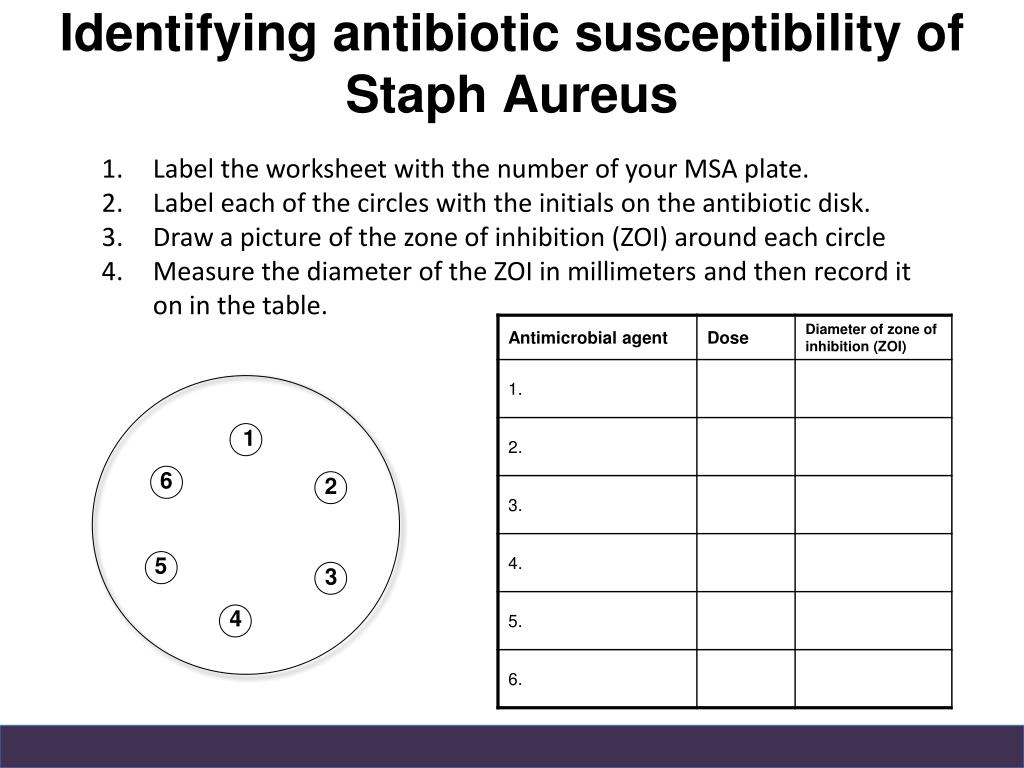
The zone of inhibition is used to determine whether a particular bacterium is susceptible to the action of a particular antimicrobial An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or inhibits their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function.Antimicrobial
What is a zone of inhibition test?
Zone of Inhibition Test for Antimicrobial Activity. A Zone of Inhibition Test, also called a Kirby-Bauer Test, is a qualitative method used clinically to measure antibiotic resistance and industrially to test the ability of solids and textiles to inhibit microbial growth.
What are the factors that affect the zone of inhibition?
Zone of inhibition also affected by the Concentration of bacteria spread onto agar plate, Drug antagonists, incubation temperature, incubation time, size of the plates, proper spacing of the disks, reading of the zone, etc. 1. Zone of inhibition testing is fast and inexpensive relative to other laboratory tests for antimicrobial activity.
What is the standard for measuring the zone of inhibition in antibiotic overlay?
What is the standard for measuring the zone of inhibitions in antibiotic overlay assay (i.e. isolates spot-inoculated on agar then overlaid with soft agar with the test strain)? 1. Measure the diameter of the whole zone of inhibition like that of kirby-bauer disc diffusion assay, or 2.
Why is the disc included in the zone of inhibition?
The reason for including the disc especially where there is activity is that the disc itself sits in the centre of the zone of inhibition, so the area it occupies is part of the zone of inhibition. I was wondering if we could use the "Area" measurement of Image J for antimicrobial activity.
How to measure inhibition zone?
What is the purpose of the diameter of the zone of inhibition chart?
What is the zone of inhibition?
Why do antibiotics grow at a certain distance from the disk?
What is the purpose of a macrolide?
Where to measure the diameter of an antibiotic disk?
What is the name of the drug that interferes with the cell walls of bacteria?
See 4 more
About this website

Why is the Zone of Inhibition important?
Zone of Inhibition Testing is a fast, qualitative means to measure the ability of an antimicrobial agent to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. In the world of antimicrobial substances/surfaces, the degree to which these materials are inhibitory can be of vital importance to the health of the consumer.
What does the inhibition zone tell you?
The zone of inhibition is a uniformly circular zone of no bacterial growth around the antibiotic disk. The larger this zone is, the more sensitive the bacteria is to that antibiotic. The smaller the zone is, the more resistant (and, thus, less sensitive) the bacteria is.
What measurement is used in zone of inhibition?
All Answers (21) The zone is measured by the diameter (across the zone) and you do not consider the disc at all. If you have ony a partial zone due to overlapping zones by neighbouring disks, you can measure the radius from the middel (center) of the disc to the edge of the zone and multiply by two.
What happens if there is no zone of inhibition?
While it might do a very effective job in protecting the product itself, a lack of a visual zone under the Zone of Inhibition test standards might falsely lead the inexperienced evaluator to think that the antimicrobial is ineffective.
What affects the zone of inhibition?
Zones of inhibition were larger when the incubation temperature was lower than that which was commonly used and/or when the nutrient level was decreased; the zones were smaller when the incubation temperature was raised and/or when an increased nutrient level was used.
What does zone of inhibition mean in microbiology?
Definition. (microbiology) The clear region around the paper disc saturated with an antimicrobial agent on the agar surface.
What is the relationship between the zone of inhibition and the antibiotic concentration?
The size of a zone of inhibition in a KB test is inversely related to the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), which is the amount of antibiotic required to prevent bacterial growth in an overnight culture.
What does zone of inhibition mean in microbiology?
Definition. (microbiology) The clear region around the paper disc saturated with an antimicrobial agent on the agar surface.
What is the zone of inhibition in bacterial cultures?
0:006:42Zone Inhibition In Bacterial Cultures | Biology GCSE (9-1) | kayscience.comYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe zone of inhibition in bacterial cultures by ksites.com this here is an agar plate. And zonesMoreThe zone of inhibition in bacterial cultures by ksites.com this here is an agar plate. And zones a b c d e f and h are all zones of inhibition. Where bacteria are not growing g has no zone of
What is the Zone of inhibition quizlet?
Zone of Inhibition is an area where bacteria cannot grow due to the presence of antibiotics.
Measurement of the Zone of Inhibition of an Antibiotic | IEEE ...
Abstract: In the Disk Diffusion Antibiotic Sensitivity test (The Kirby-Bauer test) a thin film of bacteria applied on a plate is subjected to various antibiotics. The Zone of inhibition is a circular area around the spot of the antibiotic in which the bacteria colonies do not grow. The zone of inhibition can be used to measure the susceptibility of the bacteria to wards the antibiotic.
Measurement of the Zone of Inhibition of an Antibiotic | IEEE ...
Abstract: In the Disk Diffusion Antibiotic Sensitivity test (The Kirby-Bauer test) a thin film of bacteria applied on a plate is subjected to various antibiotics. The Zone of inhibition is a circular area around the spot of the antibiotic in which the bacteria colonies do not grow. The zone of inhibition can be used to measure the susceptibility of the bacteria to wards the antibiotic.
Zone of Inhibition Test for Antimicrobial Activity
A Zone of Inhibition Test, also called a Kirby-Bauer Test, is a qualitative method used clinically to measure antibiotic resistance and industrially to test the ability of solids and textiles to inhibit microbial growth. Researchers who develop antimicrobial textiles, surfaces, and liquids use t ...
Which method is used to find the zone of inhibition?
In order to find zone of inhibition the disk diffusion method is followed.
Why do antibiotics have zones of inhibition?
However, due to the indiscriminate and careless use of antibiotics many bacteria have developed resistance to most of the antibiotics available. The zone of inhibition is used to determine whether a particular bacterium is susceptible to the action of a particular antimicrobial agent or not; this may help the physician to choose a more effective ...
What is the method of testing for sensitivity to antimicrobial agents?
The testing for sensitivity of an organism to antimicrobial agents is usually done using agar diffusion or disk diffusion test. The parameters of this test were specified (or standardized) by the scientists W. M. M. Kirby and A. W. Bauer and is also referred to as the Kirby-Bauer antibiotic testing. In this method, antibiotics are impregnated on a certain special type of paper disks and are placed on the surface of agar containing the bacterium of our interest. This results in the diffusion of antimicrobial agent into the surrounding medium.
What determines the effectiveness of an antibiotic?
The diameter of the zone of inhibition will determine the effectiveness of the antibiotic; the larger the diameter, the greater will be the sensitivity of the bacterium to the antibiotic. The zone sizes are compared to a standardized chart to determine if the bacterium is sensitive, resistant, or shows intermediate sensitivity to that antibiotic.
What is the pH of an antibiotic?
pH. The pH of the medium may affect the activity of the antibiotic, and thus, may alter the size of the zone of inhibition. Ideally, the pH of the medium is maintained between 7.2 – 7.4. If the pH is too low, certain drugs like macrolides, quinolones and aminoglycosides lose their potency, whereas other drugs like tetracyclines show higher activity.
Can antibiotics inhibit growth?
However, as the antibiotic diffuses further, its concentration is reduced. After a certain point, its concentration is so low that it can no longer inhibit the growth of the bacterium. Therefore, there is an area around the disks that will be clear ...
Can you have more than one antibiotic on a plate?
Note: Usually, more than one antibiotic can be used on a plate. If, however, the zones of inhibition of two antibiotics merge, the readings should not be considered, and the experiment should be repeated. « Previous Post. Next Post ».
What does it mean when the zone of inhibition is larger?
The size of the zone of inhibition is usually related to the level of antimicrobial activity present in the sample or product - a larger zone of inhibition usually means that the antimicrobial is more potent.
What is zone of inhibition?
Zone of inhibition testing is fast and inexpensive relative to other laboratory tests for antimicrobial activity. Zone of inhibition testing is especially well suited for determining (albeit qualitatively) the ability of water-soluble antimicrobials to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. A number of samples can be screened for antimicrobial ...
What is the purpose of the Kirby-Bauer test?
A Zone of Inhibition Test, also called a Kirby-Bauer Test, is a qualitative method used clinically to measure antibiotic resistance and industrially to test the ability of solids and textiles to inhibit microbial growth.
Where is the zone of inhibition on a bacterial agar plate?
If the bacterial or fungal strain is susceptible to the antimicrobial agent, then a zone of inhibition appears on the agar plate, such as on the agar plate on the left-hand side of the photo below.
Is zone of inhibition quantitative or qualitative?
The method is not classically quantitative (though sometimes the diameter of the zones of inhibition are measured and recorded). Zone of Inhibition Testing is a fast, qualitative means to measure the ability of an antimicrobial agent to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. In the world of antimicrobial substances/surfaces, ...
Can you test for antimicrobial properties?
A number of samples can be screened for antimicrobial properties quickly using this test method. A variety of antimicrobial product types can be tested using this method. Liquids, coated antimicrobial surfaces, and antimicrobial-impregnated solid products can all be tested for their ability to produce a zone of inhibition.
Can growth agar interfere with antimicrobials?
Microbial growth agars themselves may interfere with the function of some antimicrobial agents.
How to measure a partial zone?
If you have ony a partial zone due to overlapping zones by neighbouring disks, you can measure the radius from the middel (center) of the disc to the edge of the zone and multiply by two. Be sure to consider bacteriostatic vs bactericide measuring priniples according to what kind of antibiotic you are testing and what kind of bacteria.
Where to measure well in a zone?
Measure it from the edge of the zone from one end to the next edge. the well should not be included.
What is zone inhibition?
Zone of inhibition testing is especially well suited for determining the ability of water-soluble antimicrobials to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. 3. A number of samples can be screened for antimicrobial properties quickly using this test method. 4.
What factors affect zones of inhibition?
Factors that affect zones of inhibition: 1. Pathogen susceptibility. Selection of the antibiotic is based on the type of organism being tested. If the organism is susceptible to the antibiotic, they will not grow near the disk. However, if they are resistant, they will grow right up to the disk. 2.
What are the strengths of Zone of Inhibition?
Strengths of Zone of Inhibition Testing: 1. Zone of inhibition testing is fast and inexpensive relative to other laboratory tests for antimicrobial activity. In addition, it requires media, reagents, equipment and supplies that are readily accessible to most clinical laboratories. 2.
How to determine methicillin resistance?
The resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and related drugs can be reliably determined by using the Kirby-Bauer method of susceptibility testing if the incubation temperature is 35 °C or below, but resistance may be missed at 37 °C. The 1-aug discs of oxacillin and nafcillin or the 5-gg discs of methicillin may be used for this purpose but not the 1-, gg discs of cloxacillin.
Why is the size of the inoculated organism standardized?
The reasons are because if the size of the inoculum is too small, the zone of inhibition will be larger than what it is supposed to be and if the inoculum are also large, the zone of inhibition will be smaller. 6. Presence of other metals:
Does zinc reduce carbapenems?
Excess zinc ions may reduce the zone size of carbapenems against P. aeruginosa. Zone of inhibition also affected by the Concentration of bacteria spread onto agar plate, Drug antagonists, incubation temperature, incubation time, size of the plates, proper spacing of the disks, reading of the zone, etc.
Can agars interfere with antimicrobials?
2. Microbial growth agars themselves may interfere with the function of some antimicrobial agents.
Why is the Kirby-Bauer test standardized?
All aspects of the Kirby-Bauer test are standardized to assure reliability of comparison with the published standards.
How long does it take to use a tilted culture on a Kirby-Bauer test?
In clinical applications of the Kirby-Bauer Test, tilted cultures (for the McFarland standard comparison) must be used within 30 minutes. Why is this important?
How to measure the diameter of a clearing?
Using a metric ruler, and a dark non reflective background, we measure the diameter of each clearing. Or we measure the radius and multiply it by 2.
When to use Mueller-Hinton II plates?
The Mueller-Hinton II plates are supposed to be used within a specific time after their preparation and should be free of visible moisture. What negative effects might moisture have on the test?
Can too long incubation cause larger zones?
Too long incubation can cause larger zones, which would result in false sensitive/ susceptible results.
Most recent answer
Hi Dan, How did the agar-overlay approach go? I am wondering if I could use a similar approach for my bio-control assay. Thank you!!!
All Answers (5)
Its always ideal of measuring zone of inhibition as similar that of kirby-baurer disc diffusion assay only.
How to measure inhibition zone?
To measure the zone of inhibition, first place the plate on a non-reflective surface. Take a ruler or caliper that measures in millimeters and place the "0" in the center of the antibiotic disk. Measure from the center of the disk to the edge of area with zero growth. Take your measurement in millimeters.
What is the purpose of the diameter of the zone of inhibition chart?
Besides naming this practice and protocol, scientists Kirby and Bauer also created standardized charts that used the diameter of the zone of inhibition to determine the bacteria's sensitivity or resistance to the bacteria.
What is the zone of inhibition?
The zone of inhibition is a uniformly circular zone of no bacterial growth around the antibiotic disk. The larger this zone is, the more sensitive the bacteria is to that antibiotic. The smaller the zone is, the more resistant (and, thus, less sensitive) the bacteria is.
Why do antibiotics grow at a certain distance from the disk?
At a certain distance from the disk, you'll start to see bacterial growth again because the antibiotic concentration is too low to affect the bacteria. The area around the antibiotic disk that has no bacterial growth is known as the zone of inhibition.
What is the purpose of a macrolide?
Macrolide antibiotics target bacterial ribosomes. This prevents bacteria from synthesizing proteins, which means that the bacteria cannot survive . A common example is erythromycin, an antibiotic that's used to treat a variety of infections including bronchitis and a number of skin infections.
Where to measure the diameter of an antibiotic disk?
You can also measure directly across the zone of inhibition from edge to edge crossing through the center of the antibiotic disk to directly measure the diameter instead of measuring the radius.
What is the name of the drug that interferes with the cell walls of bacteria?
For example, penicillin (one of the most famous antibiotics) interferes with bacterial cell walls, which leads to them not functioning properly and, thus, dying. Medications that work like this are called beta-lactam antibiotics.