Recrystallization
In chemistry, recrystallization is a technique used to purify chemicals. By dissolving both impurities and a compound in an appropriate solvent, either the desired compound or impurities can be coaxed out of solution, leaving the other behind. It is named for the crystals often formed when the co…
What is Recrystallization in chemistry?
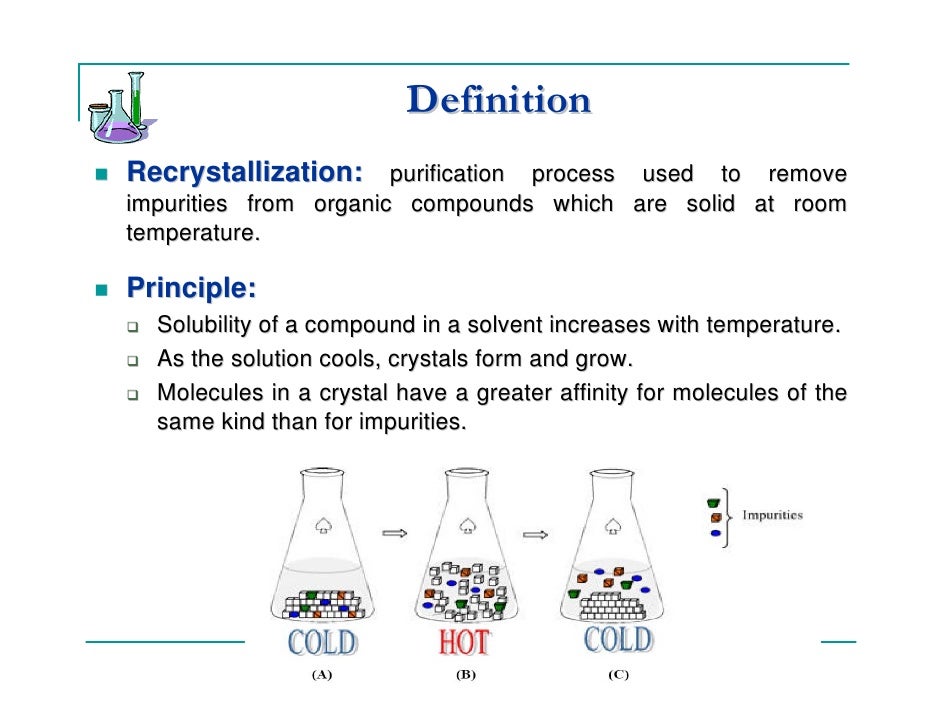
Recrystallization is a purification technique for solid compounds. To perform recrystallization, an impure solid compound is mixed with hot solvent to form a saturated solution. As this solution cools, the solubility of the compound decreases, and pure crystals grow from solution.
What happens to impurities during recrystallization?
During recrystallization, an impure solid compound is dissolved in a hot liquid until the solution is saturated, and then the liquid is allowed to cool. 2 The compound should then form relatively pure crystals. Ideally, any impurities that are present will remain in the solution and will not be incorporated into the growing crystals ( Figure 1 ).
What are the benefits of purifying reactants by recrystallization?
Purifying reactants by recrystallization improves product purity and yield. Once a solid product has been isolated and washed, reaction yield can also be increased by removing volatiles from the filtrate and recrystallizing the product from the resulting solid.
What makes a good recrystallization solvent?
If it takes more than 3 mL to dissolve the sample in the hot solvent, the solubility in this solvent is probably too low to make it a good recrystallization solvent. If the first choice of solvent is not a good recrystallization solvent, try others.

How does recrystallization work?
To perform recrystallization, an impure solid compound is mixed with hot solvent to form a saturated solution. As this solution cools, the solubility of the compound decreases, and pure crystals grow from solution.
How to recrystallize a compound?
To start recrystallization, heat the solvent to boiling on a hot plate in an Erlenmeyer flask with a stir bar. Place the compound to be recrystallized in another Erlenmeyer flask at room temperature. Next, add a small portion of hot solvent to the compound.
How to clean a Büchner crystal?
Rinse the crystals on the Büchner funnel with a small amount of fresh, cold solvent (the same solvent used for recrystallization) to remove any impurities that may be sticking to the crystals.
What is the difference between crystallization and recrystallization?
Although the terms "crystallization" and "recrystallization" are sometimes used interchangeably, they technically refer to different processes. Crystallization refers to the formation of a new, insoluble product by a chemical reaction; this product then precipitates out of the reaction solution as an amorphous solid containing many trapped impurities. Recrystallization does not involve a chemical reaction; the crude product is simply dissolved into solution, and then the conditions are changed to allow crystals to re-form. Recrystallization produces a more pure final product. For this reason, experimental procedures that produce a solid product by crystallization normally include a final recrystallization step to give the pure compound.
How to purify a compound?
Recrystallization is a technique used to purify solid compounds. 1 Solids tend to be more soluble in hot liquids than in cold liquids. During recrystallization, an impure solid compound is dissolved in a hot liquid until the solution is saturated, and then the liquid is allowed to cool. 2 The compound should then form relatively pure crystals. Ideally, any impurities that are present will remain in the solution and will not be incorporated into the growing crystals ( Figure 1 ). The crystals can then be removed from the solution by filtration. Not all of the compound is recoverable — some will remain in the solution and will be lost.
What is the process of recrystallization?
Recrystallization is a purification technique for solid compounds. To perform recrystallization, an impure solid compound is mixed with hot solvent to form a saturated solution. As this solution cools, the solubility of the compound decreases, and pure crystals grow from solution.
Why is recrystallization important in the pharmaceutical industry?
The pharmaceutical industry also makes heavy use of recrystallization, since it is a means of purification more easily scaled up than column chromatography. 3 The importance of recrystallization in industrial applications has triggered educators to emphasize recrystallization in the laboratory curriculum. 4 For example, the drug Stavudine, which is used to reduce the effects of HIV, is typically isolated by crystallization. 5 Often, molecules have multiple different crystal structures available, so it is necessary for research to evaluate and understand which crystal form is isolated under what conditions, such as cooling rate, solvent composition, and so forth. These different crystal forms might have different biological properties or be absorbed into the body at different rates.
Why do scientists use recrystallization?
Scientists use recrystallization to purify solids, typically products, from different chemical reactions. The process involves dissolving a solid into solution, then allowing the dissolved substance to gradually crystallize. This produces compounds high in purity, a quality which can be seen by the presence of uniform crystals.
What is the application of recristallization?
Recrystallization has applications that extend into the industrial, medical, and pharmaceutical industries. Techniques such as texture control, drug development, and treatment purification all involve the procedure.
Why do scientists use multiple solvents?
Scientists typically employ multiple solvents when no singular solvent meets all the criteria for that given recrystallization procedure. Each solvent pair contains a “soluble solvent,” one in which the compound is soluble, and an “insoluble solvent,” one in which the compound is insoluble. The soluble solvent and insoluble solvent must be miscible, so that the proportions used do not limit their solubility in solution.
What is the purification of a compound?
The definition of recrystallization is a technique for the purification of compounds in which a compound is dissolved in a solvent and slowly cooled to form crystals, which are a purer form of the compound.
What happens to the crystals in a solution as the temperature decreases?
As the temperature decreases, so does the solubility of the compound in solution. Soon, the solution becomes supersaturated, prompting crystal formation. As discussed, these crystals then precipitate out of the solution at the cooler recrystallization temperature.
How to accelerate crystallization?
To expedite crystallization and recrystallization processes, scientists can employ a technique called seeding. Seeding involves first dipping a small crystal, or seed, of solute into the saturated solution. Following this step, larger crystals can form and subsequently grow on this seed crystal.
How much of a compound is needed for recrystallization?
But this substance must contain approximately 80% of your desired compound; in other words, it should be mostly pure. Otherwise, the recrystallization will not proceed smoothly.
How does recrystallization work?
The principle behind recrystallization is that the amount of solute that can be dissolved by a solvent increases with temperature . In recrystallization, a solution is created by dissolving a solute in a solvent at or near its boiling point. At this high temperature, the solute has a greatly increased solubility in the solvent, so a much smaller quantity of hot solvent is needed than when the solvent is at room temperature. When the solution is later cooled, after filtering out insoluble impurities, the amount of solute that remains dissolved drops precipitously. At the cooler temperature, the solution is saturated at a much lower concentration of solute. The solute that can no longer be held in solution forms purified crystals of solute, which can later be collected.
How to keep solutes from crystallizing?
As the filtrate begins to accumulate, heat the receptacle beaker; the resulting vapors will help to prevent any crystallization in the funnel or on the filter paper.
How to transfer crystals in a beaker?
Either use a portion of the filtrate to rinse the beaker or use a rubber policeman on the end of your stirring rod to scrape the remaining crystals into the Buchner funnel.
How to determine if a particulate is insoluble?
Heat the beaker containing the solute and continue adding boiling solvent incrementally until all of the solute has been dissolved. If additional solvent can be added with no appreciable change in the amount of solute present, the particulate matter is probably insoluble impurities.
How to dry crystals?
Spreading the crystals out in a beaker or a crystallizing dish will provide for the most efficient drying as the crystals will have a maximum of exposed surface area.
What happens if you heat a funnel before filtration?
If the funnel was properly heated before filtration, all of the solution will have passed through and no crystals will have formed on the paper or in the funnel. If crystals have formed, pouring a small amount of boiling solvent through the funnel will dissolve these. If the solution is still discolored after using activated carbon and filtering, either the color is from the compound and will not go away or you need to repeat the step with the addition of activated carbon.
How to make crystals grow faster?
First, the solution should be cooled in an ice bath. Slow cooling of the solution leads to slow formation of crystals and the slower crystals form, the more pure they are. Rate of crystallization slows as temperature decreases so cooling with an ice bath should only be used until crystals begin to form; after they do, the solution should be allowed to warm to room temperature so crystal formation occurs more slowly. If no crystals form even after the solution has been cooled in an ice bath, take a fire polished stirring rod and etch (scratch) the glass of your beaker. The small pieces of glass that are etched off of the beaker serve as nuclei for crystal formation. If crystals still do not form, take a small amount of your solution and spread it on a watch glass. After the solvent evaporates, the crystals that are left behind can serve as seeds for further crystallization. Both these methods of nucleation (i.e. etching and seed crystals) cause very rapid crystallization, which can lead to the formation of impure crystals.
What is Recrystallization?
Recrystallization is a purification technique to separate a high value crystalline product from unwanted impurities dissolved in the mother liquor. Strictly speaking, recrystallization is a process in which an initially solidified crystalline material is redissolved and crystallized again to produce final product crystals of desired size, shape, purity, and yield. The underlying mechanisms, dissolution ,and recrystallization can also minimize the crystal's internal energy in order to reach a more global energy equilibrium resulting a stable polymorph. While recrystallization is usually applied deliberately to optimize crystals and processes, uncontrolled recrystallization can lead to the unwanted formation of hydrates and solvates or polymorph transformation.
What is the first step in recrystallization?
Step 1: Solvent Screening. The first step of recrystallization is a solvent selection procedure based on properties like: Depending on its molecular structure, a solute can be classified as soluble, partially soluble, or insoluble in these solvents or solvent mixture.
How does supersaturation occur?
A system is supersaturated when the concentration of dissolved solute exceeds the solubility limit at a given temperature. Depending on kinetics, the solution has the ability to remain supersaturated over a range of temperature and time before it recrystallizes. The elapsed time between the creation of supersaturation and the formation of the first crystals is called induction time. Increasing supersaturation reduces induction time to a point where the formation of crystals happens spontaneously as soon as supersaturation is further increased. This point is defined as the Metastable Boundary, the difference between solubility curve and Metastable Curve being the Metastable Zone Width.
Why is solubility important in crystallization?
For solution crystallization, the solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature.
Why is careful control of the degree of supersaturation and an understanding what particle mechanisms crystals go through important?
Careful control over the degree of supersaturation and an understanding what particle mechanisms crystals go through is essential to design efficient recrystallization processes with optimal downstream performance.
What happens to the solute during a chemical reaction?
The progressing chemical reaction increases supersaturation of the solute, which eventually recrystallizes. Creation of supersaturation can be extremely fast, leading to local high supersaturation at the point of mixing, extensive nucleation, poor process control, and difficult downstream handling.
Why is seed crystal important?
The help of seed crystals is often critical to start the recrystallization processes robustly and repeatedly. Unseeded processes often show uncontrolled spontaneous nucleation, which can lead to extreme process variation, especially during scale-up and large-scale manufacturing.
How to do recrystallization?
Pick the solvent. In the introductory organic lab course, the solvent for recrystallization is usually determined for you. The criteria used to choose an appropriate recrystallization solvent includes: 1 finding a solvent with a high temperature coefficient . The solvent must not dissolve the compound at low temperatures (that includes room temperature), but must dissolve the compound at high temperatures. The solute must dissolve in order to rid its lattice of impurities, but must not remain dissolved at room temperature (after all, recovery of the solid is essential!). 2 using a solvent that dissolves impurities readily or not at all . If the solvent dissolves the impurities readily (even at room temperature) then the impurities will not become trapped in the developing crystal lattice, but will remain dissolved in the solvent. If the impurities do not dissolve (even at elevated temperatures) then they can be easily removed by gravity filtration . (see the section on gravity filtration) 3 insuring the solvent will not react with the solute . As mentioned earlier, recrystallization does not chemically alter a molecule. No chemical bonds must be broken in the solute molecule. The crystal lattice is dissolved at elevated temperatures, but this only involves overcoming the intermolecular attractive forces. 4 using a solvent that is nonflammable, inexpensive and volatile . Solvents with low boiling points (i.e., volatile) can be easily removed from the resultant crystals by simply allowing the solvent to evaporate.
What solvent is used to remove crystals?
using a solvent that is nonflammable, inexpensive and volatile . Solvents with low boiling points (i.e., volatile) can be easily removed from the resultant crystals by simply allowing the solvent to evaporate.
What happens if a solution is white?
This will cause the colored molecules to adsorb onto the surface of the decolorizing carbon, thereby ridding the solution of these impurities. Should these impurities remain in solution, they may become trapped in the developing crystal during cooling. Review the material about decolorizing carbon.
Does recrystallization alter a molecule?
insuring the solvent will not react with the solute . As mentioned earlier, recrystallization does not chemically alter a molecule. No chemical bonds must be broken in the solute molecule. The crystal lattice is dissolved at elevated temperatures, but this only involves overcoming the intermolecular attractive forces.
Can you remove impurities from crystals with gravity filtration?
If the solvent dissolves the impurities readily (even at room temperature) then the impurities will not become trapped in the developing crystal lattice, but will remain dissolved in the solvent. If the impurities do not dissolve (even at elevated temperatures) then they can be easily removed by gravity filtration . (see the section on gravity filtration)
How to recrystallize a compound?
(This is a better choice than a beaker, since the sloping sides help trap solvent vapors and slow the rate of evaporation.) Heat the solvent in a separate flask to its boiling point on a hotplate. (Remember to add boiling chips while the solvent is still cool, to keep it boiling smoothly). Add hot solvent to the flask containing the compound in small portions, swirling after each addition, until the compound is completely dissolved. Keep the solution hot at all times during the dissolution process by resting it on the hotplate too. Do not add more hot solvent than is necessary to just dissolve the sample.
What are the impurities in organic compounds?
Solid organic compounds frequently contain small amounts of colored impurities, enough to turn the solution yellow, brown, blue, etc. These impurities may be by-products from a synthesis or isolation process, or they may derive from oxidation and degradation reactions that occur when a compound is improperly stored.
How does precipitation occur in a crystal?
However, if the solution is cooled too quickly, precipitation occurs. In a precipitation, the crystals are formed so rapidly that impurities are trapped in the crystal lattice. The small crystals of precipitates also have a large surface area on which even more impurities can adhere. If your melting point indicates impurities or your crystals are small or not pure in appearance, repeat the process using a longer period of cooling.

CORE Concepts
Topics Covered in Other Articles
What Is Recrystallization
- The definition of recrystallizationis a technique for the purification of compounds in which a compound is dissolved in a solvent and slowly cooled to form crystals, which are a purer form of the compound. Scientists use recrystallization to purify solids, typically products, from different chemical reactions. The process involves dissolving a soli...
Recrystallization vs Crystallization
- Although the procedures of crystallization and recrystallization display similarities, their respective definitions diverge. Firstly, crystallization is a separation technique. It involves precipitating crystals from solution through transitions in the solute’s solubility conditions. The resulting crystals can be readily distinguished and subsequently filtered out from the solution. S…
Types of Recrystallization
- 1. Single Solvent Recrystallization
This type of recrystallization is the most basic and, as a result, the most frequently employed. The process involves dissolving a compound, “A,” and impurity, “B,” in a heated solvent system. As this solution cools back to room temperature, the solubility of the compounds in the solution drops, … - 2. Multi-Solvent Recrystallization
This method of recrystallization closely resembles the first in terms of the procedure involved. However, multi-solvent recrystallization requires two, and sometimes more, solvents. The compound, “A,” and impurity, “B,” dissolve in the first solvent. Then, the addition of a second solv…
How to Perform A Simple Recrystallization Procedure
- Below is a stepwise guidefor completing a basic recrystallization procedure. 1. First, weigh the impure solvent and record that value. Then add the impure compound to a solvent system. 2. Heat this solvent system to your target temperature, or its boiling point. Be sure to raise the temperature in gradual increments to ensure that the rest of the process proceeds smoothly. 3. …
Limitations of Recrystallization
- Although quite useful, recrystallization possesses some limitations and ramifications. Firstly, the compound in question must occupy a solid state at standard conditions. This means that substances including oils, greases, and waxes cannot be crystalized or recrystallized under standard conditions. The purity of your crude material also comes into play. The success of recr…
Applications of Recrystallization to Today’S World
- Recrystallization has applications that extend into the industrial, medical, and pharmaceutical industries. Techniques such as texture control, drug development, and treatment purification all involve the procedure. But the pharmaceutical industry actually makes the most use of recrystallization procedures. Purification and separation processes are key to the isolation of dif…