Based on what you learned in the lab, your body need to break down starch into glucose because: Starch molecules are too large to diffuse into cells. Log in for more information.
What happens to starch when it is digested?
During digestion, enzymes in your body break starches down, turning them into glucose. Your body can then use the glucose for energy immediately or store it in the liver or muscles. Starch digestion begins in the mouth, where enzymes in your saliva start to turn starch into sugar.
What enzymes break down starch into sugar?
When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose, maltotriose and maltose, by an enzyme called amylase found in your saliva and small intestine. These compound sugars are further broken down into simple sugars by other enzymes, including maltase, lactase, sucrase and isomaltase.
What happens to glucose after it is digested?
When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. The stomach and small intestines absorb the glucose and then release it into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored in our bodies, to be used later.
What happens to carbohydrates in the stomach when digested?
When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. The stomach and small intestines absorb the glucose and then release it into the bloodstream.
See more

Why does your body break down starch?
Starch is the most important energy source for humans. The body digests starch by metabolizing it into glucose, which passes into the bloodstream and circulates the body. Glucose fuels virtually every cell, tissue, and organ in the body. If there is excess glucose, the liver stores it as glycogen.
Why do we turn starch into sugar?
Plants still need to continue their metabolic processes during these times, so the starch grains stored in the leaf provide the needed energy. The stored starch within the leaf converts back to sugar, which combines with oxygen to release carbon dioxide, water and energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Can humans break down starch into glucose?
When starch is consumed, it dissolves into glucose molecules with the help of molecular machines, known as enzymes. Specifically, enzymes called amylases aid in breaking starch into glucose with the help of water.
How do you turn starch into glucose?
Transfer the ground grain into a container suitable for cooking and mix it with twice as much water. Heat up the mixture to roughly 150 to 168 degrees Fahrenheit. Leave the mixture at this temperature for up to two hours. During this time, enzymes in the grain convert the starch to sugar.
What happens when starch is broken down?
When all is said and done, starches have been broken down into their smallest, usable components: primarily the monosaccharide glucose, as well as some fructose and galactose. These simple sugars are known as the "end products" of starch digestion. Your body can now distribute them for use as energy or store them.
Are humans meant to eat starch?
A new study looking at the evolutionary history of the human oral microbiome shows that Neanderthals and ancient humans adapted to eating starch-rich foods as far back as 100,000 years ago, which is much earlier than previously thought.
Why do carbs turn into sugar?
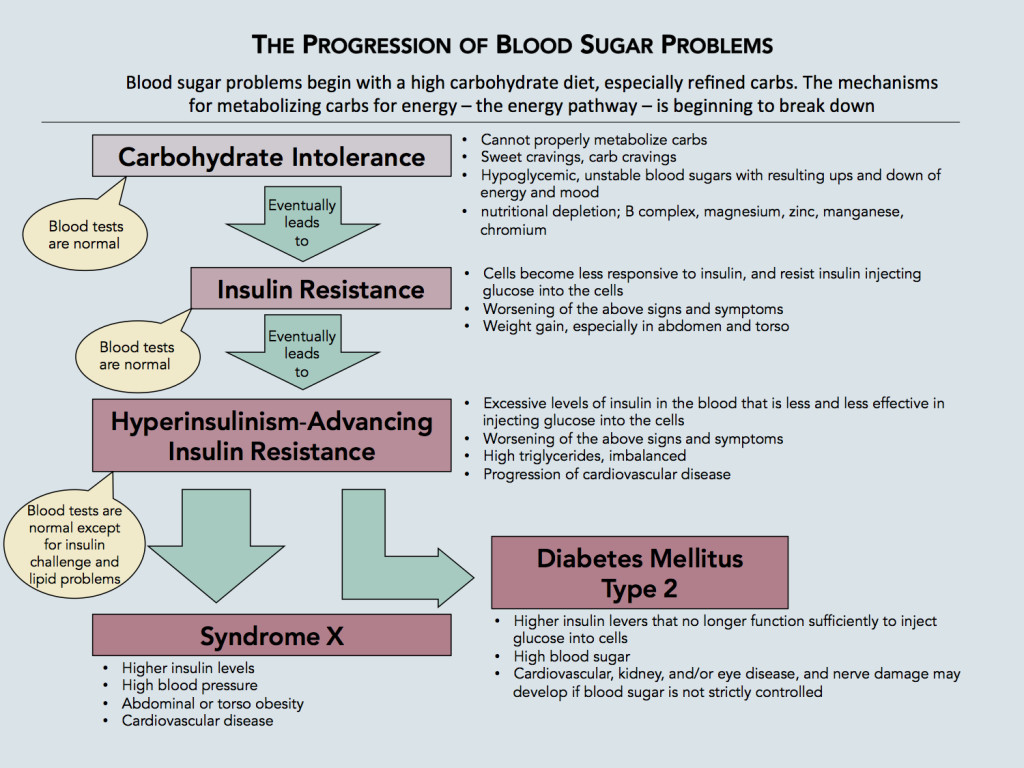
When you eat carbs, your body breaks them down into simple sugars, which are absorbed into the bloodstream. As the sugar level rises in your body, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin. Insulin is needed to move sugar from the blood into the cells, where the sugar can be used as a source of energy.
Why is starch not digested in the stomach?
Salivary glands and the pancreas secrete various enzymes such as amylase which catalyse the starch (polymer) hydrolisis into simple sugars (monomers). The hydrochloric acid in our stomach would destroy starch molecules. This organ hasn't the precise enzymes to break down complex sugars.
Why is glucose converted to starch in leaves just after photosynthesis what happens to this starch at night?
Glucose is soluble, thus it is converted to starch as it is insoluble so that it cannot escape from the cells. Another reason for conversion is storage. The stored starch (converting it into glucose) can be used later by the cells to release energy by respiration.
Why do plants convert glucose into sucrose?
Glucose and fructose are both monosaccharides, but together they make the disaccharide sucrose. This is an important process for the storage and compression of energy. Plants do this to make it easier to transport large amounts of energy, via sucrose.
How does starch turn into glucose?
Nutritionally speaking breaking starch into glucose is one of two major ways that your body uses starch. This happens in the small intestine and uses enzymes in pancreatic fluid. This becomes blood sugar. Any starches which are resistant to these enzymes will, most of them, be metabolized into short chain fatty acids by the bacterial community in the colon. SCFAs are very beneficial
What is the purpose of starch?
Starch exists to store solar energy in a stable, compact and easily retrieved manner. It can only fulfill its destiny by being depolymerized into its monomer units, glucose. It is glucose that is the universal energy source to life on Earth, with only a handful of exceptions.
How are glucose residues linked together?
In starch the glucose residues are linked together by α-1,4 glycosidic bond while in cellulose they are bonded via β-1,4 glycosidic bond. Humans have enzymes known as Amylase that is capable of breaking only α-1,4 Glycosidic bond (found in starch) and not the β-1,4 GB (cellulose) and thus can digest starch but not cellulose.
Where does amylase occur?
Alpha amylase, which occurs in the saliva and is also secreted by the pancreas of many mammals, acts quite similar to beta amylase but instead of glucose it hydrolyses the disaccharide MALTOSE (a disaccharide containing two glucose units) from the ends of the chains of Amylose and Amylopectin. In the intestines Maltose is acted upon by Maltase to give glucose and the branched portion of amylopectin left over is acted upon by debranching enzmes, alpha amylase and maltase to produce glucose.
What is the enzyme that digests cellulose?
An enzyme called Cellulase is produced by some symbiotic protozoans (e. g., Trichonympha) in the gut of ruminants and termites that is capable of digesting the cellulose (β-1,4 GB).
Where is glucose stored?
Glucose is stored in plants as starch as an energy supply for the germination of seeds and energy for plant necessity. It also related as a gravitation sensor.
What is the first part of digestion?
The first part of digestion is mechanical digestion. The grinding action of the teeth will increase the surface area of the food and therefore allow enzymes to more effectively break down the macromolecules.
What Types Of Carbohydrates Turn To Sugar?
The three types of carbohydrates are sugar, starch and fiber. During the digestive process, both sugars and starches are turned into the sugars that the body uses for energy. People lack the enzymes needed to digest fiber, so it passes through the digestive tract without turning into to sugar. Some foods contain simple sugars, which don't need to be further broken down during digestion. The three main simple sugars are glucose, fructose and galactose. Glucose is found in honey and fruit, fructose is found in fruits, vegetables and honey and galactose is found in plants. Glucose and galactose are easily absorbed, but some people have difficulties absorbing fructose if it isn't accompanied by glucose or galactose. Compound Sugars Compound sugars include sucrose, a combination of fructose and glucose; lactose, a combination of galactose and glucose; and maltose, which is a combination of two glucose molecules. Sucrose is found in sugar and maple syrup, lactose is found in milk and maltose is found in malt, fruits and grains. During digestion, the enzymes break the bonds between the sugar molecules to turn compound sugars into simple sugars. Starches Plants form starches, which are also called complex carbohydrates, by stringing together sugars. When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose, maltotriose and maltose, by an enzyme called amylase found in your saliva and small intestine. These compound sugars are further broken down into simple sugars by other enzymes, including maltase, lactase, sucrase and isomaltase. Factors Affecting Carbohydrate Digestion The glycemic index measures how much a particular carbohydrate-containing food increases blood-glucose levels or how quickly carbohydrates are turned into sugar. Foods with a low Continue reading >>
Can Starch Turn Into Sugar?
Starches are complex carbohydrates found in rice, wheat, legumes, potatoes, corn and many other foods. These carbohydrates turn into sugar during digestion, providing energy for the bodys functions. Carbohydrates should account for 40 to 60 percent of your total daily calorie intake. Starches are polysaccharides, which plants store as energy reserves. Starches contain 300 to 1,000 conjoined units of glucose, a type of sugar. Your body must break starches down before it can use their glucose for energy. Starches and other complex carbohydrates, including soluble and insoluble dietary fiber, take longer to digest than simple carbohydrates, or sugars, which your body can use for energy immediately. During digestion, enzymes in your body break starches down, turning them into glucose. Your body can then use the glucose for energy immediately or store it in the liver or muscles. Starch digestion begins in the mouth, where enzymes in your saliva start to turn starch into sugar. High-starch carbohydrates include legumes, such as dry beans, peas, lentils and soybeans, starchy vegetables, such as potatoes, pumpkin, corn and green peas and grains such as rice and wheat. Diabetes exchange lists group starchy vegetables with other carbohydrates, because your body processes them more like grains than other vegetables. Current dietary guidelines do not provide a recommended daily intake for carbohydrates other than dietary fiber. You should get at least 14 g of dietary fiber for every 1,000 calories in your diet. Whole grains should account for at least half of y Continue reading >>
Answer
Starch can't be used by the organism the way it is, because cells aren't able to do anything with it.
Answer
Starch molecules are too large to diffuse into cells. Give me brainliest please!
New questions in Biology
Don is jogging while pushing his daughter in a baby stroller. He is pushing on the stroller forward with a force of 45 newtons. Friction is opposing t … he forward motion with a force of 45 newtons. If the stroller is moving at a constant speed of 2.5 meters per second, which graph shows the distance the stroller travels through time?