As the pH value is increased above or decreased below the optimum pH the enzyme activity decreases. Explanation At very acidic and alkaline pH values the shape of the enzyme is altered so that it is no longer complementary to its specific substrate. This effect can be permanent and irreversible and is called denaturation.
How does pH influence the rate of enzyme reaction?
pH Effects Enzyme Activity The structure of the enzyme has a great influence on the activity of the enzyme. In other words, changes in the structure of the enzyme affect the rate of chemical reactions. When the pH value of the reaction medium changes, the shape and structure of the enzyme will change.
Why do enzymes work better at their optimum pH?
well enzyme activity is is affected by factors like temp (C), salt concentration and pH. so the lower the pH the higher the H+ ions hence the higher the rate of reaction due the high probability of collisions of reactants. also the higher the pH the higher the rate due to the presence of OH- ions.
Why is the shape of an enzyme important to its function?
The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. Why do enzymes have different shapes?
How are enzymes affected by changes in pH?
How pH Affects Enzymes. A pH environment has a significant effect on an enzymes. It can affect the intramolecular forces and change the enzyme's shape -- potentially to the point where it is rendered ineffective. With these effects in mind, typical enzymes have a pH range in which they perform optimally. For example, alpha amylase, which found in the mouth, operates most effectively near a neutral pH.

Why does high pH affect enzyme activity?
Changing the pH will affect the charges on the amino acid molecules. Amino acids that attracted each other may no longer be. Again, the shape of the enzyme, along with its active site, will change. Extremes of pH also denature enzymes.
Why does enzyme activity decrease when pH is higher or lower than the optimal pH?
pH Effects Enzyme Activity The structure of the enzyme has a great influence on the activity of the enzyme. In other words, changes in the structure of the enzyme affect the rate of chemical reactions. When the pH value of the reaction medium changes, the shape and structure of the enzyme will change.
Why does pH slow enzyme activity?
Changes in pH cause amino acids' component atoms and molecules to ionize. This can make an enzyme change shape. These shapes determine function, so changing the shape can impair the enzyme's function, preventing it from speeding up chemical reactions.
Why do enzymes denature at high pH?
When an enzyme is in a non-optimum pH, the differing proportion of hydrogen ions (which cause changing pH)) will affect those bonds which contain a charge. These are the ionic and hydrogen bonds. Extreme pHs can therefore cause these bonds to break.
What happens to an enzyme when the pH decreases?
At extremely low pH values, this interference causes the protein to unfold, the shape of the active site is no longer complementary to the substrate molecule and the reaction can no longer be catalysed by the enzyme. The enzyme has been denatured.
How does pH affect enzyme activity experiment?
2:015:29√ The Experiment Effect of pH on Enzymes Explained. Watch this ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo when it's added to a lower or higher pH. Outside its optimum pH range the enzyme will denatureMoreSo when it's added to a lower or higher pH. Outside its optimum pH range the enzyme will denature and therefore not perform its function of converting hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
What happens to an enzyme when the pH increases quizlet?
As pH increases, enzyme activity increases until it reaches an optimal point in which enzymes denatures and as pH increases, enzyme activity decreases.
How does pH affect the rate of reaction?
Optimal pH increases enzyme rate of reaction while less than optimal pH decreases it. Increasing temperature also increases enzyme rate of reaction, until things get too hot, then the enzyme denatures and ceases to function.
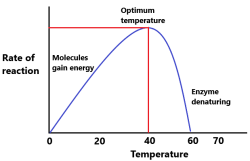
Why does enzyme activity decrease at higher temperature?
Enzymes are proteins. The proteins get denatured at high temperature. Hence, enzyme activity decreases at high temperature.
Do enzymes denature at high pH?
Extreme pH values can cause enzymes to denature. Enzyme concentration: Increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the reaction, as long as there is substrate available to bind to. Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.
What happens to proteins at high pH?
Hydrogen Bonding Changing the pH disrupts the hydrogen bonds, and this changes the shape of the protein.
What happens to an enzyme when the pH increases quizlet?
As pH increases, enzyme activity increases until it reaches an optimal point in which enzymes denatures and as pH increases, enzyme activity decreases.
Do enzymes denature at low pH?
Yes, a low pH can also denature an enzyme. It doesn't matter if it is a higher pH than normal or a lower pH than normal; if there is a pH change then it will change the shape of the active site and render the enzyme useless.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Our stomach produces powerful acids that acid helps start to digest our foods. This acid helps us digest, but it also kills harmful microorganisms that we eat from our food.
What happens if you increase the pH of an enzyme?
Results: If you increase or decrease the pH above or below the optimum pH, the enzyme’s active site would be nature. The active site changes shape, and the substrate no longer binds. So, therefore, less product is formed, and the rate of reaction is going to decrease. The rate of reaction will decrease.
What happens when catalase is added to a higher pH?
Hypothesis: When catalase which is an enzyme, is added to a medium higher or lower pH outside its optimum pH range, the enzyme will denature. And therefore not perform its function of converting hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Why does amylase stop working?
The action of amylase on starch stops when the food passes into the stomach. This is because the low pH of the gastric juice makes it inactive. So the amylase cannot work or perform its function with a pH of 1.5 to 3. pH for Rennin: The protein digestive enzyme rennin is found in gastric juice in the stomach function.
Why does the reaction rate decrease when you go above the pH optimum?
This is because the enzyme denatures. It changes shape above or below the optimum pH.
What happens to the enzyme at point X?
At point X, which is low pH. The enzyme is protonated, which means it has a positive charge. Therefore, the substrate cannot bind effectively at the active site. So at low pH, the enzyme is protonated.
What enzymes work best with a narrow pH range?
Enzymes work best with a narrow pH range. Any variation above or below a specific level reduces their rate of activity. Examples of enzymes: Pepsin , Trypsin, Amylase, Rennin, etc. pH for Pepsin: Pepsin is a very powerful enzyme, and it digests proteins in the stomach.
What happens to enzymes at very acidic and alkaline pH values?
Explanation. At very acidic and alkaline pH values the shape of the enzyme is altered so that it is no longer complementary to its specific substrate. This effect can be permanent and irreversible and is called denaturation. The diagram below shows what happens to an enzyme when denaturation occurs.
What is the pH range of catalase?
Catalase has an optimum pH of 9 and a working range of between pH 7-11. Most other enzymes function within a working pH range of about pH 5-9 with neutral pH 7 being the optimum. previous. 1. 2. 3.
Does each enzyme have a pH?
Each enzym e has an optimum pH but it also has a working range of pH values at which it will still work well. This depends on the type of enzyme.
Why pH Affects Enzyme Activity?
The rate of a chemical reaction and/or the enzyme activity is greatly influenced by the structure of the enzyme. Or in other words, a change in the structure of the enzyme affects the rate of reaction. When pH of a particular medium changes, it leads to an alteration in the shape of the enzyme. Not only enzymes, the pH level may also affect the charge and shape of the substrate.
Which enzyme is most active at an acidic pH?
For example, the enzyme pepsin (a protease enzyme) is most active at an acidic pH, whereas the enzyme trypsin (another protease enzyme) performs best at a slightly alkaline pH. Thus, the optimum pH of an enzyme is different from that of another enzyme.
How do ions affect enzymes?
These ions alter the structure of the enzymes and at times the substrate, either due to formation of additional bonds or breakage of already existing bonds. Ultimately, the chemical makeup of the enzyme and substrate are changed. Also, the active site of the enzyme is changed, after which the substrate can no longer identify the enzyme. For more information on enzymes, you can refer to enzyme substrate complex.
What is enzyme in biochemistry?
Enzymes are proteinaceous catalysts, which speed up the rate of a biochemical reaction. They reduce the activation energy that is essential for starting any type of chemical reaction. With a low energy requirement for activation, the reaction takes place faster.
What are the factors that affect enzyme performance?
The overall performance of an enzyme depends on various factors, such as temperature, pH, cofactors, activators, and inhibitors. You might have a fair idea regarding the effect of pH on enzymes.
Can a pH change be reversed?
Within a narrow pH range, changes in the structural shapes of the enzymes and substrates may be reversible. But for a significant change in pH levels, the enzyme and the substrate may undergo denaturation. In such cases, they cannot identify each other. Consequently, there will be no reaction. This is why pH is a determining factor of enzyme activity.