Cells of the spongy mesophyll
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively. Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for p…
What is the spongy mesophyll?
How are glucosides stored in plants?
What are the enzymes that make black cherry seeds cyanogenic?
What are the structures of henbane leaf?
How does remote sensing help with vegetation?
Can mutants replicate?
See 3 more
About this website

Palisade Mesophyll Function, Definition and Structure
Illustration of the Function of Mesophyll Palisade. Photo: Ist/Net – The main function of the palisade mesophyll is for photosynthesis. Because these cells contain many chloroplasts. The palisade cells contain intercellular spaces leading to spongy tissue intended for gas exchange. Photosynthesis is the process of forming carbohydrates in the leaves. This process requires carbon dioxide, […]
What is spongy mesophyll and palisade mesophyll? | Socratic
Spongy mesophyll and palisade mesophyll are types of cells involved in the the processes leading up to photosynthesis as well as photosynthesis itself and are located in the leaves of vascular plants. Monocot leaves usually have 1 type of mesophyll; however, eudicots tend to have 2 types of mesophyll - the spongy and palisade. These cells, as can be deduced, contain chloroplast.
Mesophyll - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Miquel Nadal, Jaume Flexas, in Water Scarcity and Sustainable Agriculture in Semiarid Environment, 2018. Abstract. Mesophyll conductance is a vital component of photosynthesis, whose importance for accurate characterization of photosynthetic limitations has increased during the last two decades. Carbon dioxide diffusion across the leaf mesophyll is a complex process implying both biochemical ...
Plant tissues - epidermis, palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll ...
Plant cells, tissues and organs are adapted to their functions. The stem, root and leaves form an organ system that transports substances into, around and out of a plant.
palisade mesophyll | Encyclopedia.com
palisade mesophyll Chlorenchyma tissue, comprising tightly packed, columnar cells, each containing many chloroplasts, in a leaf.In mesophytes it is found together with spongy mesophyll and is usually on the upper (adaxial) side of the leaf. In many xerophytes it is found on both sides of the leaf and often forms the bulk of the mesophyll.
Plant tissues - epidermis, palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll ...
Plant cells, tissues and organs are adapted to their functions. The stem, root and leaves form an organ system that transports substances into, around and out of a plant.
How is Ru5P phosphorylated?
Ru5P is phosphorylated into RuBP using ATP via Phosphoribulokinase. This step regenerates the RuBP used by RuBisCO to fix C O 2.
Which part of a plant is responsible for photosynthesis?
All those green parts of a plant are capable of photosynthesis. For example plant parts like leaf stem flower to some extent contain chlorophyll pigments and carry out photosynthsis more or less.
How did C4 and C3 plants evolve?
Enter C4 and CAM plants. C4 plants evolved from C3 plants about 30 million years ago, during the Oligocene period, when increasingly dry, hot weather challenged the survival of many plants. C4 plants became ecologically significant about 6 million years ago, during the Miocene period, when dryer climate reduced forests and their under-canopy shaded environment, and thus "forced" many grasses to more open environments. Genetic analysis of C4 plants shows their characteristic pathways and leaf anatomy changes evolved independently in up to 40 different occasions in different families of C3 plants, facilitated by the fact that many of the changes weren't directly related to photosynthesis and involved variations in already-existing pathways.
What is the spongy layer of a leaf?
The spongy layer of a leaf features small air spaces between cells that allow for the exchange of gases in photosynthesis. Together with the palisade, the spongy layer makes up the mesophyll of the leaf.
What is the function of the spongy layer in the Palisade layer?
It is also believed that the spongy layer acts as a temporary storage space for sugars and amino acids that have been synthesized in the palisade layer.
What is the spongy mesophyll?
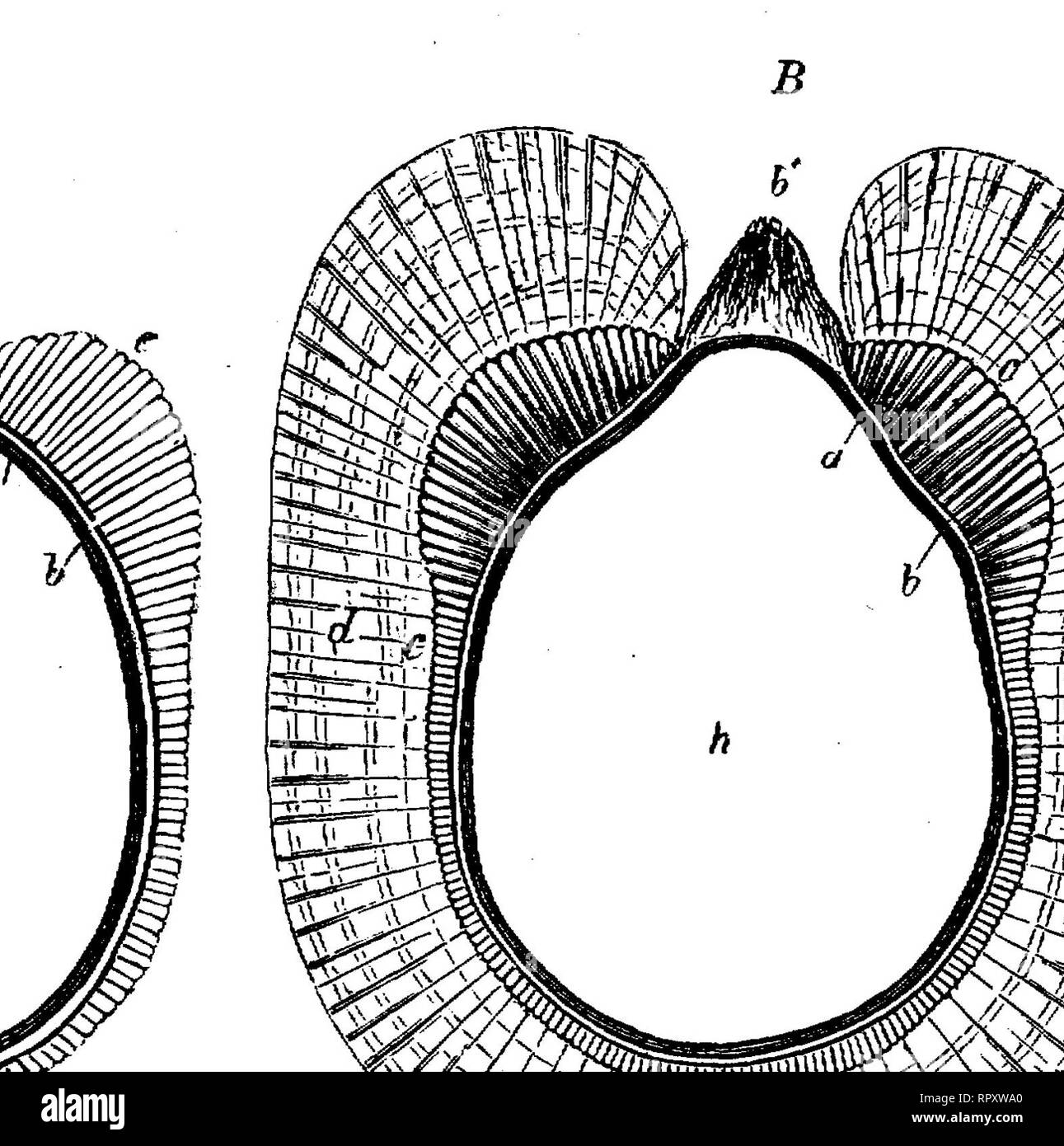
Similar hairs are found on the stems. The spongy mesophyll contains calcium oxalate, mainly in the form of single and twin prisms, but clusters and microsphenoidal crystals are also present (Fig. 26.7B,D ).
How are glucosides stored in plants?
Consistent with a role in plant defense, cyanogenic glucosides are stored and separated from the catabolic enzymes in the intact plant by compartmentation at either tissue or subcellular levels. Information about compartmentalization is not available for many cyanogenic species but it is clear, from those which have been studied, that the details of compartmentation differ between species.
What are the enzymes that make black cherry seeds cyanogenic?
47–51 The kernels of black cherry seeds contain large quantities of the cyanogenic diglucoside ( R )-amygdalin ( 12) and three catabolic enzymes: the diglucosidase amygdalin hydrolase; the monoglucosidase, prunasin hydrolase; and an α-hydroxynitrile lyase, ( R )- (+)-mandelonitrile lyase. These enzymes first appear in the seeds about 6 weeks after flowering. The two β-glucosidases are restricted to protein bodies in the procambium, whereas the hydroxynitrile lyase occurs primarily in protein bodies in the cotyledonary parenchyma cells, which is also the location of the cyanogenic diglucoside, amygdalin ( 12 ). Thus, in black cherry, cyanogenesis in intact tissues of the developing seed is prevented by segregation of the first degrading enzyme, amygdalin hydrolase, and amygdalin ( 12) in different tissues.
What are the structures of henbane leaf?
26.7A ). Both surfaces have a smooth cuticle, epidermal cells with wavy walls, stomata of both anisocytic and anomocytic types, and a large number of hairs, which are particularly abundant on the midrib and veins. The hairs are up to 500 μm long; some are uniseriate and two to six cells long, while others have a uniseriate stalk and a large, ovoid, glandular head, the cuticle of which is often raised by the secretion ( Fig. 26.7E). Similar hairs are found on the stems. The spongy mesophyll contains calcium oxalate, mainly in the form of single and twin prisms, but clusters and microsphenoidal crystals are also present (Fig. 26.7B,D ). The broad midrib contains a vascular bundle, distinctly broader than that of stramonium, showing the usual bicollateral arrangement, which is also to be seen in the stems. The mesophyll of the midrib is made up of two thin zones of collenchyma immediately within the epidermi and a ground mass of colourless parenchyma showing large, intercellular air spaces and containing prisms or, occasionally, microsphenoidal crystals of calcium oxalate.
How does remote sensing help with vegetation?
In addition to providing a means for examining vegetation characteristics, remote sensing can be used to identify, categorize, and map anthropogenic features. Maps designed to show both natural and human-created features, known as land use and land cover maps, may be of tremendous value to groups as diverse as urban planners, economists, transportation managers, real estate developers, demographers, natural resource managers, and conservationists. The premise of land use and land cover mapping is the same as that for vegetation studies: different urban materials, such as concrete, blacktop asphalt, and asphalt shingles, have unique spectral properties that distinguish them from other such materials and vegetation. Two other similarities to remote sensing of vegetation are that different portions of the electromagnetic spectrum are better suited for extracting different types of information (e.g., estimating building perimeter and area vs identifying different land use types), and there is a tradeoff between the detail of the information needed and the spatial resolution of the data needed to capture such features. In general, because of the fine scale of many objects of interest in urban and suburban landscapes, it is frequently important to have data with extremely high spatial resolution (typically <5 m and often <1–2 m), limiting the utility of some of the primary sensor platforms more commonly used in Earth resource applications.
Can mutants replicate?
Applying Agrobacterium -mediated inoculation of PSTVd cDNAs onto tomato, it was found that some mutants could not replicate at all, some mutants did replicate but were restricted to specific tissues such as galls and roots, whereas the corresponding inoculation with wild-type PSTVd led to systemic infection.
