Why do tectonic plates move simple answer? Plates at our planet’s surface move because of the intense heat in the Earth’s core that causes molten rock in the mantle
Mantle
The mantle is a layer inside a terrestrial planet and some other rocky planetary bodies. For a mantle to form, the planetary body must be large enough to have undergone the process of planetary differentiation by density. The mantle lies between the core below and the crust above.
What causes the tectonic plates to continuously move?
convection currents are a process in which the materials inside the mantle heat up and rise to the surface whilst the cooler liquid sinks; as it sinks it then heats up and rises again. This continuous cycle is established: hot liquid rising, cold liquid descending. These currents cause the tectonic plates to move.
What is the main reason why Earth's tectonic plates move?
Tectonic plates are able to move because Earth's lithosphere has greater mechanical strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection; that is, the slow creeping motion of Earth's solid mantle.
Why do tectonic plates move towards each other?
The main driving force of plate tectonics is gravity. If a plate with oceanic lithosphere meets another plate, the dense oceanic lithosphere dives beneath the other plate and sinks into the mantle: this process is called subduction. The sinking oceanic lithosphere drags the rest of the tectonic plate: this is the main cause of plate motion.
What layer of Earth causes tectonic plates to move?
- Tectonic plates are 62 miles thick and are made up of the continental crust and the oceanic crust.
- Slab pull is the most relevant force that affects the movement of tectonic plates.
- Convection refers to specific cells within the Earth’s mantle that create heat. The heat makes the solid rocks move upwards while the colder rocks move downwards.

What is the main force behind the tectonic plates?
It is the biggest driving force behind all of the tectonic plate movement. However, the main force that is behind all of the previously mentioned forces is gravity itself. Gravity is the reason why all of these other forces are capable of moving the tectonic plates.
Why are tectonic plates moving?
The first of the possible reasons is the mantle convection currents. These currents are warm, and they can carry and drive the tectonic plates that make up the lithosphere in a way that resembles a conveyor belt. The second reason often cited by researchers is the ridge push. The ridge push occurs at the resilient upwelling mantle at ridges placed on the mid-ocean level.
What is the third force that causes tectonic plates to move?
The third force that causes the tectonic plates to move is the slab pull. This force occurs when the older plates start to sink. As the plates age, they become colder, which makes them denser than the mantle beneath them. They start to sink and pull the warmer parts of the plate with them.
Why are the newly formed plates placed at the oceanic ridges still warm?
The newly formed plates placed at the oceanic ridges are still warm once they are formed, so their elevation is higher than colder, denser plate material that is placed further in the ridge. Gravity causes the higher plates to push away the lithosphere that is placed in the further parts of the ridge. The third force that causes the tectonic plates ...
What happens when the plates meet?
To explain all of this more simply, once the plates meet each other, oceanic plates will dive beneath other plates and sink deeper into the mantle. We call this process subduction. The rest of the tectonic plate gets dragged along with the oceanic lithosphere, and this causes the plates to move.
How thick are tectonic plates?
Tectonic plates are large pieces of the Earth’s crust and its topmost mantle. When viewed together, they form the lithosphere. These plates are 62 miles thick and are made up of two types of material. These materials are the continental crust and the oceanic crust. Their compositions differ greatly.
What are the materials that make up the continental crust?
Their compositions differ greatly. The oceanic crust consists of mafic basaltic rocks, while the continental crust is made up of lower-density felsic granitic rocks. Multiple theories try to explain why the tectonic plates are moving. According to the most recent research, ...
IRIS ingests, curates, and distributes geoscience data
IRIS provides management of, and access to, observed and derived data for the global earth science community.
IRIS operates, provides, and maintains geoscience instrumentation
IRIS facilitates seismological and geophysical research by operating and maintaining open geophysical networks and providing portable instrumentation for user-driven experiments.
IRIS provides a wide range of education, workforce, and outreach resources
Our mission is to advance awareness and understanding of seismology and earth science while inspiring careers in geophysics.
Why do plates move?
Plates at the surface of the Earth move due to intense heat from the core of the planet. The heat makes the molten rock to move in convection cells pattern, consequently causing the plates to move.
What is the theory of plate tectonics?
Developing the Theory of Plate Tectonics. The mechanism of the tectonic plate movement has been the debate among the Earth scientists. They once based their argument on the convection cells that the Earth's tectonic plates surfed on them. However, they currently have the belief that the movement of the tectonic plates does not only depend on ...
What is the difference between the new and old plates?
The new parts of the plates constitute the warm and the thin sections, while the old parts constitute the cold and dense part. Through the ridge push, hot magma rises and forms crust on the surface, pushing the other portion of the plates outwards. On the other hand, the old parts sink down into the mantle at subduction zones through the slab pull process because they are denser than the material in the mantle. The theory of plate tectonics develops from the ridge push and the slab pull which together lead to the motion of the tectonic plates.
Why do old parts sink down into the mantle?
On the other hand, the old parts sink down into the mantle at subduction zones through the slab pull process because they are denser than the material in the mantle. The theory of plate tectonics develops from the ridge push and the slab pull which together lead to the motion of the tectonic plates.
What is a tectonic plate?
Introduction. A tectonic plate is a large slab of solid rock with an irregular shape that is made up of the oceanic and continental lithosphere. The size of the plate varies to a large extent, ranging from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers. Plates at the surface of the Earth move due to intense heat from the core of the planet.
Which theory of tectonics is based on the fact that there are warmer and thinner parts of answer?
The theory of plate tectonics is based on the fact that there are warmer and thinner parts of tectonic plates that have high tendency to rise and colder and denser parts which have high tendency to sink. The new parts of the plates constitute the warm and the thin sections, while the old parts constitute the cold and dense part.
Why does the material further away from the inner core sink down?
On the other hand, the material further away from the inner core sinks down due to its weight (since it is still cold) and replaces the warm material that has risen. As this material sinks down, the heat from the inner core makes it warm and it rises while the material above it gets cold and sinks down.
Why do plates move?
Why Plates Move. Both plate boundaries and plates move over time. As previously described, plates can change the locations of trenches and subduction zones, as well as the positions of midoceanic ridges and transform faults. For example, subduction at a convergent boundary can stop in one location and begin nearby in another.
How do plates move apart?
Mechanisms of plate movement and subduction. Three mechanisms (in order of importance) have been proposed to explain why plates move apart and subduct: slab‐pull, ridge‐push, and trench‐suction. Slab‐pull is the result of a plate subducting at a steep angle through the mantle; this downward motion tends to pull the other side of the plate away from the ridge crest. The ridge‐push theory maintains that new crust cools as it moves away from the ridge, becoming more dense, sinking, and forming a slope on the midoceanic ridge. A parallel slope may develop underneath the plate at the base of the lithosphere. These surfaces are zones of weakness that help the plate move away from the ridge. When a plate is subducted at a steep angle, it also creates trench‐suction that pulls the overlying plate, and the trench, toward the ridge.
How does convection affect plate tectonics?
It is reasonable to assume that the heat radiated from the core creates convection currents in the mantle, and the mantle rocks begin to move plastically. Convection movement in the uppermost layers of the mantle may pull on the lithospheric rocks, breaking them into huge plates that move slowly on the more plastic, lubricated surface of the asthenosphere. Another possibility is that the 670‐kilometer boundary in the mantle breaks the convection pathways into an upper and lower part; convection in the lower part may induce the convection currents in the upper part (less than 670 kilometers deep) that move the plates. Still others believe that plate motion on the surface creates the underlying mantle convection—that is, when plates diverge, hotter mantle rock rises upward to fill the space between the plates, helping to push them apart; as the plates move away from the spreading center they cool and begin to sink, creating downward currents.
What Causes the Movement of Tectonic Plates?
Scientists have theorized three mechanisms that cause plate movement. One is mantle convection. Convection occurs when materials move in currents due to differences in heat and density. During convection, heated particles begin to circulate, and hot particles move to the top while cold particles move to the bottom. Inside Earth's mantle, when pieces of rock and crust become very hot and less dense, they rise, whereas the cooling parts of the mantle at the surface become less dense and sink.
How do plates move?
Over time, plates move by internal heat from inside Earth. The main driving factors include both heath and gravity. Subsequently, these forces drive mechanisms to build new Earth material and recycle old back into Earth. These mechanisms include convection, ridge push, and slab pull.
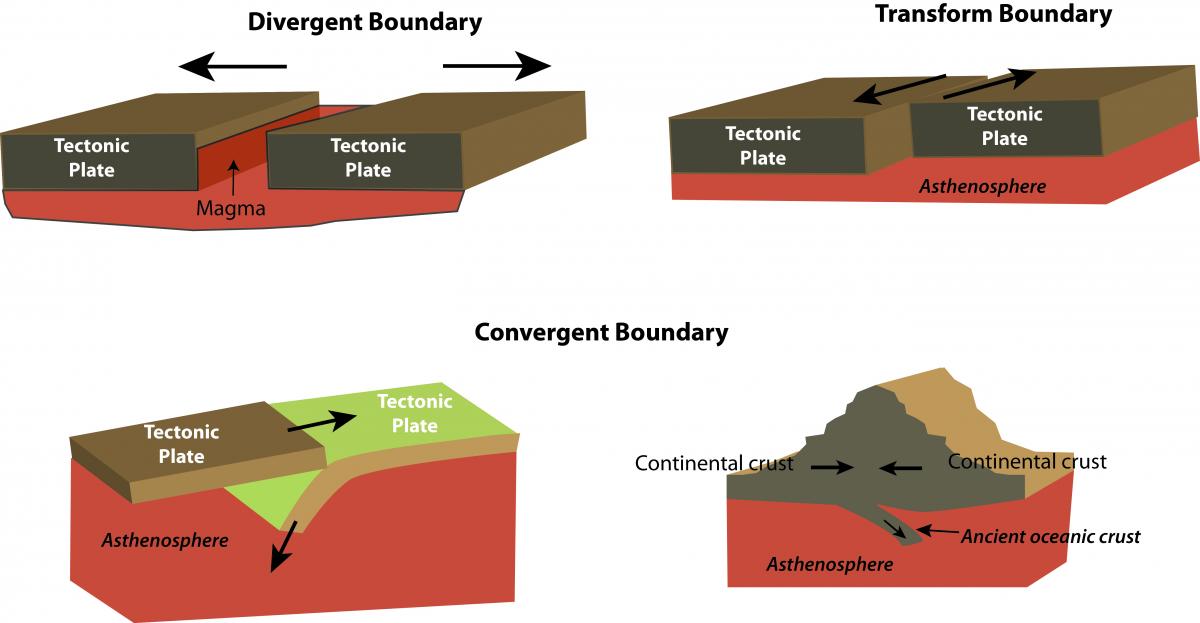
What is convergent boundary?
In a convergent plate boundary, two plates collide together. There are three main types of convergent bo undaries. In a continent-continent collision, the plates are pushed against each other, and some of the crust is pushed upward to create mountains. In a continent-ocean collision, the oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate because the oceanic lithosphere is denser. In an ocean-ocean collision, the denser plate sinks below the less dense plate.
What is the theory that the Earth's lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates?
Scientists have taken their knowledge of seafloor spreading, Earth's crust, and continental drift to form a single theory called plate tectonics . This theory argues that pieces of Earth's lithosphere called tectonic plates are in slow, constant motion, driven by forces in the mantle.
What are the causes of volcanoes?
Other phenomena that occur due to plate movement include earthquakes and volcanic activity . Divergent and convergent plate boundaries, as well as hot spots, can also form volcanoes. For example, the Hawaiian Islands are formed through hot-spot activity. A hot spot is a geographic place where a column of very hot mantle rock, known as a mantle plume, rises through the asthenosphere and into the lithosphere. When it reaches the lithosphere, it melts to form magma, which can then rise and form a volcano on Earth's surface. Tectonic plates move over hot spots, or mantle plumes, where volcanoes form and then move on with the tectonic plate. The fixed plume stays in place and is able to form another volcano.
What is the third theory of plate movement?
The third theory of plate movement relates to subduction zones and a process known as slab pull. Slab pull occurs as dense tectonic plates sink beneath less dense plates. This creates a pull on the rest of the plate behind it. Both slab pull and ridge push create a conveyer belt effect among tectonic plates. Because subducting plates create the fastest type of tectonic plate movement, many scientists think that slab pull may be the most significant force behind plate movements.
What evidence supports Hess's theory of seafloor spreading?
Several pieces of evidence supported Hess's theory of seafloor spreading: eruptions of molten material (volcanoes), magnetic stripes in oceanic rocks, and the ages of oceanic rocks. One intriguing point is the fact that Earth's poles have reversed many times during Earth's life. Scientists have studied these "striped" seafloor rocks, also known as magnetic reversals, and determined that they hold a record of reversals that have occurred over time.
Why do tectonic plates move?
Tectonic plates move because they are floating on top of the mantle. The mantle itself moves due to convection currents: hot rock rises, gives off some heat, then falls. This creates vast swirls of moving rock under the crust of the earth, which jostles the plates of crust on top.
What would happen if the tectonic plates stopped moving?
If it ended, we would end. Erosion - which, if the tectonic plates stopped moving, would tear the mountains down, then the land masses, until the earth was covered completely in about a mile of water (there is roughly 330 million cubic miles of water on the earth).
Why are the plates dragged around?
The plates are dragged around by the movements of the molten rock in the mantle beneath. The mantle is boiling or “convecting” due to heat escaping from the Earth’s core.
What is the role of water in subduction?
Water. Subduction is assisted by the presence of liquid water, which allows for partial melting of the downgoing slab and it thought to ‘lubricate’ the subduction zone. The critical importance of water to plate tectonics. The role of liquid water in maintaining plate tectonics and the regulation of su.
Why does the mantle flow under pressure?
Beneath the plates, the mantle due to heat and pressure is much more ductile, and will flow under pressure. One primary theory is that the heat of the core induces convection in the mantle in order to distribute heat upward, and allow cooler denser rocks to descend. This convection motion results in upwelling a.
How long does plate tectonics last?
Plate tectonics occurs over periods of hundreds of thousands to millions of years. It doesn't all
What causes the heat to move from the core to the surface?
That constant movement to equalize all energy causes the heat to move from core to surface and for the surface itself to move about. Combine these gravitational forces with the percolating heat from inside the core, and what you get are plates that float around on top of the juicy, flavorful liquid center.
How do plates move?
The plates can be thought of like pieces of a cracked shell that rest on the hot, molten rock of Earth’s mantle and fit snugly against one another. The heat from radioactive processes within the planet’s interior causes the plates to move, sometimes toward and sometimes away from each other.
What is the tectonic shift?
Tectonic shift is the movement of the plates that make up Earth’s crust. The Earth is made up of roughly a dozen major plates and several minor plates. The Earth is in a constant state of change. Earth’s crust, called the lithosphere, consists of 15 to 20 moving tectonic plates. The plates can be thought of like pieces of a cracked shell ...
How fast do land masses move?
Earth’s land masses move toward and away from each other at an average rate of about 0.6 inch a year. That’s about the rate that human toenails grow! Some regions, such as coastal California, move quite fast in geological terms — almost two inches a year — relative to the more stable interior of the continental United States. At the “seams” where tectonic plates come in contact, the crustal rocks may grind violently against each other, causing earthquakes and volcano eruptions. The relatively fast movement of the tectonic plates under California explains the frequent earthquakes that occur there.
What is plate motion?
This movement is called plate motion, or tectonic shift. Our planet looks very different from the way it did 250 million years ago, when there was only one continent, called Pangaea, and one ocean, called Panthalassa. As Earth’s mantle heated and cooled over many millennia, the outer crust broke up and commenced the plate motion ...
Why do earthquakes occur in California?
At the “seams” where tectonic plates come in contact, the crustal rocks may grind violently against each other, causing earthquakes and volcano eruptions. The relatively fast movement of the tectonic plates under California explains the frequent earthquakes that occur there.

Introduction
Convection Cells in The Mantle
- The interior part of the Earth consists of both metal and rock. In the inner core, the temperature is higher than the temperature on the surface of the Sun, setting the materials on the outer core and the molten rock in the mantle in motion. In essence, the material close to the inner core is warm due to the intense heat in that region, and as a result, it becomes lighter than the one above it an…
Developing The Theory of Plate Tectonics
- The mechanism of the tectonic plate movement has been the debate among the Earth scientists. They once based their argument on the convection cells that the Earth's tectonic plates surfed on them. However, they currently have the belief that the movement of the tectonic plates does not only depend on the convection cells in the mantle but also the plates' motion that corresponds t…
Controversy Surrounding Tectonic Plate Movement
- From the convection cells in the mantle and the theory of plate tectonics, the operation of the plates movement appears to lack more details to explain it fully. Earth's scientists are still debating amongst themselves on the mechanism by which the Earth's tectonic plates move. Therefore, the process of the movement in detail is highly controversial.