can be thought of as the opposite of beta decay. A proton is split to make a neutron and a positron. (A positron has the same mass as an electron, but the opposite charge.) The positron is then ejected from the nucleus. Positron emission tomography (PET) is commonly used in medicine.
What is the half life of a radioactive sample?
Half-life#N#( t 1 / 2)#N#(t_ {1/2}) (t1/2#N##N#) is defined as the time taken for half of the original number of atoms in a radioactive sample to disintegrate. The half-life remains constant. Even if the sample has undergone one half-life, the time period for the next half-life remains unchanged.
Why do some nuclei decay while others don't?
Every atom seeks to be as stable as possible. In the case of radioactive decay, instability occurs when there is an imbalance in the number of protons and neutrons in the atomic nucleus.
What happens to the atomic nucleus during gamma decay?
In gamma decay, the atomic nucleus releases excess energy in the form of high-energy photons (electromagnetic radiation). The atomic number and mass number remain the same, but the resulting nucleus assumes a more stable energy state.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay a the spontaneous process through which an unstable atomic nucleus breaks into smaller, more stable fragments. Have you ever wondered why some nuclei decay while others don't? It's basically a matter of thermodynamics.
How many forms of radioactive decay are there?
There are three forms of radioactive decay: which of these an atomic nucleus undergoes depends on the nature of the internal instability. Some isotopes can decay via more than one pathway.
Why are isotopes more stable?
This is because the nucleons (protons and neutrons) aren't fixed in place in the nucleus, but move around, and the protons repel each other because they all carry a positive electrical charge.
What is the particle that decays in an alpha nucleus?
In alpha decay, the nucleus ejects an alpha particle, which is essentially a helium nucleus (two protons and two neutrons), decreasing the atomic number of the parent by two and the mass number by four.
What is the half life of radioactive isotopes?
This means stable isotopes include those that never break, like protium (consists of one proton, so there's nothing left to lose), and radioactive isotopes, like tellurium -128, which has a half-life of 7.7 x 10 24 years. Radioisotopes with a short half-life are called unstable radioisotopes.