Full Answer
What happens during plasmolysis in plants?
Mar 19, 2020 · Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the cytoplasm of a plant cell in response to diffusion of water out of the cell and into a high salt concentration solution. During plasmolysis, the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall. This does not happen in low salt concentration because of the rigid cell wall.
Why does plasmolysis occur in a hypotonic solution?
During the concave plasmolysis, both the cell membrane and protoplasm shrink away and begins to detach from the cell wall, which is caused due to the loss of water. Concave plasmolysis is a reversible process and it can be revised by placing the cell in a hypotonic solution, which helps calls to regain the water back into the cell.
What happens to the protoplasm During concave plasmolysis?
Apr 11, 2022 · Plasmolysis due to excessive loss of water from the cell due to osmotic actin. Why does the cell wall not shrink during Plasmolysis? Note how the inside of the cell is shrinking and the gap between the plasma membrane and the cell wall (the cell wall does not shrink because it is somewhat rigid due to the presence of cellulose microfibrils).
Why can’T cells stop plasmolysis?
Sep 28, 2016 · The thing that keeps the plant upright is the cells absorbing water and swelling forcing the plant to stand. without water, the cells shrink …

Why do cell walls not shrink?
The cell membrane is just like that of animals, it is flexible and can shrink and swell from osmosis. But the cell wall is not flexible. It forms a box around the cell to provide structure, and it will not shrink or expand from osmosis.Oct 25, 2019
Does the cell wall shrink during plasmolysis?
If a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the plant cell loses water and hence turgor pressure by plasmolysis: pressure decreases to the point where the protoplasm of the cell peels away from the cell wall, leaving gaps between the cell wall and the membrane and making the plant cell shrink and crumple.
Does the cell wall change during plasmolysis?
In concave plasmolysis, the plasma membrane separates from the cell wall by the formation of several concave pockets (Figure 1b). Plasmolysis is reversible and the addition of hypotonic solutions or plain water will lead to the re-expansion of the protoplast and the reinstatement of the original turgor pressure [1].
How do cells not shrink?
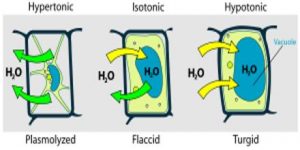
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will leave the cell, and the cell will shrink. In an isotonic environment, there is no net water movement, so there is no change in the size of the cell.
Can a cell wall shrink?
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is often due to water loss via exosmosis, thereby resulting in gaps between the cell wall and the plasma membrane.Jul 28, 2021
Is plasmolysis hypertonic or hypotonic?
Plasmolysis is more common and happens in extreme cases of water loss. Some real-life examples of Plasmolysis are: Shrinkage of vegetables in hypertonic conditions. Blood cell shrinks when they are placed in the hypertonic conditions.Aug 31, 2019
Why are cells plasmolysis in hypertonic solution?
When a cell is placed into a hypertonic solution, there is a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell, so water flows out of the cell to balance the concentration on both sides of the membrane. Since plasmolysis is the loss of water from a cell, it occurs when a cell is in a hypertonic solution.Mar 29, 2019
What fills the space between cell wall and membrane after plasmolysis?
Thus, the space between the cell wall and condensed protoplast is filled with hypertonic solution in a plasmolyzed cell.
What happens to a cell that has a rigid cell wall when placed in a hypotonic solution?
Cells with a cell wall will swell when placed in a hypotonic solution, but once the cell is turgid (firm), the tough cell wall prevents any more water from entering the cell. When placed in a hypertonic solution, a cell without a cell wall will lose water to the environment, shrivel, and probably die.Mar 5, 2021
What causes shrinking of a cell?
A hypertonic solution has increased solute, and a net movement of water outside causing the cell to shrink. A hypotonic solution has decreased solute concentration, and a net movement of water inside the cell, causing swelling or breakage.
What happens when the cell shrinks?
If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a lower concentration outside ). So if you get thirsty at the beach drinking seawater makes you even more dehydrated.
What causes cells to shrink and shrivel?
When a cell enters a solution with a higher osmotic pressure – such as a sugary liquid – its porous membrane tries to protect the cell by letting water out. This causes the cell membrane to shrivel up, compacting the cell to withstand the pressure from without.May 15, 2014
What is the process of plasmolysis?
Osmosis is responsible for the occurrence of plasmolysis. Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that occurs when water flows into or out of a membrane such as a cell’s plasma membrane. It occurs based on the type of solution that a cell is in. A solution is a mixture that contains a fluid, or solvent (usually water), and a solute that is dissolved in the solvent. When a cell is placed into a hypertonic solution, there is a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell, so water flows out of the cell to balance the concentration on both sides of the membrane. Since plasmolysis is the loss of water from a cell, it occurs when a cell is in a hypertonic solution. Conversely, when a cell is placed into a hypotonic solution, there is a lower solute concentration outside the cell than inside, and water rushes into the cell. In an isotonic solution, solute concentrations are the same on both sides, so there is no net gain or loss of water.
How does concave plasmolysis work?
During concave plasmolysis, the protoplasm and the plasma membrane shrink away from the cell wall in places due to the loss of water; the protoplasm is then called protoplast once it has started to detach from the cell wall. Half-moon-shaped “pockets” form in the cell as the protoplast peels from the surface of the cell wall. This can be reversed if the cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, which will cause water to rush back into the cell.
What happens when a plant loses water?
Water flows out of the cells and into the surrounding fluid due to osmosis. This causes the protoplasm, all the material on the inside of the cell, to shrink away from the cell wall. Severe water loss that leads to the collapse of the cell wall can result in cell death. Since osmosis is a process that requires no energy on the part of the cell and cannot be controlled, cells cannot stop plasmolysis from taking place.
What happens when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution?
When a cell is placed into a hypertonic solution, there is a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell, so water flows out of the cell to balance the concentration on both sides of the membrane. Since plasmolysis is the loss of water from a cell, it occurs when a cell is in a hypertonic solution. Conversely, when a cell is placed ...
What is the cell wall of a plant?
Cell wall – Found in plant and fungi cells, a tough layer surrounding the outside of the cell that provides structural support. Ctyorrhysis – Permanent and irreversible collapse of the cell wall due to too much water being lost through plasmolysis. Protoplasm – The material comprising the inside of the cell; it is called protoplast ...
What are the mechanisms of water loss?
Plants have a couple mechanisms to protect against water loss. Stomata, which are small holes on the underside of a plant’s leaves, close to help keep water in the plant. Plants also naturally produce wax that is another defense against water loss.
Do animal cells have a cell wall?
Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have a cell wall in addition to their cell membrane. When animal cells are placed in a hypotonic solution and too much water rushes in, they will lyse, or burst. They fare best in isotonic solutions instead. This figure shows a plant cell in different types of solutions:
How does plasmolysis work?
The process of plasmolysis can be easily explained in the laboratory by placing a living cell in a strong salt solution. When the plant cells are placed in the concentrated salt solution, because of osmosis, water from the cell sap moves out. Therefore, the water travels through the cell membrane into the neighbouring medium.
What happens when a plasmolysed cell is placed in a hypotonic solution?
When the plasmolysed cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, (the solution in which solute concentration is less than the cell sap), the water travels into the cell, due to the higher concentration of water outside the cell. Then the cell swells and becomes turgid . This is known as deplasmolysis.
What are some examples of plasmolysis?
Plasmolysis is more common and happens in extreme cases of water loss. Some real-life examples of Plasmolysis are: 1 Shrinkage of vegetables in hypertonic conditions. 2 Blood cell shrinks when they are placed in the hypertonic conditions. 3 During extreme coastal flooding, ocean water deposits salt onto land. 4 Spraying of weedicides kills weeds in lawns, orchards and agricultural fields. This is due to the natural phenomena-Plasmolysis. 5 When more amount of salt is added as the preservatives for food like jams, jellies, and pickles. The cells lose water due to higher concentration outside and become less conducive to support the growth of microorganisms.
What happens during concave plasmolysis?
Concave Plasmolysis. During the concave plasmolysis, both the cell membrane and protoplasm shrink away and begins to detach from the cell wall, which is caused due to the loss of water. Concave plasmolysis is a reversible process and it can be revised by placing the cell in a hypotonic solution, which helps calls to regain the water back into ...
Why do cells lose water?
The cells lose water due to higher concentration outside and become less conducive to support the growth of microorganisms. Also read: Osmosis.
How does water pass through the cell membrane?
How do Water Pass through the Cell Membranes? During the process of Plasmolysis within the plant cell, the cell membrane separates the interiors of the cell from the surrounding. It allows the movement of water molecules, ion and other selective particles across the membrane and stops others.
Why does water leave the cell?
Water leaves the cell, because the surrounding salt solution contains a lower concentration of water compared to the inside of the cell SEE DIAGRAM 1 (Remember, water diffuses from high to low concentration). Why is a red onion used in experiments?
What happens when you bathe in salt water?
Being bathed in a hypertonic solution (the salt water) causes osmosis (the diffusion of water) from inside of the cell to the outside of the cell. As a result, the cell shrinks. Click to see full answer.

Plasmolysis Definition
Plasmolysis and Osmosis
- Osmosis is responsible for the occurrence of plasmolysis. Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that occurs when water flows into or out of a membrane such as a cell’s plasma membrane. It occurs based on the type of solution that a cell is in. A solution is a mixture that contains a fluid, or solvent (usually water), and a solute that is dissolved in the solvent. When a cell is placed int…
Types of Plasmolysis
- Concave Plasmolysis
Concave plasmolysis is a process that can usually be reversed. During concave plasmolysis, the protoplasm and the plasma membrane shrink away from the cell wall in places due to the loss of water; the protoplasm is then called protoplast once it has started to detach from the cell wall. H… - Convex Plasmolysis
Convex plasmolysis is more severe than concave plasmolysis. When a cell undergoes complex plasmolysis, the plasma membrane and protoplast lose so much water that they completely detach from the cell wall. The cell wall collapses in a process called ctyorrhysis. Convex plasmol…
Defenses Against Plasmolysis
- Plasmolysis happens in extreme cases of water loss, and does not happen very often in nature. Plants have a couple mechanisms to protect against water loss. Stomata, which are small holes on the underside of a plant’s leaves, close to help keep water in the plant. Plants also naturally produce wax that is another defense against water loss.
Examples of Plasmolysis
- Although plasmolysis more commonly happens in a laboratory setting, it can happen in real-life settings as well. For example, during periods of extreme coastal flooding, ocean water deposits salt onto land. Too much salt causes the water to flow out of any plants on the affected land, killing them. Chemical weedicides are also used to kill unwanted plants through plasmolysis. Thi…
Related Biology Terms
- Osmosis– Process by which water diffuses across a membrane to balance out the solute concentration on either side of the membrane.
- Cell wall – Found in plant and fungicells, a tough layer surrounding the outside of the cell that provides structural support.
- Ctyorrhysis– Permanent and irreversible collapse of the cell wall due to too much water bein…
- Osmosis– Process by which water diffuses across a membrane to balance out the solute concentration on either side of the membrane.
- Cell wall – Found in plant and fungicells, a tough layer surrounding the outside of the cell that provides structural support.
- Ctyorrhysis– Permanent and irreversible collapse of the cell wall due to too much water being lost through plasmolysis.
- Protoplasm– The material comprising the inside of the cell; it is called protoplast when it separates from the cell wall through plasmolysis.
Quiz
- 1. In what type of solution does plasmolysis occur? A. Hypertonic B. Isotonic C.Hypotonic 2. What mechanisms do plants use to defend themselves against plasmolysis? A. The plants’ stomata close to help keep water inside. B. The plants produce wax that keep water inside. C. The plants pump water into their cells through reverse osmosis. D.Both A and B 3. What type of solution is …