What is the difference between impulse and change in momentum?
• Since impulse is only change in momentum, it has same units as that of momentum which is kg m/s • Momentum of a moving body is the product of its mass and its velocity whereas impulse is change in momentum which is the product of mass and difference in velocities.
What could be described as impulse equals change in momentum?
The quantity Fnet Δ t is given the name impulse. Impulse is the same as the change in momentum. Change in momentum equals the average net external force multiplied by the time this force acts. The quantity Fnet Δ t is given the name impulse. There are many ways in which an understanding of impulse can save lives, or at least limbs.
Why does impulse affect momentum?
TRUE – In a collision, there is a collision force which endures for some amount of time to cause an impulse. This impulse acts upon the object to change its velocity and thus its momentum. The impulse encountered by an object in a collision causes and is equal to the momentum change experienced by that object.
How do you calculate a change in momentum?
Steps Download Article
- Find the mass. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. To measure the mass of an object, you can use a balance.
- Find the velocity. Velocity is the speed and the direction that the object travels. Right now, we will only concentrate on the speed part.
- Multiply the mass by the velocity. That is the momentum! The measurement for momentum is kg*m/s. ...
What are momentum and impulse?
Learn what momentum and impulse are, as well as how they are related to force.
What is momentum in physics?
This is also the essence of the meaning in physics, though in physics we need to be much more precise. Momentum is a measurement of mass in motion: how much mass is in how much motion. It is usually given the symbol . Where is the mass and is the velocity.
What is the term for the overall effect of a force acting over time?
Impulse is a term that quantifies the overall effect of a force acting over time. It is conventionally given the symbol and expressed in Newton-seconds. For a constant force, . As we saw earlier, this is exactly equivalent to a change in momentum . This equivalence is known as the impulse -momentum theorem.
How many s is the specific impulse of the jet engines?
Exercise 1b: The specific impulse of the jet engines is known to be around 6000 s. How many kilograms of fuel were burned in getting the aircraft up to take-off speed?
Why is impulse important?
One of the reasons why impulse is important and useful is that in the real world, forces are often not constant. Forces due to things like people and engines tend to build up from zero over time and may vary depending on many factors. Working out the overall effect of all these forces directly would be quite difficult.
What is specific impulse?
Specific impulse is impulse measured relative to the weight of fuel—on earth—used to produce the impulse. Because we are dividing an impulse by a force—the force on the fuel due to earth's gravity—the force units cancel out, and the units for specific impulse are simply seconds. A rocket might have a specific impulse of 300 s.
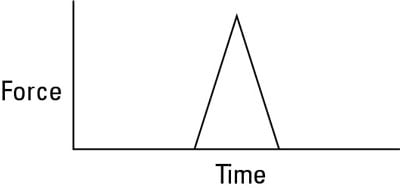
Why is area important in a force time curve?
This is equivalent to finding the area under a force-time curve. This is useful because the area can just as easily be found for a complicated shape—variable force— as for a simple rectangle—constant force. It is only the overall net impulse that matters for understanding the motion of an object following an impulse.
What is the meaning of impulse momentum?
Impulse Momentum Theory Explained. Impulse is defined as a quantity which describes the effect of a net force that acts upon an object. Think of it as a moving force. It is the product of the average net force that acts an object, includes the duration, and is a force-time integral with a vector quantity. That is because force is ...
What is impulse momentum theory?
We see the impulse momentum theory applied every day in some way as it is an equivalent to Newton’s second law. The application for variable mass allows momentum and impulse to be used as analysis tools , which are applied to vehicles that use rocket or jet engine propulsion.
Why is impulse a quantity?
Because impulse is a quantity which is closely related to momentum, applying force for an amount of time allows an object with momentum to have the value of that momentum change to a new value . The impulse is equal to the change in momentum that occurs.
Why is it important to remember that an item which is stationary still has momentum on our planet?
It is important to remember that an item which is stationary still has momentum on our planet because our planet is always moving. The size of our planet negates tangible awareness of that movement, such as the rotation of the planet or how it orbits the sun, but the evidence of its existence is still present.
What is the conservation of momentum?
The conservation of momentum is used to describe collisions which occur between objects, but only if it is an isolated system. There cannot be an external impulse that has the capability of applying force to the system.
How fast does the Earth move at the equator?
The surface of the Earth at the equator moves at a speed of nearly 1,000 miles per hour as it rotates and the planet orbits the sun at a speed of about 67,000 miles per hour. In summary, impulse momentum theory allows us to calculate a new value when a force is applied to the current value. YouTube.
How does momentum change in tennis?
The momentum of the ball shifts to a new value because a large force (the racket, powered by the swing of an arm) is applied to the tennis ball for a specific amount of time. Using a golf club to hit a golf ball would be another action of impulse that changes the momentum value.
What is the impulse momentum theorem?
The impulse-momentum theorem states that the change in momentum of an object equals the impulse applied to it. If mass is constant, then…. If mass is changing, then…. The impulse-momentum theorem is logically equivalent to Newton's second law of motion (the force law).
What is the unit of momentum?
The SI unit of momentum is the kilogram meter per second.
Why does impulse cause change in momentum?
Impulse still causes change in momentum because it is counting force, which itself causes change in momentum! But on the other hand, it can be said to mean that impulse is the change in momentum, because force is the instantaneous change in momentum.
What is the sum of the change in momentum caused by force?
Impulse literally is the sum of the change in momentum caused by force. Impulse doesn't "cause" a change in momentum -- force causes that change! Impulse is just a fancy way of keeping track of the total amount of force applied to an object.
What does "impulse" mean in math?
But here's where the ambiguity lies: "Impulse is just a fancy way of keeping track of the total amount of force applied to an object."; This can be taken to mean two things. On one hand, it can be said to mean that impulse counts force, not change in momentum.
What is force F?
Force F ( t) is a basic quantity describing instantaneous influence of one body on another, in general having a magnitude and direction, but let's have everything in the same direction here for simplicity. The formula for force has to be inferred from other laws of physics - it can be due to gravity ( m g ), spring ( − k x ), or air resistance ( − c v 2) or others or their combination.
Which side of the mass is the force on the mass due to the spring?
We recognize the left hand side as the time rate of change of momentum and the right hand side as the (negative of the) spatial rate of change of the potential energy. But, on the Newtonian view, the right hand side is the force on the mass due to the spring, not the left hand side.
Which side of the potential energy is the spatial rate of change?
We recognize the left hand side as the time rate of change of momentum and the right hand side as the (negative of the) spatial rate of change of the potential energy.
Is impulse a force?
Impulse causes a change in momentum -- it isn't the change in momentum itself.". This, to me, is downright bogus. Impulse isn't force, it's caused by force. Impulse literally is the sum of the change in momentum caused by force.
How to find the change in momentum of a body?
The change in the linear momentum of a body is equal to the impulse received by the body. In equation form it is Δp = F ( Δt) where Δp is the change in the linear momentum of a body, F is the applied force and Δt is the elapsed very short time. The product of F and Δt is collectively called the impulse imparted to the body.
What are the two main concepts of impulse?
There's two main concepts here: impulse (change in momentum) and pressure (force over some area).
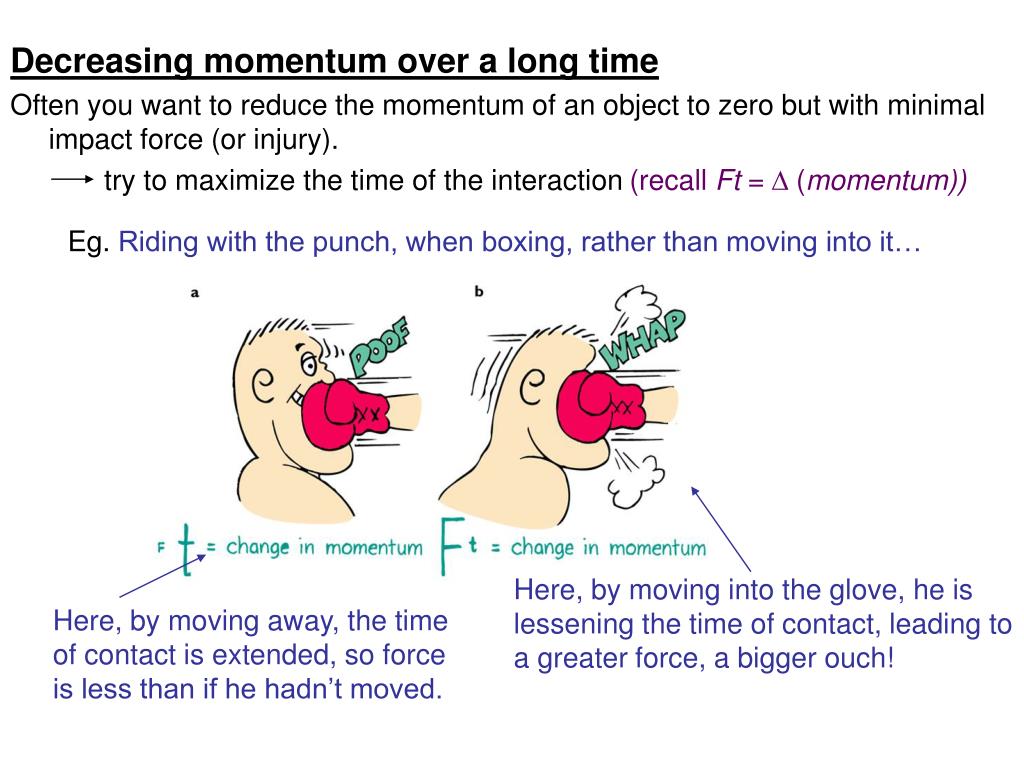
What happens when you start with V I in a car crash?
In a car crash, you decelerate from some initial velocity which you were driving at to rest. Regardless of any specifics of the crash, if you start with some v i, your change in momentum will be the same. So our goal to reduce the amount of force acting on you is to increase the time over which this deceleration occurs.
How does a neck bag work?
What the bag does, is decelerate your head enough to prevent a broken neck, by inflating into your face and changing the force from an instant application all at once, to a gradual force over a small amount of time as pressure from the push of your head deflates the bag.
What happens when a plastic bag expands?
As the bag expands, it blows the plastic cover off the steering wheel and inflates in front of the driver. The bag is coated with a chalky substance such as talcum powder to help it unwrap smoothly. The driver (moving forward because of the impact) pushes against the bag.
Is the impulse the same with or without an airbag?
This happens with or without the airbag, so the impulse is the same.
Do airbags have momentum?
Airbags do nothing for momentum. Your velocity on impact is what it is but the airbag deaccelerates you over a distance reducing the g forces your head goes throu allowing a greater chance of survival.
Why is momentum in the opposite direction?
Note that even though the momentum remains in the same direction the change in momentum is in the opposite direction because the magnitude of the final momentum is less than the magnitude of the initial momentum.
What is the final momentum vector?
We know that the final momentum vector must be the sum of the initial momentumvector and the change in momentum vector, Δ→p = mΔ→v Δ p → = m Δ v → .This means that, using tail-to-head vector addition, Δ→p Δ p →, mustbe the vector that starts at the head of →p i p → i and ends on the head of →p f p → f as shown in this picture:
What happens when particles collide with other particles?
Change in Momentum. Particles or objects can collide with other particles or objects, we know that this will often change their velocity (and maybe their mass) so their momentum is likely to change as well. We will deal with collisions in detail a little bit later but we are going to start by looking at the details of the change in momentum ...
Can momentum change when particles collide?
Particles or objects can collide with other particles or objects, we know that this will often change their velocity (and maybe their mass) so their momentum is likely to change as well . We will deal with collisions in detail a little bit later but we are going to start by looking at the details of the change in momentum for a single particle or object.
