
Copper (II) hydroxide catalyzes the oxidation of ammonia solutions in presence of dioxygen, giving rise to copper ammine nitrites, such as Cu (NO 2) 2 (NH 3) n. Copper (II) hydroxide is mildly amphoteric. It dissolves slightly in concentrated alkali
Alkali metal
The alkali metals are a group (column) in the periodic table consisting of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). This group lies in the s-block of the periodic table of elements as all alkali metals have their outermost electron …
Full Answer
What happens when copper hydroxide reacts with ammonia?
Copper (II) hydroxide reacts with a solution of ammonia to form a deep blue solution of tetramminecopper [Cu (NH 3) 4] 2+ complex ion . Copper (II) hydroxide catalyzes the oxidation of ammonia solutions in presence of dioxygen, giving rise to copper ammine nitrites, such as Cu (NO 2) 2 (NH 3) n. Copper (II) hydroxide is mildly amphoteric.
Can we use copper in anhydrous ammonia?
Copper is not usually used in ammonia system because with the presence of water ammonia becomes ammonium hydroxide, the OH combined with Cu making cupric hydroxide of blue color. I want to know, if water was not there, could we use copper in ammonia system. The common metals are not affected by anhydrous ammonia.
What happens when you add sulfuric acid to copper hydroxide solution?
Further addition of ammonia causes the copper ion to go back into solution as a deep blue ammonia complex. The addition of 12M sulfuric acid reverses the changes through the copper hydroxide precipate back to clear, light blue color of the original solution.
Why do hydroxides dissolve in ammonia?
All hydroxides can be dissolved in ammonia and/or water. This is because ammonia and water form hydrogen bonds. This bond allows ammonia and water to be strong enough to pull the metal and hydroxide ions apart, thereby dissolving the salt.

Why does copper hydroxide dissolve in excess ammonia?
Reactions of hexaaquacopper(II) ions with ammonia solution The ammonia acts as both a base and a ligand. With a small amount of ammonia, hydrogen ions are pulled off the hexaaqua ion exactly as in the hydroxide ion case to give the same neutral complex. That precipitate dissolves if you add an excess of ammonia.
Why does copper dissolve in ammonia?
Ammonia can etch copper in the presence of oxidizers by dissolving the oxide film on the copper surface and the dissolution rate varied from about 8 to 30 nm/min, depending on the hydrodynamic conditions. The copper dissolution rate in NH4NO3 or (NH4)2SO4 solution does not vary significantly with solution pH.
Does copper hydroxide dissolve in ammonia?
Copper hydroxide is dissolved by aqueous ammonia, forming a complex salt (tetra-ammonium copper hydroxide). The refined linters are added to copper ammonium solution which contains copper hydroxide as a precipitate. Cellulose forms a complex with tetra-ammonium copper hydroxide which dissolves in the solution.
What happens when copper hydroxide reacts with ammonia?
Copper(II) ion reacts with stoichiometric quantities of aqueous ammonia to precipitate light blue Cu(OH)2. Some basic salts may also form.
Does ammonia affect copper?
The common metals are not affected by anhydrous ammonia. But, even if there is a little moisture, ammonia will react rapidly with copper, brass, zinc and many alloys, especially those containing copper and corrode them. Besides moist ammonia will not react with iron or steel.
What happens when ammonia reacts with copper sulphate solution?
Ammonia reacts with copper sulfate. When copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4) is dissolved in water, it forms a blue aquo complex (hexaaquacopper(II), [Cu(H2O)6]2+). When ammonia (NH4OH) is poured into the solution, at first pale blue copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) precipitate is formed.
Which hydroxide is soluble in ammonia?
Solution. The hydroxide soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide is Zinc hydroxide.
How does copper metal react with ammonia give the reaction with the product formed?
2NH3+3CuO→N2+3H2O+3Cu.
What is soluble in excess ammonia solution?
Silver chloride precipitates are dissolved in excess of ammonical solution but it is insoluble in cold water.
What does ammonia do to metal?
Ammonia corrosion can cause stress corrosion cracking in steels. This occurs when contaminants in the ammonia are brought into contact with the steel, a situation that commonly occurs with pressure vessels. Care must be taken to ensure that pressure vessels are not subjected to this type of corrosion.
Is copper chloride soluble in ammonia?
Environmental Fate and Behavior. Copper is slightly soluble in dilute acid, and slowly soluble in ammonia water.
What is the negative ion of ammonium hydroxide?
And so in answer to the question, the negative ion of ammonium hydroxide is hydroxide, i.e. H O −, in smallish concentrations…
What happens when you combine zinc and hydroxide?
Since hydroxide ions from the water combine with Zinc, you get the remaining hydrogen ions which are left in the solution. If you add a nitrate ion there now, you get:
What is the name of the sulfate that is dissolved in water?
Presumably, the hydrated copper sulfate (CuSO4–5 H2O) has been dissolved in water which places the copper ions (Cu2+) in solution. If a drop or two of ammonium hydroxide is added to this solution, initially, a small amount of copper (II) hydroxide will form by the following reaction.
Why is potassium not in the net ionic equation?
The potassium isn’t in the net ionic equation because the potassium doesn’t participate in the reaction at all.
What happens when you get acid and base as a product?
Z n ( N O 3) 2 and H 2 O! An equilibrium is not established because as soon the salt turns into the hydroxide, it again reacts to give back the salt and this salt again turns into the hydroxide and so on. The mixture would now be uncontrollable and soon kaboom. This makes no sense.
Which ligands displace the weaker H20 ligands?
The stronger NH3 ligands displace the weaker H20 ligands from [Cu (H2O)6]^2+ (aq) by forming stronger dative bonds with Cu2+ to give a more stable [Cu (NH3)4 (H20)2]^2+ complex.
What is the ionic equation for the reaction of chlorine with potassium iodide?
What is the ionic equation for the reaction of chlorine with potassium iodide? The answer says 2I+ Cl2 → I2 + 2 Cl−, what happened to the potassium?
Which elements do not form complexes with hydroxide or ammonia but form insoluble hydroxides?
This question is really asking which elements do not complex with hydroxide or ammonia but form insoluble hydroxides. Alkali earth metals do not form complexes with hydroxide or ammonia and produce insoluble hydroxide compounds. Iron is one of the few transition metals that do not form complexes with hydroxide or ammonia but do form insoluble hydroxide compounds. There may be other transition metals with this property also
What is the name of the compound that forms complexes with ammonia?
The cupric ion readily forms complexes with aqueous ammonia, yielding [Cu (NH3)4 (H2O)2] (OH)2 … looks like this:
What is transition metal hydroxide?
most transition metal hydroxides are of low solubility at high pH - they are non-polar, with a symmetric arrangement of hydroxide ions around the metal ion. This property is commonly used to remove metals from aqueous solution in wastewater treatment - alkaline precipitation. For more extreme treatment, metal sulfides can be formed; they are really insoluble!
What is the process of adding standard solution until the reaction is complete?
The process of adding standard solution until the reaction is just complete is termed as titration and the substance to be determined is said to be titrated.
What is the purpose of the indicator in titration?
It is a chemical reagent used to recognize the attainment of end point in a titration. After the reaction between the substance and the standard solution is complete, the indicator should give a clear colour change.
How to find the weight of a substance?
Weight of the substance (g per litre) = Normality × gram equivalent weight of the substance.
Is there a free energy change in mixing caustic soda and cupric hydroxide?
There is no free energy change in mixing caustic soda with cupric hydroxide and therefore there is no driving force to solubilise the copper hydroxide. Neither is there a chemical complex involving caustic soda and cupric hydroxide. However ammonia and any soluble copper salt forms a beautiful, divalent, deep blue and stable complex ion, Cu (NH3)4, known as the cuprammonium ion. It is formation of this ion from insoluble cupric hydroxide that accounts for the solubilisation when an excess of ammonium hydroxide is added to precipitated cupric hydroxide.
How is copper hydroxide made?
A purer product can be attained if ammonium chloride is added to the solution beforehand. Alternatively, copper hydroxide is readily made by electrolysis of water (containing a little electrolyte such as sodium sulfate, or magnesium sulfate) with a copper anode .
What is copper II hydroxide used for?
It is sometimes used in the synthesis of aryl amines. For example, copper (II) hydroxide catalyzes the reaction of ethylenediamine ...
What reacts with ammonia to form a deep blue solution?
Copper (II) hydroxide reacts with a solution of ammonia to form a deep blue solution of tetramminecopper [Cu (NH 3) 4] 2+ complex ion.
What is the chemical formula for copper?
Copper (II) hydroxide is the hydroxide of copper with the chemical formula of Cu (OH) 2. It is a pale greenish blue or bluish green solid. Some forms of copper (II) hydroxide are sold as "stabilized" copper (II) hydroxide, although they likely consist of a mixture of copper (II) carbonate and hydroxide. Cupric hydroxide is a strong base, although its low solubility in water makes this hard to observe directly.
When was copper smelting first used?
Copper (II) hydroxide has been known since copper smelting began around 5000 BC although the alchemists were probably the first to manufacture it by mixing solutions of lye (sodium or potassium hydroxide) and blue vitriol (copper (II) sulfate). Sources of both compounds were available in antiquity.
Does copper kill fish?
It is also used widely in the aquarium industry for its ability to destroy external parasites in fish, including flukes, marine ich, brook and marine velvet, without killing the fish. Although other water-soluble copper compounds can be effective in this role, they generally result in high fish mortality.
Does copper hydroxide convert to carboxylic acid?
Copper (II) hydroxide also converts acid hydrazides to carboxylic acids at room temperature. This conversion is useful in the synthesis of carboxylic acids in the presence of other fragile functional groups. The yields are generally excellent as is the case with the production of benzoic acid and octanoic acid:
Can you mix copper with ammonia?
Its not advisable to use copper with ammonia though you have pure ammonia. Copper is not suitable with ammonia as it forms a very stable copper ammonia complex [Cu (NH3)6]2+. The complex is very stable and its presence can be verified by a deep blue colouration of the solution or media in which the copper is present.
Does ammonia corrode copper?
Christos Polatides. Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. The common metals are not affected by anhydrous ammonia. But, even if there is a little moisture, ammonia will react rapidly with copper, brass, zinc and many alloys, especially those containing copper and corrode them.
Is copper used in ammonia?
Is copper suitable in ammonia system? Copper is not usually used in ammonia system because with the presence of water ammonia becomes ammonium hydroxide, the OH combined with Cu making cupric hydroxide of blue color. I want to know, if water was not there, could we use copper in ammonia system. Chemical Engineering. Ammonia. Copper.
Can ammonia react with steel?
Besides moist ammonia will not react with iron or steel. Therefore only steel or ductile iron should be used for ammonia systems, ammonia containers, valves, fittings and piping. Cite. 3 Recommendations.
Does ammonia react with iron?
Popular Answers (1) The common metals are not affected by anhydrous ammonia. But, even if there is a little moisture, ammonia will react rapidly with copper, brass, zinc and many alloys, especially those containing copper and corrode them. Besides moist ammonia will not react with iron or steel.
Why is ammonia corrosion common for copper and its alloys?
Why ammonia corrosion are common for copper and its alloys? Ammonia is an important raw material for the manufacture of nitric acid, ammonium salt and amine. Ammonia is gas at room temperature and can be liquefied under pressure. Most metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, titanium, etc.
Which metals are most susceptible to ammonia?
Most metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, titanium, etc. have excellent corrosion resistance to ammonia gas, liquid ammonia and ammonia water, except copper and other copper alloys. Copper – Zinc alloys including navy brass and aluminum brass are copper alloys that most susceptible to ammonia-induced stress corrosion cracking ...
What is the pH of NH3?
To reduce the corrosion rate and minimize the amount of inhibitor used, neutralizing amines or NH3 can neutralize the tower topwater condensate to a pH of 6 to 7. However, in some cases, NH3 can cause stress corrosion cracking of navy brass tubes in overhead condensers.
What is the cause of corrosion in a tube?
The low flow rate leads to ammonium salt deposition and local corrosion; Some media, such as cyanide, aggravate the corrosion, and oxygen (which enters with the injected water) accelerates the corrosion.
Where does NH3 come from?
NH3 exists in the effluent of the pretreatment reactor and reforming reactor and is dissolved in water to form ammonia, causing rapid stress-corrosion cracking of the copper-based alloy.
What is the main component of a quench and vent?
Quench and vent vapors and liquids usually contain large amounts of H2S, NH3, NH4Cl, NH4HS, and cyanide, which are released from the thermal cracking reaction of the feed to the coking plant. Due to the presence of NH3 in the coking unit, ammonia-induced stress corrosion cracking occurs in copper alloy tubes at a high pH value.
How to destroy ammonia ion?
The ammonia ion may be destroyed by oxidation with chlorine or ozone. Eliminating the ammonia destroys the complex. However, the cost is prohibitive when compared to other methods.
How do heavy metals precipitate?
Most heavy metal ions readily precipitate by raising the pH of solution, forming the respective metal hydroxide compound. A hydroxide precipitation curve is attached demonstrating the relationship
How to break an ammonical complex?
The most economical method is to add soluble sulfide ions and break the ammonical complex by precipitating the metallic sulfide compounds. The sulfide solubility chart below demonstrates the solubility of the metal sulfide compounds. Copper sulfide, for example, is a very insoluble compound and the presences of soluble sulfide precipitates the copper as it dissociates from the ammonical complex. Ultimately, the copper is all removed from the complex and precipitated as copper sulfide. The ammonia remains in the solution.
What happens when you raise the pH of a solution?
By raising the pH value of a solution with a common alkaline material such as lime, or sodium hydroxide the corresponding metallic hydroxide compounds become insoluble and precipitate from solution. Below is a metal hydroxide solubility curve showing the solubility of the common heavy metal ions and their respective solubility versus pH.
What is the lowest solubility of chromium?
Chromium reaches its least theoretical chromium solubility of 0.08 at pH of 7.5. If both chromium and nickel are present a pH value that precipitates both ions must be chosen. It is common to utilize a pH of 9.0 – 9.5 to precipitate both metals. The theoretical solubility usually does not exist in practice.
What is the pH of chromium?
The effluent limitations for chromium and nickel are both 2.4 mg/l to discharge to a city sewer in the U.S. A pH value of 9 – 9.5 will usually precipitate both ions to their required level. If chromium must be precipitated to a level less than 0.5 mg/l the pH must be operated at 7.0-8.0.
Can ferrous sulfate be added to iron hydroxide?
The addition of soluble ferrous ion as either ferrous sulfate or ferrous chloride will co-precipitate the metallic ion with the iron hydroxide. The most economical method is to add soluble sulfide ions and break the ammonical complex by precipitating the metallic sulfide compounds. The sulfide solubility chart below demonstrates the solubility ...
How many lone pairs does H X 2 O have?
You can sort of see this in the structures of the ligands. N H X 3 has one lone pair, H X 2 O has 2 lone pairs, and H O X − has 3 lone pairs. σ-bonding interactions involve free lone pairs on the ligands, so in this case you can see that more lone pairs means a greater ability to σ-bond. Now look up how the spectrochemical series ranks these three ligands in terms of increasing σ-donor/decreasing π-acceptor strength.
Is ammonia a ligand?
In general, you can (and should) assume that the shape a complex assumes (in solution and in crystal structures) is the most stable or at least more stable than other easily accessible variations. Ammonia, in general, does give a stronger ligand-metal interaction with transition metals than water as a ligand.
Is N H X 3 a better ligand than water?
You're absolutely correct that N H X 3 is a better ligand than water -- this explains why the first four molecules substitute readily into the C u ( I I) coordination environment. However, if the remaining "axial coordination sites" are really not coordination sites at all, but instead are part of a non- or weakly-coordinating solvation shell, then it just becomes a statistical competition between excess N H X 3 solutes and the H X 2 O solvent, in which case the water will win out until the ammonia concentration is quite high.
Does ammonia have a stronger ligand-metal interaction than water?
Ammonia, in general, does give a stronger ligand-metal interaction with transition metals than water as a ligand. Therefore, there should be a general trend towards amination to give more stable complexes. However, in the case of axial ligands in a Jahn-Teller distorted complex it is actually slightly better to have a slightly weaker ligand there. The hexaammin complexes can be attained in liquid ammonia but when dissolved in water two ammin ligands redissociate and are replaced by aqua ligands.
Why is precipitation favored over complex ion formation?
It's simply because of the concentration. In aqueous solution, the formation of a precipitate is favored over the formation of a complex ion, and it can be shown using solubility equilibria and K f (but it won't be pretty).
Is ammonia a Lewis base?
When I was going through the chapter on pnicotgens, I got to know that ammonia acts as a Lewis base and it dissociates in water giving out hydroxide ion and the further hydroxide of ammonia, which we refer to as ammonium hydroxide, precipitates metal salts in a form of metal hydroxides.
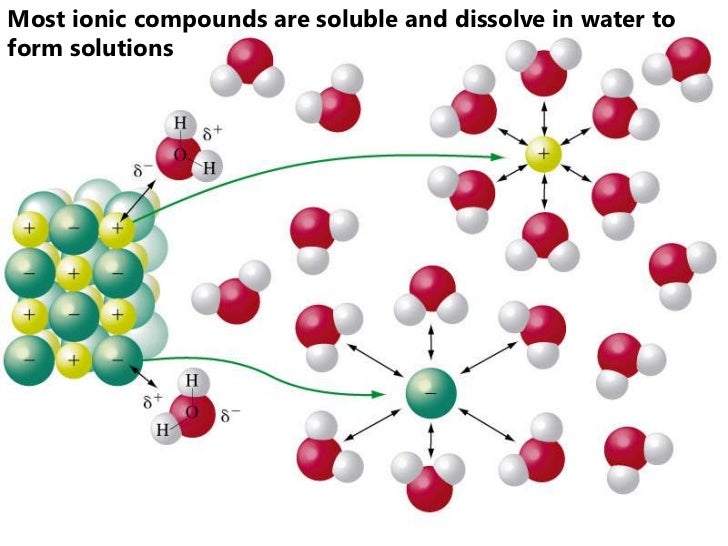
Overview
Reactions
It is stable to about 100 °C.
Copper(II) hydroxide reacts with a solution of ammonia to form a deep blue solution of tetramminecopper [Cu(NH3)4] complex ion.
Copper(II) hydroxide catalyzes the oxidation of ammonia solutions in presence of dioxygen, giving rise to copper ammine nitrites, such as Cu(NO2)2(NH3)n.
Occurrence
Copper(II) hydroxide has been known since copper smelting began around 5000 BC although the alchemists were probably the first to manufacture it by mixing solutions of lye (sodium or potassium hydroxide) and blue vitriol (copper(II) sulfate). Sources of both compounds were available in antiquity.
It was produced on an industrial scale during the 17th and 18th centuries for use in pigments suc…
Production
Copper(II) hydroxide can be produced by adding sodium hydroxide to a solution of a soluble copper(II) salt, such as copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O):
2NaOH + CuSO4·5H2O → Cu(OH)2 + 6H2O + Na2SO4
The precipitate produced in this manner, however, often contains water and an appreciable amount of sodium containing impurities. A purer product can be attained if ammonium chloride i…
Structure
The structure of Cu(OH)2 has been determined by X-ray crystallography The copper center is square pyramidal. Four Cu-O distances in the plane range are 1.96 Å, and the axial Cu-O distance is 2.36 Å. The hydroxide ligands in the plane are either doubly bridging or triply bridging.
Uses
Copper(II) hydroxide in ammonia solution, known as Schweizer's reagent, possesses the interesting ability to dissolve cellulose. This property led to it being used in the production of rayon, a cellulose fiber.
It is also used widely in the aquarium industry for its ability to destroy external parasites in fish, including flukes, marine ich, Brooklynellosis, and marine velvet, without killing the fish. Although o…
Other copper(II) hydroxides
Together with other components, copper(II) hydroxides are numerous. Several copper(II)-containing minerals contain hydroxide. Notable examples include azurite, malachite, antlerite, and brochantite. Azurite (2CuCO3·Cu(OH)2) and malachite (CuCO3·Cu(OH)2) are hydroxy-carbonates, whereas antlerite (CuSO4·2Cu(OH)2) and brochantite (CuSO4·3Cu(OH)2) are hydroxy-sulfates.
External links
• Material Safety Data Sheet