Healthcare providers use enzyme marker tests for different purposes:
- Screenings: As part of a routine physical examination, an enzyme marker test can identify potential problems like organ or muscle damage or stress.
- Diagnosis: You may get an enzyme marker test to diagnose a specific disease or heart problem.
- Monitoring: Test results can show if a treatment is working or if medications are damaging organs.
What does it mean to have high cardiac enzymes?
What does it mean when your heart enzymes are high? High levels of cardiac enzymes can mean a number of things, but they often signal some type of damage to the heart. Enzymes are proteins that promote specific biochemical reactions within cells.
What does it mean when you have elevated heart enzymes?
These enzymes are normally present in low quantities in the bloodstream. When these levels are elevated, it indicates that the heart muscle may be injured or may not be getting enough oxygen. In this article, we take a look at the cardiac enzyme test and the possible causes behind elevated cardiac enzyme levels.
What causes low cardiac enzymes?
Low levels of this metabolic enzyme indicate good health while high levels demonstrate that some sort of muscular event has taken place in your body. Injury, such as injuries sustained to your heart muscles after a heart attack, causes the enzyme to leak out from your muscle tissue into your bloodstream.
What is the normal range of cardiac enzymes?
Normal cardiac enzyme levels are between 0 and 3 for creatine kinase, between 0 and 3 nanograms per millimeter for creatine kinase-MB, less than 0.4 nanograms per millimeter for troponin and 38-120 nanograms per millimeter for total creatine kinase, according to the University of Minnesota. These levels are checked during a cardiac enzyme study to diagnose injuries to a patient's heart muscle ...
Why would a doctor order a cardiac enzyme test?
A cardiac enzyme test is a tool used by doctors to determine if someone is having or has already had a heart attack. This test checks for levels of enzymes that are released by the heart muscle when it is injured, such as during a heart attack.
When should cardiac enzymes be tested?
A cardiac enzyme test is one tool doctors use to see if you're having -- or already had -- a heart attack. You might also get the test if you have symptoms of a blockage in your heart's arteries such as: Chest pain or pressure. Dizziness.
What are the symptoms for elevated cardiac enzymes?
If you're having chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, and abnormal electrocardiography (ECG) results, for instance, knowing your enzyme levels can help determine whether you are in the midst of a heart attack.
Do elevated cardiac enzymes always indicate heart attack?
Elevations of cardiac enzymes are commonly used to indicate myocardial ischemia, but they can be elevated due to other conditions.
Can anxiety raise heart enzymes?
BACKGROUND: Stress-induced cardiomyopathy is usually associated with an increased level of cardiac enzymes, leading to difficulties in differentiating this condition from acute coronary syndrome.
What does it mean when your enzymes are elevated?
Elevated liver enzymes often indicate inflammation or damage to cells in the liver. Inflamed or injured liver cells leak higher than normal amounts of certain chemicals, including liver enzymes, into the bloodstream, elevating liver enzymes on blood tests.
How do you fix elevated heart enzymes?
If a doctor determines that a heart attack caused the elevated cardiac enzymes levels, the person will require treatment in the hospital with medications or surgery to restore blood flow to the heart.
What are 3 cardiac enzymes that can be diagnostic?
Cardiac enzymes ― also known as cardiac biomarkers ― include myoglobin, troponin and creatine kinase. Historically, lactate dehydrogenase, or LDH, was also used but is non-specific. Cardiac enzymes are released into the circulation when myocardial necrosis occurs, as seen in myocardial infarction.
When should troponin levels be checked?
Your health care provider will order this test if you have chest pain and other signs of a heart attack. The test is usually repeated two more times over the next 6 to 24 hours. Your provider may also order this test if you have angina that is getting worse, but no other signs of a heart attack.
How often do you check troponin levels?
Testing is usually repeated two or more times in a 24-hour period. This is done to see if there are any changes in troponin levels over time.
What are 3 cardiac enzymes that can be diagnostic?
Cardiac enzymes ― also known as cardiac biomarkers ― include myoglobin, troponin and creatine kinase. Historically, lactate dehydrogenase, or LDH, was also used but is non-specific. Cardiac enzymes are released into the circulation when myocardial necrosis occurs, as seen in myocardial infarction.
Which cardiac enzyme is the best early indicator of MI?
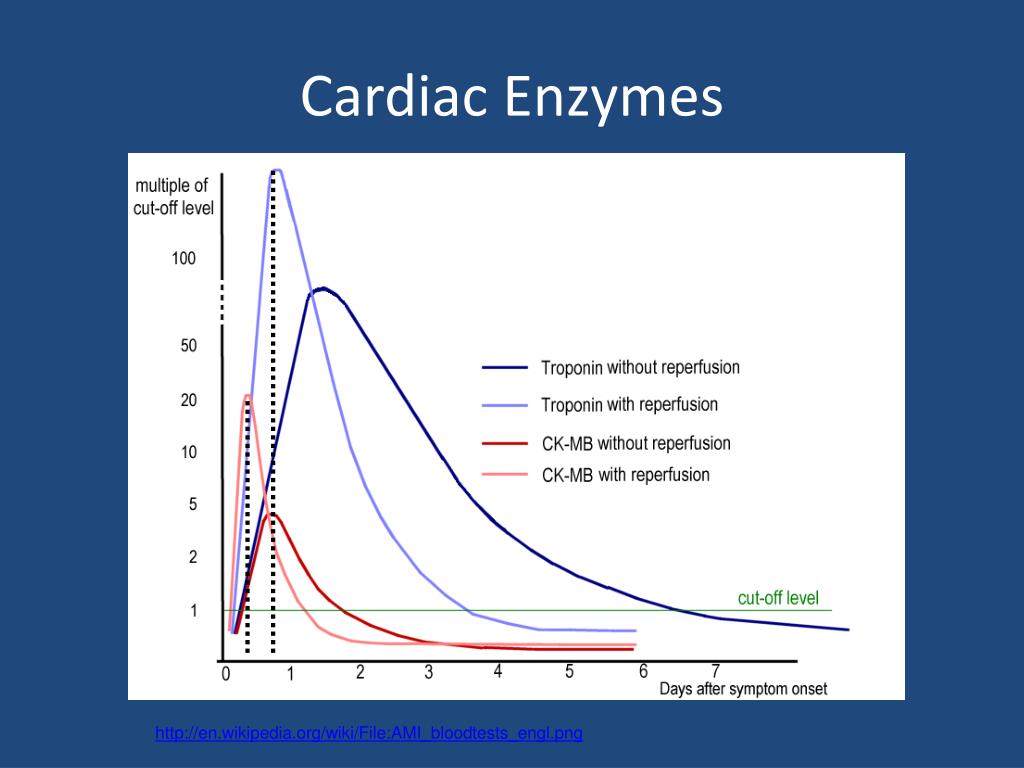
Troponins are the most widely recognized and important cardiac enzymes used in the diagnosis of acute myocardial ischemia in modern medicine. The majority of patients with an acute MI will have elevation in troponins within 2 to 3 hours of arrival at the emergency department, versus 6 to 12 hours with creatine kinase.
Where do you get a cardiac enzyme marker test?
In an emergency situation, the blood draw takes place in the emergency department or hospital. For non-urgent situations, the test may take place at your healthcare provider’s office or a blood-testing lab.
Who needs a cardiac enzyme (cardiac biomarker) test?
Your healthcare provider may order a cardiac enzyme test if you have symptoms of a possible heart problem. These symptoms include:
What is the normal range for cardiac enzymes (cardiac biomarkers)?
Heart enzyme results vary depending on the specific cardiac enzyme and test. The tests measure enzyme levels in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that help your body manage metabolism and other chemical processes. Thousands of types of enzymes perform specialized functions, like:
Why do you need a cardiac enzyme test?
Reasons for a Cardiac Enzyme Test. A doctor will administer a cardiac enzyme test if you suspect you have had or are having a heart attack. Other symptoms of a heart artery blockage that might yield a cardiac enzyme test include: Chest pain or pressure. Dizziness.
What is the most common enzyme in a heart test?
There are several different kinds of cardiac enzymes, the most common of which is troponin, a protein released from heart cells when they’re damaged.
What to do if you have a heart attack?
If you had a heart attack or are having one, your doctor will speak to you about treatment, medicine, lifestyle changes and follow-up care. Your doctor may request multiple enzyme tests over time to see how your levels change.
How long does it take to get blood tested for a syringe?
A pinch or sting should be the extent of the discomfort you feel. The blood will be tested, a process that typically only takes a few minutes.
Can a blood test detect enzymes?
The test can detect incredibly small amounts of enzyme that have been released. Your doctor will help you understand the test results and will give you a physical exam or other tests to get a full picture of the reasons for your symptoms.
Why do you need a cardiac enzyme test?
This is because other factors besides heart attacks can cause high cardiac enzyme levels.
What does a cardiac enzyme test show?
The results of a cardiac enzyme test can indicate if someone had a heart attack.
How is troponin measured?
Doctors and scientists measure troponin in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). The more nanograms per milliliter found in the blood, the higher the likelihood of a heart attack.
Why do doctors check troponin levels?
Both troponin types are commonly checked because they are the most specific enzymes to a heart attack. Doctors may also check the levels of creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and myoglobin in some situations. These enzymes are normally present in low quantities in the bloodstream. When these levels are elevated, it indicates that ...
What is pulmonary embolism?
pulmonary embolism, a blockage of an artery in the lungs. kidney disease. congestive heart failure. weakening of the heart muscle. injury or trauma to the heart muscle, such as from a car accident. prolonged exercise. swelling of the heart muscle. open heart surgery. cardiac stenting.
What causes a high enzyme level in the heart?
Other causes. There are a few other factors that may cause cardiac enzyme levels to be elevated. These include the following: pulmonary hypertension. tachycardia, where the heart beats faster than normal. pulmonary embolism, a block age of an artery in the lungs. kidney disease. congestive heart failure.
What is the best treatment for a heart attack?
nitroglycerin. beta-blockers. ACE inhibitors. pain medications. A doctor may recommend that a person who has just had a heart attack should have surgery in addition to treatment with medications. Doctors may suggest coronary stenting or coronary artery bypass surgery.
What is a cardiac enzyme test?
What Is Cardiac Enzyme Testing? Cardiac Enzyme Testing is a test carried out by doctors to understand if the patient is having or has had a heart attack before. This test is also done in cases where patients have heart arteries blockage symptoms like pain in the chest, fatigue, feeling tired, breathing difficulty, etc.
What are the biomarkers of cardiac enzymes?
Cardiac Enzymes which are otherwise called Cardiac Biomarkers include Myoglobin, Troponin, and Creatine Kinase.
What is the result of a cardiac test?
The result of the Cardiac test mainly shows the measure of different enzymes and proteins like the Troponin. Troponin is actually very low in the blood and is undetectable in blood tests. But, when a heart attack or injury to the heart occurs, then the level of Troponin increases. Usually, Troponin is measured in ng/ml. The higher the value of Troponin the more is the probability of a heart attack.
What causes a heart attack?
A heart attack is caused when the blood that flows to the heart is obstructed, mostly by the fat or cholesterol, or anything else as such that in turn forms a plaque in the arteries that pump blood to the heart. The more common or risk making causes of Coronary heart attack include, but not limited to; Smoking.
Why do enzymes rise after a heart attack?
Post heart attack, these enzymes level rises abnormally because of the damage of a muscle due to overstress on the heart. So, checking the count of these enzymes is highly considered to perceive if something severe is happening.
What biomarker is used to determine if a patient has a heart attack?
These Biomarkers help the doctor to see the history of any heart attacks that the patient might have. Troponin T is the main biomarker that’s measured during the Cardiac Enzyme Test.
Why does my enzyme blood test go down?
The causes of such irregular values may be Sepsis, atrial fibrillation, certain heart conditions like cardiomyopathy, valvular heart problems, injuries, etc.