Femoral nerve pain can also be the result of a complication from other medical conditions including:
- Kidney tumors or growths
- Fractured pelvis
- Abdominal bleeding
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Masses occurring on the thigh muscles
- Inflammation related to an infection
- Exposure to toxic substances
- Vitamin deficiency
How do I relieve femoral nerve pain?
Treatment
- Conservative measures
- Medications. Corticosteroid injections. Injections can reduce inflammation and temporarily relieve pain. ...
- Surgery. Rarely, surgery to decompress the nerve is considered. This option is only for people with severe and long-lasting symptoms.
What are the symptoms of femoral nerve dysfunction?
Symptoms of femoral nerve dysfunction include tingling, pain, numbness, burning and decreased sensation in the knee, thigh or leg, reports MedlinePlus. Additional symptoms are weakness in the leg and difficulty going up or down stairs, including a feeling of the knee trying to give way. In order to determine if the femoral nerve is damaged, a ...
What causes genitofemoral nerve pain?
Some causes include: 2
- Abdominal or pelvic surgery: The genitofemoral nerve can be damaged during certain types of surgery.
- Trauma to the abdomen and/or pelvis.
- Compression of the psoas muscle.
What causes sacrum joint pain?
What are the Causes of Sacroiliac Joint Pain?
- This condition of sacroiliac joint pain often occurs due to an overuse of overloading of the joints.
- Degeneration of the cartilage in the sacroiliac joints can lead to the bones rubbing against each other and degenerative osteoarthritis occurs. ...
- A physical abnormality like difference in leg lengths can give rise to sacroiliac joint pain.
See 7 key topics from this page & related content
See 4 key topics from this page & related content

How do you treat femoral nerve pain?
Medications for femoral nerve pain include corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling and inflammation in your leg. Conversely, painful and uncomfortable symptoms can be relieved by prescribed or over-the-counter pain medications.
How do you relax the femoral nerve?
Kneeling on one knee, with your foot resting on a chair behind you. Tuck your bottom under and lunge slightly forwards into hip extension. Once you feel a gentle stretch slowly curl your head an upper back down to intensify the stretch for a few seconds then repeat.
Is femoral nerve pain serious?
Femoral neuropathy, or femoral nerve dysfunction, occurs when you can't move or feel part of your leg because of damaged nerves, specifically the femoral nerve. This can result from an injury, prolonged pressure on the nerve, or damage from disease. In most cases, this condition will go away without treatment.
What aggravates femoral nerve?
Accidents and trauma. Broken leg, broken hip or pressure from a cast or splint. Complications from surgeries, such as hip replacement or hysterectomy, or from femoral artery catheterization procedures. Diabetes.
What does femoral nerve pain feel like?
Sensation changes in the thigh, knee, or leg, such as decreased sensation, numbness, tingling, burning, or pain. Weakness of the knee or leg, including difficulty going up and down stairs -- especially down, with a feeling of the knee giving way or buckling.
Does stretching help femoral nerve pain?
Graded exposure stretching, whether performed independently by the client or by the manual therapist appears to be helpful in relieving femoral nerve compression due to lumbar spine pathology (L2-L4) or musculotendinous entrapment.
Why is femoral nerve pain worse at night?
At night our body temperature fluctuates and goes down a bit. Most people tend to sleep in a cooler room as well. The thought is that damaged nerves might interpret the temperature change as pain or tingling, which can heighten the sense of neuropathy.
How long does it take for femoral nerve to heal?
In patients with femoral neuropathy associated with positional compression or retraction compression during surgery or delivery, recovery typically occurs over 3-4 months.
How do you test the femoral nerve?
0:151:25How to test the Femoral Nerve (Lumbar Plexus L2,3,4) or reverse ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut either way the pain is going to be in the front of a leg in here. Now. If I slowly bend the kneeMoreBut either way the pain is going to be in the front of a leg in here. Now. If I slowly bend the knee at 90 degrees some patients might feel some discomfort already.
Where is femoral nerve pinched?
Femoral nerve entrapment is the pinching of the femoral nerve at some point along its course. Most often, that occurs at the spine. Pinching of the femoral nerve will cause pain, numbness or weakness felt in the front of the thigh.
Is the femoral nerve part of the sciatic nerve?
The femoral nerve is the major nerve that serves the tissues of the thigh and leg, including the muscles and skin. While the much larger sciatic nerve also passes through the thigh on its way to the lower leg and foot, only the femoral nerve innervates the tissues of the thigh.
Can sciatica cause femoral nerve pain?
It controls the muscles in the back of your knee, as well as other leg muscles. Where the two conditions differ is the cause: Pressure on or damage to the sciatic nerve causes sciatica, while pressure on the femoral nerve causes femoral neuropathy. Sciatica tends to affect the back of the leg more than the front.
How can I sleep with femoral nerve pain?
The best option is to sleep on the side opposite the discomfort with a pillow between your legs. (If the burning is in your left thigh, sleep on your right side.) This can help ease the compression of the nerve enough to allow you to get to sleep.
How long does it take for femoral nerve to heal?
In patients with femoral neuropathy associated with positional compression or retraction compression during surgery or delivery, recovery typically occurs over 3-4 months.
Why is femoral nerve pain worse at night?
At night our body temperature fluctuates and goes down a bit. Most people tend to sleep in a cooler room as well. The thought is that damaged nerves might interpret the temperature change as pain or tingling, which can heighten the sense of neuropathy.
Can a chiropractor help with femoral nerve entrapment?
Chiropractic is a common technique used for femoral neuropathy as it incorporates, adjustments, interferential stimulation, low level laser, massage, thumper, acupuncture and exercises to relieve the tight muscle group.
What are the symptoms of femoral nerve damage?
Common symptoms include pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling in the thigh that may extend to the knee and as far as the foot. In some cases, it c...
What is the treatment for femoral neuropathy?
Treatment options include medication and physical and manual therapy. In some cases, a person may need surgery.
Is femoral neuropathy permanent?
In most cases, symptoms will improve over time, although some people may have permanent nerve damage. In some cases, a person will need surgery.
What is the term for a loss of sensation in the legs?
Femoral nerve dysfunction. Femoral nerve dysfunction is a loss of movement or sensation in parts of the legs due to damage to the femoral nerve.
What is a direct injury?
Direct injury (trauma) Prolonged pressure on the nerve. Compression, stretching, or entrapment of the nerve by nearby parts of the body or disease-related structures (such as a tumor or abnormal blood vessel) The femoral nerve can also be damaged from any of the following: A broken pelvis bone.
What causes a broken pelvis bone?
A broken pelvis bone. A catheter placed into the femoral artery in the groin. Diabetes or other causes of peripheral neuropathy. Internal bleeding in the pelvis or belly area (abdomen) Lying on the back with the thighs and legs flexed and turned (lithotomy position) during surgery or diagnostic procedures.
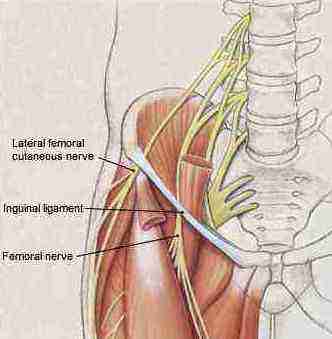
Where is the femoral nerve located?
The femoral nerve is located in the pelvis and goes down the front of the leg. It helps the muscles move the hip and straighten the leg. It provides feeling (sensation) to the front of the thigh and part of the lower leg. A nerve is made up of many fibers, called axons, surrounded by insulation, called the myelin sheath.
What is the purpose of nerve conduction test?
Nerve conduction tests ( NCV) to check how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is usually done at the same time as an EMG. MRI to check for masses or tumors. Your provider may order additional tests, depending on your medical history and symptoms.
What is an abnormal knee reflex?
An abnormal knee reflex. Smaller than normal quadriceps muscles on the front of the thigh. Tests that may be done include: Electromyography ( EMG) to check the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles. Nerve conduction tests ( NCV) to check how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
What is the fiber that surrounds nerves called?
A nerve is made up of many fibers, called axons, surrounded by insulation, called the myelin sheath.
How can Femoral Nerve Pain be Prevented?
Nerve damage due to diabetes can also be prevented by keeping blood sugar levels low, which will minimise the risk of contracting the condition. If obesity is a factor in the onset of diabetes or the nerve compression itself, losing weight will obviously help.
How Serious is Femoral Nerve Compression?
The femoral artery is large and so this can be very dangerous and may itself cause compression of the femoral nerve.
How is Femoral Nerve Damage Diagnosed?
A full physical examination and detailed questions about the patient’s medical history and the level of sensations experienced are normally necessary to achieve a diagnosis. These will include the examination of specific muscles that the femoral nerve control s and will also determine if other nerves are affected. Obvious signs are femoral nerve pain, weakness in the leg and unusual sensations.
What causes femoral nerve damage?
There can be several causes of injury, including direct trauma such as a blow to the lower abdomen, the groin or the front of the thigh. Diabetic muscle wasting is the most common cause of Femoral neuropathy. Also, the nerve can become entrapped as it leaves the spine or (more commonly) as it runs below the inguinal ligament at the site of the groin fold. At this point, the Femoral Nerve is in closely surrounded by the head of the femur (thigh bone), several muscle tendons and the soft tissue around the hip joint. It is vulnerable to compression from these structures. This can occur if the leg is forced into a ‘frog’ position for an extended period, from pressure from the baby during pregnancy, due to a traumatic blow or due to a build up of pressure from a tumour or significant intra-pelvic bleed. On occasion, the ‘bone cement’ used in hip replacement has been able to generate enough heat when setting to cause Femoral Nerve damage.
What nerve moves the quadriceps?
Apart from the skin sensations mentioned above, the Femoral Nerve also supplies sensation and the ability to move to Quadriceps muscles on the front of the thigh and several muscles of the groin area. See the adjacent diagram. Causes: There can be several causes of injury, including direct trauma such as a blow to the lower abdomen, ...
What are the symptoms of femoral nerve pain?
Obvious signs are femoral nerve pain, weakness in the leg and unusual sensations. neuromuscular ultrasound, a relatively new method that diagnoses and guides treatment for medical conditions affecting nerves and muscles by identifying abnormalities in the shape of the nerve.
Which nerve is responsible for compression of the thigh?
Femoral Nerve compression could be the answer. The muscles (left) and the skin (right) supplied by the Fermoral Nerve. Anatomy: The Femoral Nerve runs down the front of the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin of the front and inner thigh. As the nerve goes into the lower leg, it changes name to the Saphenous Nerve which supplies ...
How to get rid of a nerve in your leg?
Using physical therapy, you can begin reducing the amount of pain you are dealing with and regain your range of movement. Usually the nerve will be “freed” from the spine, and what will follow is a reduction in leg symptoms. The nerve may also be mobilised by working into the groin muscles if the entrapment is here.
What is the femoral triangle?
Surrounding the femoral nerve is femoral triangle, an anatomical landmark made up of other structures such as the inguinal ligament and iliopsoas tendon which can cause impingement of the nerve.
What nerve causes pain in the front of the thigh?
Femoral nerve entrapment is the pinching of the femoral nerve at some point along its course. Most often, that occurs at the spine. Pinching of the femoral nerve will cause pain, numbness or weakness felt in the front of the thigh.
Why does my femoral nerve hurt?
The femoral nerve is also commonly pinched in cases of hip arthritis, with patients often reporting pain travelling down the front of the thigh to the knee. Other causes can be anything which grows inside the body, such as a space occupying growth or tumour, but these are far less common.
Why do we need an MRI of the spine?
An MRI scan of the spine might be helpful to identify how badly the nerve is trapped.
Where is the femoral nerve located?
Your femoral nerve runs from your spine right down into your hip area, and down the front of the leg. It is located near your groin and works to control all of the muscles that help to move your hips and straighten out your legs. Without this nerve, you wouldn’t be able to feel anything in the front of your thighs and along the lower part of your legs. If it ends up getting damaged, it causes you to struggle to walk. It could end up causing problems with your ability to feel in your foot and leg.
How long does it take to get an MRI of a nerve?
This would show how badly the nerve is compressed, and any underlying issues. An MRI scan takes about 20-25 mins per region.
What is the motor branch of the femoral nerve?
The first motor branch innervates iliacus. This muscle, in conjunction with the psoas major, causes medial rotation of the hip. The anterior branch of the femoral nerve then descends to supply the sartorius (the tailor’s muscle). Once it passes through the femoral canal (as the most lateral structure of the neurovascular bundle), it supplies the pectineus, a small muscle in the medial compartment of the thigh. Finally, the posterior branch of femoral nerve supplies the four heads of the quadriceps femoris (vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and rectus femoris). The articularis genu is supplied by a branch of the nerve to vastus intermedius.
How does the femoral nerve enter the femoral triangle?
The lateral circumflex femoral artery is straddled by both sections. The nerve enters the femoral triangle by passing beneath the inguinal ligament, just lateral to the femoral artery.
What is the femoral nerve?
Femoral nerve is the main nerve of anterior compartment of thigh. It originates from the dorsal sections of the anterior primary rami of L2, L3, L4 nerves and is the largest branch of lumbar plexus .
What is the source of the nerves in the knee joint?
The knee joint is supplied by the nerves to the three vasti. The nerve to the vastus medialis contains numerous proprioceptive fibres from the knee joint, accounting for the thickness of the nerve. This is in accordance with Hilton’s law: Nerve supply to a muscle which lies across a joint, not only supplies the muscle, but also supplies the joint beneath and the skin overlying the muscle.
Which nerve supplies the skin on the anteromedial thigh?
The anterior (superficial) branch of the femoral nerve first gives rise to the intermediate and medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh. They supply the skin on the anteromedial thigh. The posterior division gives only one cutaneous branch, the saphenous nerve which supplies the skin on the medial side of the foot and leg.
Which nerve supplies the articularis genu?
The articularis genu is supplied by a branch of the nerve to vastus intermedius.
Where is the femoral nerve located?
The femoral nerve is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus. The nerve descends from the lumbar plexus in the abdomen, travelling down through the fibres of psoas major. The nerve exits psoas major at the lower part of its lateral border, passing behind the iliac fossa to approximately the mid-point of the inguinal ligament. It then traverses below the inguinal ligament of about 4 cm into the thigh and splits into an anterior and posterior division. The lateral circumflex femoral artery is straddled by both sections. The nerve enters the femoral triangle by passing beneath the inguinal ligament, just lateral to the femoral artery. In the thigh, it lies outside the femoral sheath, gives off articular branches to the hip and knee joints.
What causes lateral femoral nerve to pass through?
Extra weight. Being overweight or obese can increase the pressure on your lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Pregnancy. A growing belly puts added pressure on your gro in, through which the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve passes. Diabetes. Diabetes-related nerve injury can lead to meralgia paresthetica. Age.
What causes a pinched nerve in the thigh?
Causes. Meralgia paresthetica occurs when the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve — which supplies sensation to the surface of your outer thigh — becomes compressed, or pinched. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is purely a sensory nerve and doesn't affect your ability to use your leg muscles. In most people, this nerve passes through ...
What causes numbness in the upper thigh?
Pressure on the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which supplies sensation to your upper thigh, might cause these symptoms of meralgia paresthetica: Tingling and numbness in the outer (lateral) part of your thigh. Burning pain on the surface of the outer part of your thigh. These symptoms commonly occur on one side of your body ...
What is the pain in the upper leg called?
Meralgia paresthetica. Meralgia paresthetica. Meralgia paresthetica is a condition characterized by tingling, numbness and burning pain in the outer part of your thigh. The condition is caused by compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which supplies sensation to your upper leg. Meralgia paresthetica is a condition characterized by ...
Why does my thigh hurt?
The cause of meralgia paresthetica is compression of the nerve that supplies sensation to the skin surface of your thigh. Tight clothing, obesity or weight gain, and pregnancy are common causes of meralgia paresthetica.
How to treat meralgia paresthetica?
In most cases, you can relieve meralgia paresthetica with conservative measures, such as wearing looser clothing. In severe cases, treatment may include medications to relieve discomfort or, rarely, surgery.
Why does my groin feel compressed?
Common causes of this compression include any condition that increases pressure on the groin, including: Nerve injury, which can be due to diabetes or seat belt injury after a motor vehicle accident, for example, also can cause meralgia paresthetica.
What to do when your leg hurts when you sleep?
If your chronic pain is caused by pinched or compressed nerves, adjusting your sleep position may relieve some of the pressure. For example, people with sciatica who prefer to sleep on their side often find it helpful to sleep with their affected leg on top. People with hip or knee pain may find relief by sleeping with a pillow between their legs.
How to make your pain worse?
Adjust the Temperature. Experiment with different room temperatures when you sleep. It may take some time to find the best temperature for you: cool enough to help you sleep, not cold enough to make your pain worse. Consider keeping a journal of each night’s room temperature, sleep quality, and pain, then see what patterns you notice over time.
What to do if your pain is not working at night?
If the medications you’re taking to manage your pain are wearing off or not working as well at night, tell your doctor and discuss your options. For example, if you have rheumatoid arthritis, your doctor may recommend modified-release corticosteroids to prevent nighttime inflammation.
What happens when you lay down and you are upright?
Body Position. When you lay down, the weight of your body may put pressure on your nerves in ways that it doesn’t when you’re upright. This is particularly common with sciatica and other chronic pain caused by pinched or compressed nerves.
Why does my nerve hurt at night?
If you suffer from nerve pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, physical trauma, sciatica, lupus, arthritis, or other causes , you may find that your pain gets worse at night. While not everyone experiences this, it is quite common for people with nerve pain to report greater pain later at night or whenever they get in bed.
How to get rid of chronic pain?
Get Appropriate Exercise During the Day. Exercise during the day can help reduce some kinds of chronic pain, and it may help you rest better too. Talk with your pain management doctor about what kinds of exercise are appropriate and safe for you.
How to get rid of pain in the body?
This might include turning off the TV and other screens 1-2 hours before bedtime, reading a book, or taking a warm bath. Anything that helps you relax and unwind before you head to sleep.

Epidemiology
- According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), diabetes is the most common reason for peripheral neuropathy in people whove had diabetes for at least 25 years.
Symptoms
- This nerve condition can lead to difficulties moving around. Your leg or knee might feel weak, and you may be unable to put pressure on the affected leg. You might also feel unusual sensations in your legs. They include:
Causes
- If your nerve damage is the result of an injury, it may be possible that your femoral vein or artery is also damaged. This could cause dangerous internal bleeding. The femoral artery is a very large artery that lies close to the femoral nerve. Trauma often damages both at the same time. Injury to the artery or bleeding from the artery can cause compression on the nerve.
Diagnosis
- To diagnose femoral neuropathy and its cause, your doctor will perform a comprehensive physical exam and ask questions about recent injuries or surgeries, as well as questions about your medical history. To look for weakness, they will test specific muscles that receive sensation from the femoral nerve. Your doctor will probably check your knee reflexes and ask about changes in …
Treatment
- The first step in treating femoral neuropathy is dealing with the underlying condition or cause. If compression on the nerve is the cause, the goal will be to relieve the compression. Occasionally in mild injuries, such as mild compression or a stretch injury, the problem may resolve spontaneously. For people with diabetes, bringing blood sugar levels back to normal may allevia…
Prognosis
- You might be able to heal fully after you treat the underlying condition. If the treatment isnt successful or if the femoral nerve damage is severe, you might permanently lose feeling in that part of your leg or the ability to move it.
Prevention
- You can lower your risk of femoral neuropathy caused by diabetes by keeping your blood sugar levels under control. This helps protect your nerves from damage caused by this disease. Preventive measures would be directed at each cause. Talk to your doctor for advice about what preventive measures would be the best for you. Maintaining an active lifestyle helps to keep you…