Explore
The following conditions can also occur due to GN:
- acute kidney failure
- chronic kidney disease
- electrolyte imbalances, such as high levels of sodium or potassium
- chronic urinary tract infections
- congestive heart failure due to retained fluid or fluid overload
- pulmonary edema due to retained fluid or fluid overload
- high blood pressure
- malignant hypertension, which is rapidly increasing high blood pressure
How to rule out glomerulonephritis?
why does acute glomerulonephritis cause low GFR in general reason. the kidneys are not doing a good job at filtering urine since there is so much inflammation. how long for acute glomerulonphritis-7-12 days post infection. rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is what in general
Why does glomerulonephritis cause low GFR?
The early symptoms of the acute disease are:
- puffiness of your face in the morning
- blood in your urine (or brown urine)
- urinating less than usual.
What are the physical signs of acute glomerulonephritis (GN)?
Your doctor may tell you to:
- Eat less protein, salt and potassium
- Control your blood pressure
- Take diuretics and calcium supplements
How to treat glomerulonephritis?

What is glomerulonephritis and how can it lead to kidney failure?
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is inflammation of the glomeruli, which are structures in your kidneys that are made up of tiny blood vessels. These knots of vessels help filter your blood and remove excess fluids. If your glomeruli are damaged, your kidneys will stop working properly, and you can go into kidney failure.
How does glomerulonephritis affect the kidneys?
Glomerulonephritis is inflammation and damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomerulus). It can come on quickly or over a longer period of time. Toxins, metabolic wastes and excess fluid are not properly filtered into the urine. Instead, they build up in the body causing swelling and fatigue.
Why does CKD cause renal disease?
Mineral and bone disease occurs when kidneys damaged by CKD can't filter blood link and regulate hormones the way they should. The hormone levels and levels of minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, then become imbalanced, leading to damage.
What are the two primary causes of chronic renal failure?
In the United States, diabetes and high blood pressure are the leading causes of kidney failure, accounting for 3 out of 4 new cases.
Why does glomerulonephritis cause proteinuria?
Typically, too much protein in the urine means that the kidneys' filters — the glomeruli — are not working properly and are allowing too much protein to escape in the urine. When the glomeruli are damaged the condition is called nephritis or glomerulonephritis.
What is the pathophysiology of glomerulonephritis?
Acute glomerulonephritis (GN) comprises a specific set of renal diseases in which an immunologic mechanism triggers inflammation and proliferation of glomerular tissue that can result in damage to the basement membrane, mesangium, or capillary endothelium.
What is the relationship between calcium phosphorus and chronic renal failure?
Disturbances of calcium‐phosphate (Ca‐P) and vitamin D metabolism in chronic renal insufficiency (CRI) play a key role in the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism. This not only causes bone disease (renal osteodystrophy), but also significantly contributes to the high cardiovascular mortality of such patients.
How does chronic kidney disease cause renal osteodystrophy?
In people with bone disease related to kidney failure, bone cells called osteoclasts and osteoblasts are often not in balance. This condition is called renal osteodystrophy. The way these bone cells get out of balance is when calcium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), phosphorus and activated vitamin D are out of balance.
What happens if you get glomerular damage?
Glomerular disease damages the glomeruli, affecting their ability to properly function. Instead of keeping protein and red blood cells circulating in the blood, damaged glomeruli leak some of these products into your urine.
Which is the leading cause of chronic renal failure?
Diabetes is the most common cause of kidney disease. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. But also heart disease and obesity can contribute to the damage that causes kidneys to fail.
What causes renal failure?
What causes kidney failure? High blood pressure and diabetes are the two most common causes of kidney failure. They can also become damaged from physical injury, diseases, or other disorders.
What happens in pathophysiology of chronic renal failure?
Renal failure in disease of the tubules themselves. It is emphasized that acute renal failure only becomes chronic when interstitial fibrosis develops from the interstitial edema occurring in the early stage of the disease. 4. Renal failure occurring in primary diseases of the renal cortical interstitium.
Are There Different Types of Glomerulonephritis?
Yes. There are two types of glomerulonephritis—acute and chronic. The acute form develops suddenly. You may get it after an infection in your throa...
What Causes Acute Glomerulonephritis?
The acute disease may be caused by infections such as strep throat. It may also be caused by other illnesses, including lupus, Goodpasture's syndro...
What Causes Chronic Glomerulonephritis?
Sometimes, the disease runs in the family. This kind often shows up in young men who may also have hearing loss and vision loss. Some forms are cau...
How Is A Diagnosis of Glomerulonephritis Made?
The first clues are the signs and symptoms. Finding protein and blood cells in your urine is another sign. Blood tests will help the doctor tell wh...
Can Glomerulonephritis Be Prevented?
Not until more is known about its causes. However, good hygiene, practicing “safe sex” and avoiding IV drugs are helpful in preventing viral infect...
What Treatment Is Available For Glomerulonephritis?
The acute form may go away by itself. Sometimes you may need medication or even temporary treatment with an artificial kidney machine to remove ext...
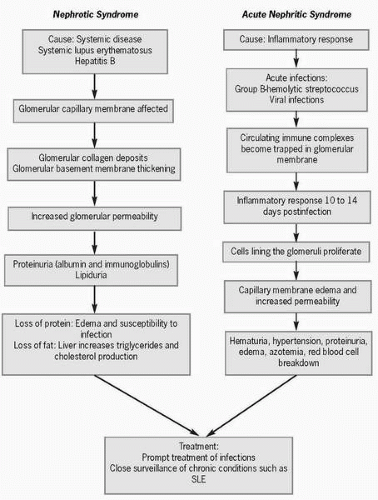
What Is Nephrotic Syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome (also called nephrosis) happens when your kidneys start losing large amounts of protein in your urine. As your kidneys get worse...
What Treatment Is Available For Nephrotic Syndrome?
Your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids, such as prednisone. If prednisone does not work, your doctor may suggest other medicines that affect you...
What causes chronic glomerulonephritis?
This kind often shows up in young men who may also have hearing loss and vision loss. Some forms are caused by changes in the immune system. However, in many cases, the cause is not known. Sometimes, you will have one acute attack of the disease and develop the chronic form years later.
How is a diagnosis of glomerulonephritis made?
The first clues are the signs and symptoms. Finding protein and blood cells in your urine is another sign. Blood tests will help the doctor tell what type of illness you have and how much it has hurt your kidneys.
Can glomerulonephritis be prevented?
Not until more is known about its causes. However, good hygiene, practicing “safe sex” and avoiding IV drugs are helpful in preventing viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis, which could lead to this illness.
What treatment is available for glomerulonephritis?
The acute form may go away by itself. Sometimes you may need medication or even temporary treatment with an artificial kidney machine to remove extra fluid and control high blood pressure and kidney failure. Antibiotics are not used for acute glomerulonephritis, but they are important in treating other forms of disease related to bacterial infection. If your illness is getting worse rapidly, you may be put on high doses of medicine that affect your immune system. Sometimes, your doctor may order plasmapheresis, a special blood filtering process to remove harmful proteins from your blood.
What is nephrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome (also called nephrosis) happens when your kidneys start losing large amounts of protein in your urine. As your kidneys get worse, extra fluids and salt build up in your body. This causes you to have swelling (edema), high blood pressure and higher levels of cholesterol. Nephrotic syndrome may come from kidney diseases or from other illnesses such as diabetes and lupus. Some medicines, IV drug abuse and HIV (the AIDS virus) may also cause it. Sometimes, nephrotic syndrome goes away after treatment. Other times, this condition may last for many years and eventually lead to kidney failure.
What is the term for a kidney that is injured?
Glomerulonephritis is a group of diseases that injure the part of the kidney that filters blood (called glomeruli). Other terms you may hear used are nephritis and nephrotic syndrome. When the kidney is injured, it cannot get rid of wastes and extra fluid in the body. If the illness continues, the kidneys may stop working completely, ...
What is the test called for kidney disease?
In some cases, a test called a kidney biopsy may be needed. In this test, a tiny piece of your kidney is removed with a special needle, and looked at under a microscope. A biopsy will help the doctor plan the best treatment for you.
How to prevent glomerulonephritis?
To prevent infections that can lead to some forms of glomerulonephritis, such as HIV and hepatitis, follow safe-sex guidelines and avoid intravenous drug use. Control high blood pressure, which lessens the likelihood of damage to your kidneys from hypertension.
What is the name of the inflammation of the tiny filters in the kidneys?
Glomerulonephritis (gloe-mer-u-low-nuh-FRY-tis) is inflammation of the tiny filters in your kidneys (glomeruli). Glomeruli remove excess fluid, electrolytes and waste from your bloodstream and pass them into your urine. Glomerulonephritis can come on suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic).
What is the term for a kidney that loses filtering ability?
Chronic kidney disease. Your kidneys gradually lose their filtering ability. Kidney function that deteriorates to less than 10 percent of normal capacity results in end-stage kidney disease, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life.
How does blood enter the kidneys?
Blood enters your kidneys through your renal arteries. Your kidneys remove excess fluid and waste material from your blood through units called nephrons. Each nephron contains a filter (glomerulus) that has a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. The glomeruli filter waste products and substances your body needs — such as sodium, phosphorus and potassium — which then pass through tiny tubules. The substances your body needs are reabsorbed into your bloodstream. The waste products flow through the ureters — the tubes that lead to the bladder.
What is IgA nephropathy?
IgA nephropathy. Characterized by recurrent episodes of blood in the urine, this primary glomerular disease results from deposits of immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the glomeruli. IgA nephropathy can progress for years with no noticeable symptoms.
Why is my urine pink?
Pink or cola-colored urine from red blood cells in your urine (hematuria) Foamy urine due to excess protein (proteinuria) High blood pressure (hypertension) Fluid retention (edema) with swelling evident in your face, hands, feet and abdomen.
What is the disease that causes a bleed in the lungs?
A chronic inflammatory disease, lupus can affect many parts of your body, including your skin, joints, kidneys, blood cells, heart and lungs. Goodpasture's syndrome. A rare immunological lung disorder that can mimic pneumonia, Goodpasture's syndrome causes bleeding in your lungs as well as glomerulonephritis. IgA nephropathy.
What is glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis is also called glomerular disease. It is a type of kidney disease caused by damage to your glomeruli due to overactivation of your immune system. This damage means the glomeruli cannot do their job to remove waste and fluid like they should. There are two types of glomerulonephritis:
What are the symptoms of glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis often does not cause symptoms at first. If the damage to your glomeruli continues, the symptoms of glomerulonephritis include:
How will I know if I have glomerulonephritis?
To see if you have glomerulonephritis, your doctors will start by testing your blood or urine to see if your kidneys might not be working as well as they should. Then, your doctor may ask you to have more tests, such as:
What is the treatment for glomerulonephritis?
The treatment for glomerulonephritis depends on what is causing it. For example, if your glomeruli were damaged by an infection, your treatment will likely focus on treating the infection. Certain medicines called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can help control your blood pressure.
How can I prevent glomerulonephritis?
You may not be able to prevent glomerulonephritis. You can lower your chance of getting glomerulonephritis by:
What is the leading cause of ESRD?
22 In contrast, data from United States Renal Data System (USRDS) shows that diabetes is the leading cause of ESRD (42.9%) followed by hypertension (26.4%) and glomerulonephritis (9.9%) in the US population. 23 In mid-2000 study, the glomerular disease constituted only 9.9 % of CRF in Pakistan. 17 In this later study, the cause was unknown in the majority of cases of CRF. 17 Very few of the above studies have mentioned the criteria for the diagnosis of glomerular diseases and the figures may be considered at best as only estimates of the true picture. As suggested by Rizvi et al. 17 the lower incidence of GN may be due to mis-classification of chronic GN cases as hypertensive nephrosclerosis of unknown causes. 17 They included only biopsy-proven cases of GN or where the history was strongly suggestive of chronic GN. 17 All types of glomerulopathies can lead to CKD. However, the rate of progression and the proportion of patients developing CKD vary significantly. It is of utmost importance to diagnose glomerular diseases at an early stage. The cases of GN should also be referred to specialist care for an optimal management. 24, 25
Is kidney disease a public health problem?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is becoming a worldwide public health problem [1]. It is reported to be around 10-15% worldwide, with a sharp increase in Asian countries [2-5]. CKD is associated with increased mortality, impaired quality of life, and most importantly, increased healthcare expenditures [6-10]. If left untreated, CKD will lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) necessitating chronic dialysis or renal transplantation. These are the only two options for patients with ESRD. Hence, the attention is focused to diagnose and treat kidney disease at an early stage. A big impediment is relative dearth of nephrology services and facilities in developing countries [11-15]. In the context of early recognition and prevention of renal disease, it is important to analyze the prevalent etiological factors of CKD in a particular population. It is well known that the epidemiology and etiology of CKD vary widely, depending on geographic location, race and ethnic background. However, the studies dealing with epidemiology of CKD are fraught with problems related to definition of CKD. Following the initiative of KDIGO for standardizing the definitions of CKD, the studies are becoming streamlined throughout the world and international communication has improved [16].
Can chronic GN cause CKD?
Chronic GN leads to CKD in a significant number of cases. Timely diagnosis and proper management of glomerular diseases can prevent the progression of glomerulopathies to CKD and ESRD and can go a long way in reducing the burden of CKD, especially in developing countries. Further research is required to determine the risk factors leading to progression of glomerulopathies to CRF and ESRD.
What age group is glomerulonephritis?
Mostly, the patient with acute glomerulonephritis is from the pediatric age group, aged 2-14 years , who acutely develops periorbital puffiness and facial swelling on the background of a poststreptococcal infection. The urine is usually dark, frothy, or scanty, and the blood pressure may be high. Nonspecific symptoms include generalized weakness, fever, abdominal discomfort, and malaise.
How long does it take for glomerulonephritis to progress?
Progression in most cases is relatively quick, and end-stage renal disease may ensue within weeks or months of the beginning of acute nephritic syndrome.
Why does edema occur when the glomerular filtration rate is decreased?
As the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is decreased, symptoms like edema and hypertension occur, majorly due to the subsequent salt and water retention caused by the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
What is hypercellular glomeruli?
Hypercellular glomeruliresulting from increased mesangial, endothelial, or parietal epithelial cells population; acute and chronic white blood cells may also be seen in diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (GN) while in crescentic GN, crescents made up of leukocytes and epithelial cells may be present.
What is GN in medical terms?
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a prominent cause of renal impairment. It leads to 10% to 15% of end-stage renal disease cases in the United States. In most instances, without timely intervention, the disease becomes progressive, eventually leading to morbidity.[4] This makes chronic glomerulonephritis the third most common cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States following diabetes mellitus and hypertension, accounting for 10% of patients on dialysis.
What is the term for a subset of renal diseases characterized by immune-mediated damage to the basement membrane,?
The term "glomerulonephritis" encompasses a subset of renal diseases characterized by immune-mediated damage to the basement membrane, mesangium, or the capillary endothelium, leading to hematuria, proteinuria, and azotemia. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of glomerulonephritis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition.
Where is glomerulonephritis most prevalent?
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis remains much more prevalent in regions such as the Caribbean, Africa, India, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, South America, and Malaysia. In Port Harcourt, Nigeria, acute glomerulonephritis in the pediatric age group 3-16 years was 15.5 cases/year, with a male-to-female ratio of 1.1:1; it is not much different currently. An Ethiopian study from a regional dialysis center found that acute glomerulonephritis was the second commonest cause of acute kidney failure requiring dialysis, comprising about 22% of cases.[6] Age-, Gender-, and Race-related Demographics
What are the symptoms of glomerulonephritis?
When rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis develops, weakness, fatigue, and fever are the most frequent early symptoms. Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and joint pain are also common. About 50% of people have a flu-like illness in the month before kidney failure develops.
How do you know if you have glomerulonephritis?
If symptoms do occur, the first to appear are tissue swelling (edema) due to fluid retention, low urine volume, and production of urine that is dark because it contains blood. Edema may first appear as puffiness of the face and eyelids but later is prominent in the legs. Blood pressure increases (see The Body's Control of Blood Pressure) as kidney function becomes impaired. Some people become drowsy or confused. In older people, nonspecific symptoms, such as nausea and a general feeling of illness (malaise), are more common.
What is acute tubular necrosis?
Acute tubular necrosis is a type of kidney injury caused by damage to the kidney tubule cells (kidney cells that reabsorb fluid and minerals from urine). Which of the following groups is most likely to develop acute tubular necrosis?
How long does it take for glomerulonephritis to resolve?
When a bacterial infection is suspected as the cause of acute glomerulonephritis, antibiotics are usually ineffective because the nephritis begins 1 to 6 weeks (average, 2 weeks) after the infection, which has, by then, usually resolved.
What is the procedure to diagnose glomerulonephritis?
Urinalysis. When doctors suspect glomerulonephritis, a biopsy of a kidney is usually done to confirm the diagnosis, help determine the cause, and determine the amount of scarring and potential for reversibility.
What is the diagnosis of kidney disease?
Diagnosis is based on tests of blood and urine and sometimes imaging tests, a biopsy of the kidneys, or both.
Is glomerulonephritis chronic or acute?
Glomerulonephritis can be. Acute: Develops over a short time. Chronic: Develops and progresses slowly. In 1% of children and 10% of adults who have acute glomerulonephritis, it evolves into rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, in which most of the glomeruli are destroyed, resulting in kidney failure.