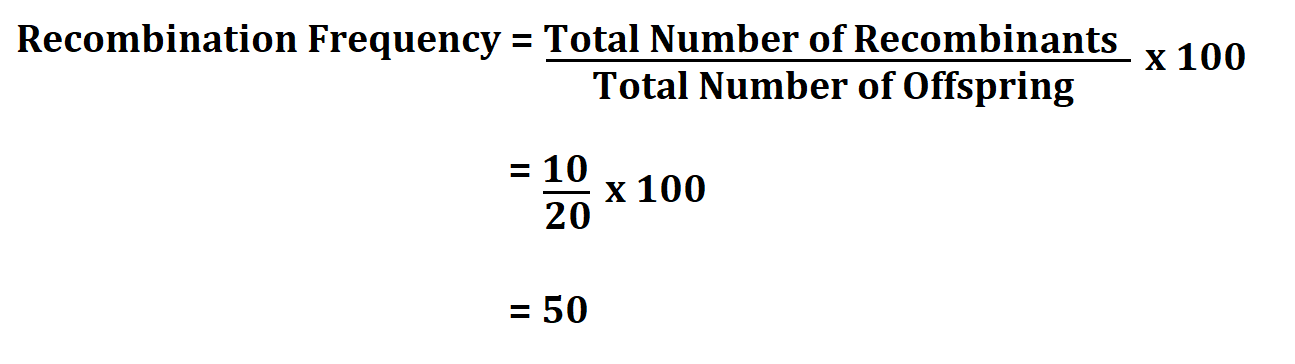
Why do recombination frequencies not add up? Because the map units are based on recombination frequencies, and not physical distance, the numbers don’t always perfectly add up. … Any two genes that are more than 50 map units apart behave as if they’re on different chromosomes and independently assorting.
Why recombination frequency is not more than 50%?
The recombination frequency between two genes cannot be greater than 50% because random assortment of genes generates 50% recombination (non-linked genes produce 1:1 parental to non-parental. Thus, the recombination frequency would be non-parental/total --> 1/(1+1) = 50%).
How do you calculate recombination frequencies?
The # of recombinant offspring / total # of offspring x 100% = recombination frequency.
Why do calculations of recombination frequencies between loci that are far apart on chromosomes underestimate the true genetic distance between the loci?
The calculated recombination frequency will underestimate the true crossover frequency because the double crossover progeny are not counted as recombinants.
What does recombination frequency depend on?
relative chromosomal locationsRecombination is defined as any process that results in gametes with combinations of alleles that were not present in the gametes of a previous generation. The recombination frequency between any two loci depends on their relative chromosomal locations.
What is the relationship between recombination frequency and the actual physical distance on a chromosome?
So, we can say that a pair of genes with a larger recombination frequency are likely farther apart, while a pair with a smaller recombination frequency are likely closer together.
Why does recombination frequency increase with distance?
This is because as the two genes are located farther apart, the chance of double or even number of crossovers between them also increases.
What is crossing over and how does it explain recombination between linked genes?
Crossing-over occurs when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis I. The closer together two genes are on a chromosome, the less likely their alleles will be separated by crossing-over.
Is recombination frequency the same as map distance?
Geneticists routinely convert recombination frequencies into cM: the recombination frequency in percent is approximately the same as the map distance in cM. For example, if two loci have a recombination frequency of 25% they are said to be ~25cM apart on a chromosome (Figure 7.6. 9).
Why does crossing over occur more often between two distantly linked genes than between two closely linked genes on the same chromosome?
a) Crossing over frequency depends on the flexibility of a specific chromosomal region. Two genes that are far apart are more likely to have a crossover between them than two genes that are close together.
What increases recombination frequency?
Haploid chromosome number Under the obligate CO requirement, a higher recombination rate could be achieved by increasing the number of chromosomes or by having smaller chromosomes; bird genomes, containing many microchromosomes, provide support for this hypothesis [37,63].
What are the limits of recombination?
The limit of recombination is 50%.
Is recombination and crossing over the same?
Recombination of genes in the gametes is the result of crossing over or in other words crossing over leads to genetic recombination. Crossing over refers to the exchange to genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at the pachytene stage of prophase 1 of meiosis I.
How do you calculate frequency?
f = 1 / T . f denotes frequency and T stands for the time it takes to complete one wave cycle measured in seconds. The SI frequency unit is Hertz (Hz), which equals 1/s (one cycle per second). Other frequency units include millihertz (mHz), kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), and terahertz (THz).
How do you calculate crossover frequency in genetics?
We use the unit centimorgan (cM) to measure distance between genes based on offspring phenotype frequency. A centimorgan = 100 times the frequency of crossovers in the offspring. In this example, the frequency of crossovers is 10/100 and the distance between the genes is 100 * 1/10 = 10 centimorgans.