Telomeres serve three major purposes:
- They help to organise each of our 46 chromosomes in the nucleus? (control centre) of our cells?.
- They protect the ends of our chromosomes by forming a cap, much like the plastic tip on shoelaces. ...
- They allow the chromosome to be replicated properly during cell division?: Every time a cell? carries out DNA replication? ...
What are telomeres and how do they function?
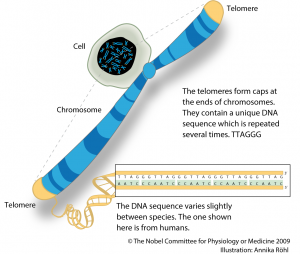
“Telomeres” are lengths of short, highly repetitive nucleotide sequences found on the ends of our DNA strands. Unlike the vital parts of our DNA, telomeres do not contain information needed to make proteins. Instead, they act as a buffer or “cap” to protect the vital coding regions. Each time a cell divides, it must replicate its DNA.
Are telomeres the key to aging and cancer?
Telomeres' Relation to Aging and Cancer Scientists can use the length of a telomere to determine the age of a cell and how many more replications it has left. As cellular division slows, it undergoes a progressive deterioration known as senescence , which we commonly refer to as aging .
How are telomeres important for preserving eukaryotic genes?
MeSH terms
- Gene Frequency
- Genetic Variation
- Genetics, Population
- Genome, Human*
- HapMap Project
- Haplotypes
- Humans
- Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
- Proteins / genetics*
- Telomere / genetics*
Why do we need telomeres?
- Telomere length shortens with age.
- Rate of telomere shortening may indicate the pace of aging.
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking, lack of physical activity, obesity, stress, exposure to pollution, etc. ...

What would happen without telomeres?
However, because the ends are protected by telomeres, the only part of the chromosome that is lost, is the telomere, and the DNA is left undamaged. Without telomeres, important DNA would be lost every time a cell divides (usually about 50 to 70 times). This would eventually lead to the loss of entire genes?.
Why is telomerase so important?
An enzyme named telomerase adds bases to the ends of telomeres. In young cells, telomerase keeps telomeres from wearing down too much. But as cells divide repeatedly, there is not enough telomerase, so the telomeres grow shorter and the cells age.
What does a telomere have to do with aging?
Telomeres get shorter each time a cell copies itself, but the important DNA stays intact. Eventually, telomeres get too short to do their job, causing our cells to age and stop functioning properly. Therefore, telomeres act as the aging clock in every cell.
Why is telomerase important in DNA replication?
Telomeres are the physical ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. They protect chromosome ends from DNA degradation, recombination, and DNA end fusions, and they are important for nuclear architecture. Telomeres provide a mechanism for their replication by semiconservative DNA replication and length maintenance by telomerase.
How does the telomerase help us stop gene erosion?
Telomeres serve as substrates for telomerase, the enzyme responsible for adding DNA to the ends of chromosomes, thus maintaining chromosome length [9, 16]. To compensate for the DNA erosion inherent in genetic stability, telomerase adds tandem array of simple-sequence repeats at the chromosome ends.
What is the role of telomerase quizlet?
Telomerase allows for telomere length and equilibrium maintenance by adding on repeats to the end of the chromosome.
What are telomeres made of?
Telomeres are structures that appear at the end of our chromosomes, comprised of DNA. Some scientists compare them to the plastic tips at the end of shoelaces that keep laces held together. Telomeres keep the chromosomes from fraying or tangling together, which can lead to a variety of health issues. However, the thing about telomeres is that they ...
What are the factors that affect telomere length?
These include: Physical exercise. Lack of sleep. Depression. Genetics and aging. At this point, you may have a bit of a “chicken or the egg” question when it comes to telomere length. Are shortened telomeres a sign of aging, like graying hair, ...
Why do telomeres get shorter?
Our cells are in a cycle of constantly replenishing themselves, but each time a cell replicates, telomeres get a little bit shorter. Eventually, the telomeres get too short to actually split. This leads to cells aging, not functioning properly, and eventually dying. Because of this, telomere length is seen as a way to determine the biological age ...
What are the consequences of telomere shortening?
The consequences of telomeres shortening go beyond wrinkles or purely cosmetic markers of aging. Studies show that things that alter the length of telomere length are associated with both an accelerated pace of aging as well as several age-associated conditions.2.
Does oxidative stress affect telomeres?
Here are some of the most studied practices: Antioxidant-Rich Foods/Vitamins: Oxidative stress is a major source of cell damage, including potentially damaging telomeres.
Does Enzymedica help with telomeres?
A naturally occurring enzyme, it lengthens telomeres while protecting them from shortening in the future. Supplements like Enzymedica’s Telomere Plus™ can help increase telomerase activity , potentially helping support telomeres and aging by association.*.
Why are telomeres important?
We all know that the cells in our body are necessary for us to live a healthy and normal life. When cells are damaged, that makes the body more prone to issues such as disease. For our body to heal and function properly, cells must divide to replace old worn out cells.
How often should you check your telomeres?
It is recommended that you get checked out for the health of your telomeres every 6 to 12 months. The same way we get work done for our physicals every year, we should also be taking a more proactive approach when it comes to our cells.
Why is it important to know where you stand when it comes to your cellular age?
Because we all know that as we age, the health deteriorates and leaves the body vulnerable. This is why it is so important to know where you stand when it comes to your cellular age. When it comes to your health, you should have as much data as possible available to know where you stand.
How to increase telomere length?
Some of the ways are: Stress Management. Being Active. Maintaining Healthy Diet. Vitamin D. These are just some of the ways to improve the length of your telomeres, but there are many others.
Do telomeres get longer as we age?
Telomeres are usually considered their longest when we are first born, but as we age, they tend to shorten. Those who have longer telomeres tend to be more youthful and have greater protection from aging. So it’s safe to say that many would consider telomeres a key driver to how we age over time.
Can you test yourself at home?
They make it very simple for you to test yourself within the comfort of your own home. When you create an account to order your test kit, they provide you with all the necessary equipment. You are even given a pre-paid package to send your sample back to them.
Does life work in a way that doesn't care much for what we want?
But for some reason, life works in a way that doesn’t care much for what we want. Although there may not be some fountain of youth that could solve our aging problem, there may be a way to at least slow down the process. When we go to our physicians to get our yearly physicals, we usually check to make sure things like blood pressure ...
Why do telomeres need to be protected from a cell's DNA repair systems?
Telomeres need to be protected from a cell's DNA repair systems because they have single-stranded overhangs, which "look like" damaged DNA. The overhang at the lagging strand end of the chromosome is due to incomplete end replication (see figure above).
Why is there no way to get the Okazaki fragment started?
When the replication fork reaches the end of the chromosome, however, there is (in many species, including humans) a short stretch of DNA that does not get covered by an Okazaki fragment—essentially, there's no way to get the fragment started because the primer would fall beyond the chromosome end.
Why are telomeres important?
Telomeres act as caps that protect the internal regions of the chromosomes, and they're worn down a small amount in each round of DNA replication. In this article, we'll take a closer look at why telomeres are needed, why they shorten during DNA replication, and how the enzyme telomerase can be used to extend them.
What enzymes can reverse telomere shortening?
Telomerase. Some cells have the ability to reverse telomere shortening by expressing telomerase, an enzyme that extends the telomeres of chromosomes. Telomerase is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, meaning an enzyme that can make DNA using RNA as a template.
What is the overhang on a chromosome?
The overhang at the leading strand end of the chromosome is actually generated by enzymes that cut away part of the DNA. In some species (including humans), the single-stranded overhangs bind to complementary repeats in the nearby double-stranded DNA, causing the telomere ends to form protective loops.
What happens to the last strand of RNA in a human cell?
In human cells, the last RNA primer of the lagging strand may be positioned as much as to nucleotides away from the chromosome end. Thus, the single-stranded overhangs produced by incomplete end replication in humans are fairly long, and the chromosome shortens significantly with each round of cell division.
What is the leading strand of DNA?
When DNA is being copied, one of the two new strands of DNA at a replication fork is made continuously and is called the leading strand. The other strand is produced in many small pieces called Okazaki fragments, each of which begins with its own RNA primer, and is known as the lagging strand.
Why is telomerase not produced?
The production of telomerase is tightly inhibited in most cells, because telomeres are only useful for cell divisions and the vast majority of your cells will either never divide again, or are one or two divisions away from their last.
Why do prokaryotes not need telomeres?
The telomeres exist at the end of the chromosomes to prevent the DNA at the end of chromosomes.But prokaryotes do not need telomeres,because their DNA is circular and thus the end of the chromosome does not degrade during replication. 880 views. Related Answer. Quora User.
What is the risk of losing sequence from the ends of a chromosome?
If you have linear chromosomes, there is a risk of losing sequence from the ends due to polymerases synthesizing in a 5’->3’ direction. Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes and solve this with telomerase to add a repeat to the 3’ end of chromosomal DNA.
What happens when a cell's telomeres get too short?
Continue Reading. When a cell’s telomeres get too short, it can no longer replicate and eventually dies. A few cells — namely adult stem cells as well as sperm and egg cells — are not limited by this process, though. These cells have an enzyme named telomerase that can rebuild telomeres when they get too short.
Why are short telomeres important?
It turns out that short telomeres (but not too short!) are a natural defense against cancer, because they prevent cells from dividing.
Why do chromosomes shorten?
The explanation you will more often hear is that the ends of chromosomes shorten with each cell division (more accurately: each replication). This would be a problem if the ends of chromosomes contained important genes.
How many strands of DNA are produced in a child duplex?
This produces 2 child duplexes, i.e. 4 single strands of DNA. The parental halves of each child are full-length, but the newly synthesized strands have lost some nucleobases at the ends. The side loosing bases is alternative over generations. So, prokaryotes want to replicate a strand.
What are telomeres? Telomeres are structures made from DNA sequences and proteins found at the ends of chromosomes. They cap and protect the end of a chromosome like the end of a shoelace
In almost all animals, from the simplest to the most complex, telomeres are required for cell division. With each cell replication, the telomeres get shorter and shorter until they're so short that your cells can no longer divide. When cells no longer divide, tissues age.
Want to learn more?
We offer fun-sized science to help you keep up with the latest breakthroughs.
