
Full Answer
Why does sodium chloride cause metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis can be caused by failure of a major organ, such as your heart, kidney, or liver. This leads to potassium depletion. A standard saline solution (sodium chloride) can make things worse by causing your body to retain fluids without getting rid of the excess of bicarbonate ions that are causing the alkalosis.
What is hypochloremic alkalosis and what causes it?
Hypochloremic alkalosis occurs when there’s a significant decline of chloride in your body. This can be due to prolonged vomiting or sweating. Chloride is an important chemical needed to maintain balance in bodily fluids, and it’s an essential part of your body’s digestive fluids.
What is chloride-resistant alkalosis?
Chloride-resistant alkalosis results when your body retains too many bicarbonate (alkaline) ions, or when there’s a shift of hydrogen ions from your blood to your cells. There’s also a condition called metabolic acidosis which occurs when your blood or fluids become overly acidic.
What causes alkalosis?
Alkalosis occurs when your body has too many bases. It can occur due to decreased blood levels of carbon dioxide, which is an acid. It can also occur due to increased blood levels of bicarbonate, which is a base. This condition may also be related to other underlying health issues such as low potassium, or hypokalemia.
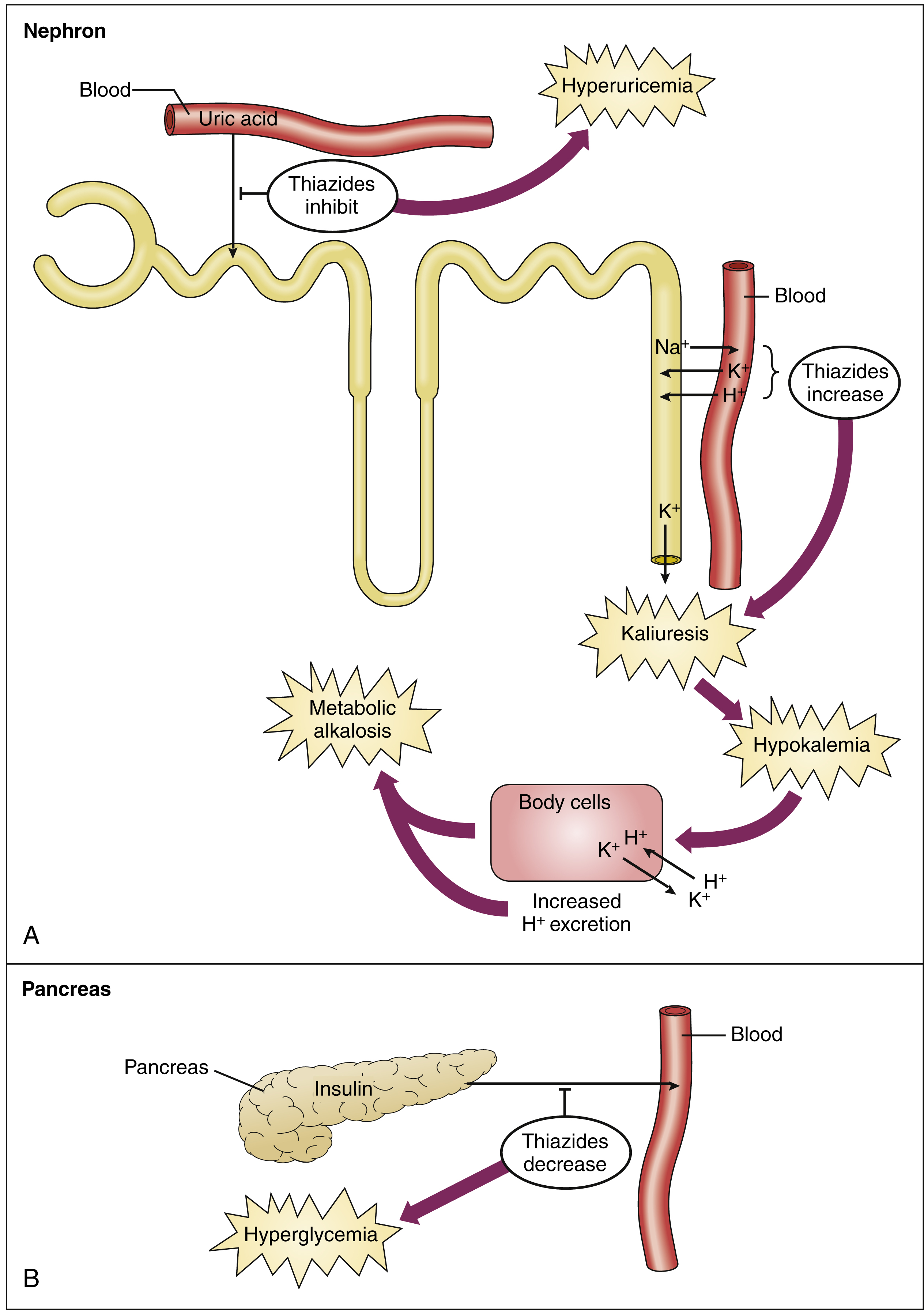
Does chloride cause alkalosis?
Chloride depletion is the commonest of the three major causes of metabolic alkalosis; the others relate to potassium depletion/mineralocorticoid excess and to very low or absent glomerular filtration with base loading and are not further discussed in detail.
How does chloride affect metabolic alkalosis?
Chloride-responsive alkalosis results from loss of hydrogen ions, usually by vomiting or dehydration. Chloride-resistant alkalosis results when your body retains too many bicarbonate (alkaline) ions, or when there's a shift of hydrogen ions from your blood to your cells.
How does hypochloremia cause alkalosis?
Hypochloremia can contribute to the maintenance of metabolic alkalosis by increasing the reabsorption of and reducing the secretion of bicarbonate in the distal tubule.
How does chloride affect Bicarb?
When substances such as ammonium chloride and hydrochloric acid are supplemented into the body, they react with bicarbonate in an attempt to buffer the pH. However, this will deplete bicarbonate stores leading to an acidotic state.
How does the loss of chloride during vomiting cause metabolic alkalosis?
When HCl is lost through vomiting (including purging, in persons with eating disorders ) or nasogastric suction, pancreatic secretions are not stimulated and a net gain of bicarbonate into the systemic circulation occurs, generating a metabolic alkalosis. Volume depletion maintains alkalosis.
What is the mechanism of metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis, a disorder that elevates the serum bicarbonate, can result from several mechanisms: intracellular shift of hydrogen ions; gastrointestinal loss of hydrogen ions; excessive renal hydrogen ion loss; administration and retention of bicarbonate ions; or volume contraction around a constant amount of ...
What does Hypochloremic alkalosis mean?
Hypochloremic alkalosis is caused by an extreme lack or loss of chloride, such as from prolonged vomiting. Hypokalemic alkalosis is caused by the kidneys' response to an extreme lack or loss of potassium. This can occur from taking certain water pills (diuretics).
Why does metabolic acidosis cause hypochloremia?
A possible explanation for this acidosis-induced hypochloremia is expansion of the extracellular compartment secondary to the extrusion of cellular cation that occurs in the process of buffering.
What is the effect of hypochloremia?
dehydration. weakness or fatigue. difficulty breathing. diarrhea or vomiting, caused by fluid loss.
How does chloride affect pH?
So more the concentration of the chloride ions and higher the acidity (lower pH),the higher is the corrosion rate, BOTH COMPLIMENT EACH OTHER UP TO A CERTAIN CONCENTRATION OF THE CHLORIDE IONS BEYOND WHICH THE CHLORIDE IONS PREDOMINATE OVER pH.
How does chloride affect blood pH?
Chloride is an important electrolyte that is responsible for maintaining the acid-base (pH) balance in your body, regulating fluids, and transmitting nerve impulses. The normal range for chloride in adults is roughly between 98 and 107 milliequivalents of chloride per liter of blood (mEq/L).
How does chloride affect acid-base balance?
Since a decreased chloride indicates loss of an acid, this result indicates a metabolic alkalosis (alkalosis = loss of acid and/or gain of base).
Why is urine chloride low in metabolic alkalosis?
The extrarenal generation of metabolic alkalosis leads to excretion of bicarbonate into the urine, which obligates a component of filtered sodium to accompany the base whereas urine chloride remains low in response to neurohumoral activation resulting from volume contraction.
What is Hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis?
Hypochloremic alkalosis results from either low chloride intake or excessive chloride wasting. Whereas low chloride intake is very uncommon, excessive chloride wasting often occurs in hospitalized children, usually as a result of diuretic therapy or nasogastric tube suctioning.
Which of the following would be most likely to cause metabolic alkalosis?
The most common causes are volume depletion (particularly when involving loss of gastric acid and chloride (Cl) due to recurrent vomiting or nasogastric suction) and diuretic use. Metabolic alkalosis involving loss or excess secretion of Cl is termed chloride-responsive.
How does alkalosis affect potassium?
A frequently cited mechanism for these findings is that acidosis causes potassium to move from cells to extracellular fluid (plasma) in exchange for hydrogen ions, and alkalosis causes the reverse movement of potassium and hydrogen ions.
What causes alkalosis in the body?
Other causes of metabolic alkalosis include medical conditions such as: Cystic fibrosis. Dehydration. Electrolyte imbalances, which affect levels of sodium, chloride, potassium and other electrolytes. High levels of the adrenal hormone aldosterone ( hyperaldosteronism ).
Why does alkalosis occur?
It can occur in a variety of conditions. It may be due to digestive issues, like repeated vomiting, that disrupt the blood ’s acid-base balance. It can also be due to complications of conditions affecting the heart, liver and kidneys.
Why is metabolic alkalosis important?
Metabolic alkalosis is usually not life-threatening. It does not have lingering effects on your health once it is treated. But it’s important to seek medical care because it can lead to severe complications. Treatment with IV fluids helps many people make a full recovery. Addressing the cause can lower your risk of future episodes.
What to do after alkalosis treatment?
You may wish to make small changes to lower your risk of future episodes. These changes may include: Decreasing the dose of or discontinuing steroids, laxatives, water pills or antacids.
What is the term for the body's acid-base balance?
What is alkalosis ? Alkalosis occurs when your blood and body fluids contain an excess of bases or alkali. Your blood’s acid-base (alkali) balance is critical to your well-being. When the balance is off, even by a small amount, it can make you sick.
What are the symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
Many metabolic alkalosis symptoms are concerning and need prompt medical evaluation. If you are experiencing an arrhythmia, seizures or confusion, seek care right away.
What tests are used to check for metabolic alkalosis?
Blood tests to measure blood gases, acid-base balance and electrolyte levels. Electrocardiogram (EKG) to check for an arrhythmia. Urinalysis that may help find the cause of the metabolic alkalosis.
What is chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis?
In chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis, this includes repletion of electrolytes, specifically chloride and potassium along with the replenishment of fluid. In scenarios, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or edematous states, diuresis is essential using potassium-sparing diuretics.
What is metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process. Before going into details about pathology and this disease process, some background information about the physiological pH buffering process is important. The primary pH buffer system in ...
What happens if the expected pCO2 does not match the measured value?
If the expected pCO2 does not match the measured value, an underlying metabolic alkalosis is a likely present.
What causes bicarbonate to increase in blood?
Several etiologies lead to increases in bicarbonate within the blood. The simplest of which is an overdose of exogenous sodium bicarbonate in a medical setting. Milk-alkali syndrome is a pathology where the patient consumes excessive quantities of oral calcium antacids, which leads to hypercalcemia and varying degrees of renal failure. Additionally, since antacids are neutralizing agents, they add alkaline substances to the body while reducing acid levels thus increasing pH. A pathology that is in line with normal physiology is the body’s natural compensation mechanism for hypercarbia. When a patient hypoventilates, CO2 retention occurs in the lungs and subsequently reduces pH. Over time, the renal system compensates by retaining bicarbonate to balance pH. This is a slower process. Once the hypoventilation is corrected, such as with a ventilator-assisted respiratory failure patient CO2 levels will quickly decrease, but bicarbonate levels will lag in reducing. This causes post-hypercapnia metabolic alkalosis, which is self-correcting. It is possible to calculate the expected pCO2 in the setting of metabolic alkalosis to determine if it is a compensatory increase in bicarbonate, or if there is an underlying pathology driving alkalosis using the following equation:
How is CO2 regulated?
CO2 levels are physiologically regulated by the pulmonary system through respiration, whereas the HCO3 levels are regulated through the renal system with reabsorption rates. Therefore, metabolic alkalosis is an increase in serum HCO3. [1][2]
What is the term for a disease where the body's pH is elevated to greater than 7.45?
A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase over this range is alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis is defined as a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some metabolic process.
Which two substances regulate cerebral blood flow in the setting of acute experimental metabolic alkalosis?
Arterial carbon dioxide and bicarbonate rather than pH regulate cerebral blood flow in the setting of acute experimental metabolic alkalosis.
How does chloride affect alkalosis?
Maintenance of the alkalosis requires a process which greatly impairs the kidney's ability to excrete bicarbonate and prevent the return of the elevated plasma level to normal. Chloride deficiency leads to a situation where the kidney reabsorbs more bicarbonate anion than usual because there is not sufficient chloride anion present. Reabsorption of an anion is necessary to maintain electroneutrality as Na + & K + are reabsorbed so the deficiency of chloride leads to a re-setting upwards of the maintained plasma bicarbonate level. Chloride and bicarbonate are the only anions present in appreciable quantities in extracellular fluid so a deficiency of one must lead to an increase in the other because of the strict requirement for macroscopic electroneutrality.
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
The two commonest causes of chronic metabolic alkalosis are loss of gastric juice and diuretic therapy. The gastric secretion of H + results in generation of new bicarbonate which is returned to the blood.
What does high chloride mean in hypokalaemia?
A high urinary chloride in association with hypokalaemia suggests mineralocorticoid excess. (provided that recent thiazide use has been excluded). If the clinical information is not sufficient to make a diagnosis the term 'idiopathic metabolic alkalosis' is sometimes used.
What causes saline resistant metabolic alkalosis?
This condition is one cause of 'saline-resistant' metabolic alkalosis. The increased aldosterone levels lead to increased distal tubular Na + reabsorption and increased K + & H + losses. The increased H + loss is matched by increased amounts of renal HCO3 - leaving in the renal vein. The net result is metabolic alkalosis with hypochloraemia and hypokalaemia, often with an expanded ECF volume.
What is the name of the condition where adenomas excrete bicarbonate?
Villous adenomas typically excrete bicarbonate and can cause a hyperchloraemic metabolic acidosis. Sometimes they excrete chloride predominantly and the result is then a metabolic alkalosis.
What happens when sodium bicarbonate is infused into the kidney?
Whenever the plasma bicarbonate rises above 24mmols/l, bicarbonate is excreted by the kidney. This response is reasonably prompt and effective so a metabolic alkalosis will be rapidly corrected. If you infuse say 100mls of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate into a healthy person with normal renal function, the rise in plasma bicarbonate is brief because of prompt bicarbonaturia. This is one way to alkalinise the urine. An infusion of alkali causes only a brief metabolic alkalosis due to this rapid renal excretion.
How many groups of alkalosis are there?
Metabolic alkalosis may be divided into two general groups based on the measured urinary chloride level.
Why does alkalosis occur?
Alkalosis occurs when your body has too many bases. It can occur due to decreased blood levels of carbon dioxide, which is an acid. It can also occur due to increased blood levels of bicarbonate, which is a base. This condition may also be related to other underlying health issues such as low potassium, or hypokalemia.
How to correct alkalosis?
Some cases of alkalosis result from an electrolyte imbalance, which may be corrected by drinking plenty of fluids or drinks that contain electrolytes. If you have an advanced case of electrolyte imbalance, it will need to be treated in the hospital. Most people recover from alkalosis once they receive treatment.
What causes a large loss of potassium or sodium in a short amount of time?
Metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis develops when your body loses too much acid or gains too much base. This can be attributed to: excess vomiting, which causes electrolyte loss. overuse of diuretics. adrenal disease. a large loss of potassium or sodium in a short amount of time. antacids.
What is the condition where the body lacks the mineral potassium?
Hypokalemic alkalosis. Hypokalemic alkalosis occurs when your body lacks the normal amount of the mineral potassium. You normally get potassium from your food, but not eating enough of it is rarely the cause of a potassium deficiency.
Why is it important to maintain the correct balance between acids and bases?
It’s important to maintain the correct balance between acids and bases. Even a slight change can cause health problems. Normally, your blood should have a slightly higher amount of bases than acids. Alkalosis occurs when your body has too many bases. It can occur due to decreased blood levels of carbon dioxide, which is an acid.
Why does chloride decrease in the body?
Hypochloremic alkalosis occurs when there’s a significant decline of chloride in your body. This can be due to prolonged vomiting or sweating. Chloride is an important chemical needed to maintain balance in bodily fluids, and it’s an essential part of your body’s digestive fluids.
What happens if you don't treat alkalosis?
If alkalosis isn’t treated right away, severe symptoms can develop. These symptoms could lead to shock or coma. Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room if you experience any of these symptoms:
