What are symptoms of urea cycle disorder?
- Irritablity
- Lethargy
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting.
What is urea cycle disease?
A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation that results in a deficiency of one of the six enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. The urea cycle involves a series of biochemical steps in which nitrogen, a waste product of protein metabolism, is removed from the blood and converted to a compound called urea in the blood.
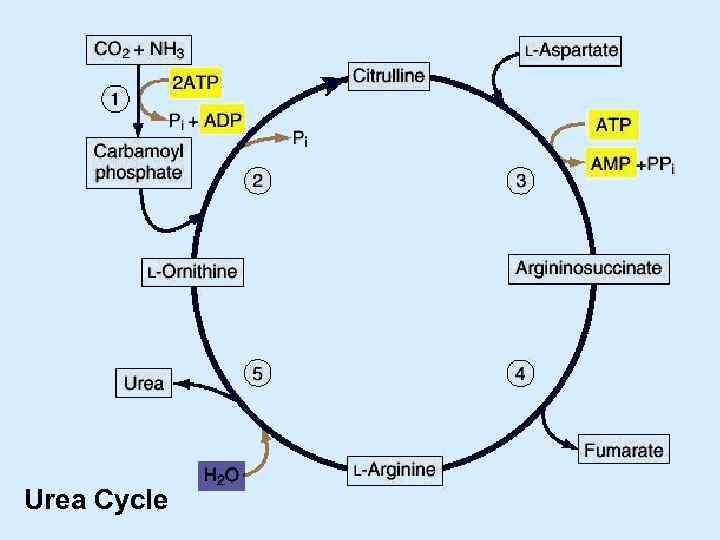
What reactions are involved in the urea cycle?
Reactions of the urea cycle. NH 4 + and aspartate provide the nitrogen that is used to produce urea, and CO 2 provides the carbon. Ornithine serves as a carrier that is regenerated by the cycle. Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized in the first reaction from NH4+, CO2, and two ATP. Inorganic phosphate and two ADP are also produced.
What is the importance of the urea cycle?
Urea is the end product of protein metabolism. So the importance of urea cycle is conversion of ammonia into urea and help in excretion of it. 10 things all bosses need to do.

Why urea synthesis takes place in liver?
NH3 and CO2 are present in the liver only.
Where does the urea cycle primarily occur?
The urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys.
Does the urea cycle happen in the brain?
In the brain, a partial urea cycle appears to function primarily to dispose of two amino acids, citrulline and arginine, which are substrates of the urea cycle (37–40). Therefore, the urea could be a product of arginine metabolism.
Which part of the body produces urea?
The liverThe liver produces several chemicals (enzymes) that change ammonia into a form called urea, which the body can remove in the urine.
What is the function of the urea cycle?
The urea cycle is the primary biochemical pathway in humans by which excess nitrogen is disposed. Through the coordinated function of six enzymes and two mitochondrial transporters, the pathway catalyzes the conversion of a molecule of ammonia, the α-nitrogen of aspartate and bicarbonate into urea.
What are the stages of urea cycle?
Step 1 or feeder reaction: ammonia (NH3) + CO2 → carbamoyl phosphate. ... Step 2: carbamoyl phosphate. ... Step 3: citrulline + aspartate. ... Step 4: argininosuccinate → arginine + fumarate. ... Step 5: arginine + H2O → urea + ornithine.More items...•
Is urea produced by hepatic cells?
Urea is produced in the liver and is a metabolite (breakdown product) of amino acids. Ammonium ions are formed in the breakdown of amino acids. Some are used in the biosynthesis of nitrogen compounds. Excess ammonium ions are converted to urea.
What is the process of urea formation?
Urea is synthesized in the body of many organisms as part of the urea cycle, either from the oxidation of amino acids or from ammonia. In this cycle, amino groups donated by ammonia and L-aspartate are converted to urea, while L-ornithine, citrulline, L-argininosuccinate, and L-arginine act as intermediates.
What is the first reaction in the urea cycle?
First reaction: entering the urea cycle. Before the urea cycle begins ammonia is converted to carbamoyl phosphate. The reaction is catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I and requires the use of two ATP molecules. The carbamoyl phosphate then enters the urea cycle.
What is the urea cycle?
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH 2) 2 CO from ammonia (NH 3 ). This cycle occurs in ureotelic organisms. The urea cycle converts highly toxic ammonia to urea for excretion.
How many enzymes are needed to enter the urea cycle?
The urea cycle consists of four enzymatic reactions: one mitochondrial and three cytosolic. This uses 6 enzymes.
Why is the urea cycle important?
The urea cycle is essential to these organisms, because if the nitrogen or ammonia are not eliminated from the organism it can be very detrimental. In species including birds and most insects, the ammonia is converted into uric acid or its urate salt, which is excreted in solid form .
What enzyme cleaves argininosuccinate?
Argininosuccinate undergoes cleavage by argininosuccinase to form arginine and fumarate. Arginine is cleaved by arginase to form urea and ornithine. The ornithine is then transported back to the mitochondria to begin the urea cycle again.
What is the name of the acid that activates CPS1?
N-Acetylglutamic acid. The synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate and the urea cycle are dependent on the presence of N -acetylglutamic acid (NAcGlu), which allosterically activates CPS1. NAcGlu is an obligate activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
Why do vertebrates use the urea cycle?
As stated above many vertebrates use the urea cycle to create urea out of ammonium so that the ammonium does not damage the body. Though this is helpful, there are other effects of the urea cycle. For example: consumption of two ATP, production of urea, generation of H+, the combining of HCO3- and NH4+ to forms where it can be regenerated, and finally the consumption of NH4+.
What are the defects in urea synthesis?
However, only defects in the first four steps cause clinical symptoms in the newborn: carbamyl phosphate synthetase deficiency, ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, citrullinemia, and argininosuccinic aciduria.
What causes urea synthesis in neonates?
Urea synthesis is the major pathway for the metabolism of ammonia ( Summar and Tuchman, 2004 ). The main causes of neonatal hyperammonemia are liver disease and disorders of urea synthesis. The typical initial feature of neonatal hyperammonemia is an acute overwhelming neurological disorder, exacerbated by protein feeding. Deficiency states of each enzyme responsible for catalyzing the five steps of urea synthesis exist. However, only defects in the first four steps cause clinical symptoms in the newborn: carbamyl phosphate synthetase deficiency, ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, citrullinemia, and argininosuccinic aciduria. Arginase deficiency does not produce symptoms in the newborn. Discussion of these syndromes, as well as transitory hyperammonemia of the premature, is in this section. The hyperglycinemias are also associated with hyperammonemia but discussed in the sections that follow.
What is the function of urea metabolism?
Urea metabolism is an important way to excrete ammonia, which is a waste product of proteins (Eghtesad et al., 2013).
How is glutamine converted to ammonia?
When glutamine is produced in excess in the liver, it is converted to ammonia by glutaminase. The liver urea cycle converts ammonia to urea that is excreted in the urine. The overall reactions of the TCA cycle and the urea cycle can be summarized: 2NH 4 + + HCO 3 − + 3ATP 4 − → urea + 2ADP 3 − + 4Pi + AMP 2 − + 5H +.
How is malate converted to fumarate?
The fumarate produced by the urea cycle is converted to malate by a cytoplasmic form of fumarase. Mitochondrial fumarase is part of the Krebs cycle. Cytoplasmic malate can enter the mitochondrion by means of a transport system, such as the malate/phosphate exchanger or the malate/α-ketoglutarate exchanger.
How do amino acids help the body?
Muscle cells can use amino acids as energy sources , and the liver can detoxify the amino groups (as ammonium ions) via the urea cycle. Alanine is a predominant amino acid in most proteins. It can be transported in the bloodstream from peripheral tissues to the liver where it can be converted to glucose. Alanine is transaminated to form pyruvate, and glucose can be formed from pyruvate through gluconeogenesis. Glucose can then be shipped to the muscle (for energy utilization) through the bloodstream. This system relating muscle and liver metabolism is known as the alanine cycle.
When was the urea cycle discovered?
The urea cycle, also called the ornithine cycle, was discovered by Hans Krebs at the University of Freiburg in Germany, in 1932 (Holmes, 1993 ). The cycle is depicted in Figure 8.11. A priming reaction is employed for introducing the nitrogen atom of the ammonium ion into the cycle.
What enzyme releases citrulline?
The third step is catalyzed by an enzyme called argininosuccinate synthetase, which uses citrulline and ATP to form a citrullyl-AMP intermediate, which reacts with an amino group from aspartate to produce argininosuccinate.
What is the fourth step of the urea cycle?
The fourth step involves the cleavage of argininosuccinate to form fumarate and arginine. Argininosuccinate lyase is the enzyme catalyzing this reaction, which can be represented as follows: In the fifth and last step of the urea cycle, arginine is hydrolyzed to form urea and ornithine.
What is the urea cycle?
These reactions are collectively called the urea cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit cycle. Ammonia is a toxic product of nitrogen metabolism which should be removed from our body. The urea cycle or ornithine cycle converts excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of liver cells. The urea forms, then enters the blood stream, ...
What is the blood test for urea cycle disorders?
Diagnosis of Urea Cycle Defects. A blood aminogram is routinely used in the diagnosis of urea cycle disorders. The concentration of the nitrogen-carrying amino acids, glutamine and alanine, in plasma is elevated in the case of OTC deficiency. In babies, elevated levels of orotic acid in the urine may be an indicator of OTC deficiency.
How much ammonia is removed from the body?
About 10 to 20 g of ammonia is removed from the body of a healthy adult every day. A dysfunctional urea cycle would mean excess amount of ammonia in the body, which can lead to hyperammonemia and related diseases. The deficiency of one or more of the key enzymes catalyzing various reactions in the urea cycle can cause disorders related to the cycle.
Which enzyme converts ammonia to phosphate?
In the first step of the Krebs-Henseleit cycle, ammonia produced in the mitochondria is converted to carbamoyl phosphate by an enzyme called carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I . The reaction can be given as follows:
What is Susha's degree?
Susha has a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree in Chemistry and Master of Science (M.Sc) degree in Biochemistry from the University of Calicut, India. She always had a keen interest in medical and health science. As part of her masters degree, she specialized in Biochemistry, with an emphasis on Microbiology, Physiology, Biotechnology, and Nutrition. In her spare time, she loves to cook up a storm in the kitchen with her super-messy baking experiments.
How does glutamate donate ammonia?
Glutamate donates the ammonia to 3 Phosphohydroxypyruvate via a transamination reaction, yielding 3 Phosphoserine and α-ketoglutarate. The α-ketoglutarate can then react, via either glutamate dehydrogenase or another transamination reaction to acquire another ammonia group, which it, in turn, can donate to another molecule of 3 Phosphohydroxypyruvate for the synthesis of another molecule of glycine, which can be eliminated from the body as hippurate. The repetitive resynthesis of glycine and its reaction with benzoyl CoA becomes the vehicle for the elimination of ammonia from the body in urine.
How is ornithine synthesized?
ornithine is synthesized from glucose; arginine is synthesized from ornithine by the urea cycle
What is the most common urea cycle deficiency?
The most common urea cycle deficiency is in ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC), which is an X-linked disorder. It occurs with a frequency of 1/20,00 - 1/80,000 live births. The variation occurs because there is a late-onset form of OTC deficiency that may be underrepresented in the data used to determine the frequency of the deficiency in the population. Whatever the cause, a diet low in protein is essential to reduce the potential for excessive amino acid degradation with its associated generation of ammonia (ammonium ion).
What is the intermediate in the TCA cycle?
Argininosuccinase releases the aspartate carbon skeleton as fumarate, a TCA cycle intermediate, but not the aspartate nitrogen, to yield the amino acid arginine. Fumarate can be converted to oxaloacetate, another TCA cycle intermediate, which can be transaminated to another molecule of aspartate that can react with another molecule of citrulline and carry another nitrogen into the urea cycle.
What is the transporter of nitrogen in the blood?
Alanine and glutamine are the major transporters of nitrogen in the blood. Alanine is produced in a single biochemical step by the transamination of pyruvate. Glutamine is produced from glutamate by the addition of an amide to the glutamate γ carboxyl group by an ATP-dependent reaction catalyzed by glutamine synthetase.
What are the two nitrogen atoms that enter the urea cycle?
Two nitrogen atoms enter the urea cycle as NH 4+ and aspartate. The first steps of the cycle take place in liver mitochondria, where NH 4+ combines with HCO 3- to form carbamoyl phosphate. Carbamoyl phosphate reacts with ornithine, a compound both required as input to, and regenerated by the cycle, to produce citrulline, which, exits the mitochondria to the cytosol, where the remaining reactions of the cycle occur. The amino acid arginine is synthesized as a product of the urea cycle. Fumarate, another product, links the urea cycle with the TCA cycle. The two entering nitrogen atoms exit the cycle as urea, which the liver releases into the blood for disposal, in urine, by the kidneys.
What happens to glycine in the body?
Benzoate (given as benzoic acid), after activation to benzoyl CoA, reacts with glycine to form hippurate, which is excreted. As a result, glycine is depleted, causing the body to synthesize more from 3 phosphoglycerate. In doing so it uses glutamate as a nitrogen donor in a transamination reaction, yielding α-ketoglutarate, which can then accept another nitrogen and continue in the synthesis of another molecule of glycine, which is conjugated to another molecule of benzoyl CoA for excretion as hippurate in repetitions of the cycle.
Where does urea cycle takes place in a cell?
Urea cycle takes place in the liver, starting in the mitochondria of hepatocytes, the only place where free ammonia is released.
Where does urea synthesis occur?
The liver is the only site where urea is synthesized and ultimately excreted by the kidneys.
Where does the first step of the urea cycle occur?
The first two steps of the urea cycle occur in the mitochondria of the cell. First, the enzyme CPS takes ammonia and bicarbonate and forms carbamoyl phosphate with the use of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is the step in the cycle that determines how fast the cycle progresses.
What is the main function of urea cycle?
The urea cycle helps to excrete two harmful gases, ammonia and carbon dioxide, from the body. The steps of this cycle take place in the mitochondria and cytoplasm.
What are the inputs to one cycle of urea cycle?
Explanation: One molecule of CO 2, one molecule of ammonia, three molecules of ATP and one molecule of aspartic acid are the inputs to one cycle of urea cycle.
Why does urea cycle occur only in liver?
Ureagenesis. The urea cycle is partly cytoplasmic and partly mitochondrial. Only the liver possesses all the enzymes required to synthesize urea from ammonia, and this pathway is strictly located in periportal hepatocytes.
How does urea cycle occur?
The urea cycle or ornithine cycle converts excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of liver cells. The urea forms, then enters the blood stream, is filtered by the kidneys and is ultimately excreted in the urine.
Why does urea cycle occur only in liver?
The urea cycle is partly cytoplasmic and partly mitochondrial. Only the liver possesses all the enzymes required to synthesize urea from ammonia, and this pathway is strictly located in periportal hepatocytes.
Where does urea synthesis occur?
The liver is the only site where urea is synthesized and ultimately excreted by the kidneys.
Where does urea go from the liver?
The urea and water are released from the liver cells to the bloodstream and transported to the kidneys where the blood is filtered and the urea is passed out of the body in the urine. Urea is very soluble and a small molecule, so it is relatively easily passed out by the kidneys as a solution in water.
How is urea produced in liver?
The liver produces several chemicals (enzymes) that change ammonia into a form called urea , which the body can remove in the urine.
What are the inputs to one cycle of urea cycle?
Explanation: One molecule of CO 2, one molecule of ammonia, three molecules of ATP and one molecule of aspartic acid are the inputs to one cycle of urea cycle.
What are the steps involved in urea cycle?
Steps of Urea Cycle:- 1. Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate 2. Synthesis of Citrulline 3. Synthesis of Argininosuccinate 4.
Does urea cycle occur in plants?
Abstract. Urea is a plant metabolite derived either from root uptake or from catabolism of arginine by arginase. In agriculture, urea is intensively used as a nitrogen fertilizer. Urea nitrogen enters the plant either directly, or in the form of ammonium or nitrate after urea degradation by soil microbes.
What are the two reactions of the urea cycle?
Reactions of the urea cycle. NH4+ and aspartate provide the nitrogen that is used to produce urea, and CO2 provides the carbon. Ornithine serves as a carrier that is regenerated by the cycle. Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized in the first reaction from NH4+, CO2, and two ATP. Inorganic phosphate and two ADP are also produced.
What is the reaction of citrulline and aspartate?
Citrulline combines with aspartate to form argininosuccinate in a reaction that is driven by the hydrolysis of ATP to AMP and inorganic pyrophosphate.
What is the purpose of the urea cycle?
Related Diseases of Urea Cycle. References. The urea cycle is the metabolic pathway that transforms nitrogen to urea for excretion from the body. Nitrogenous excretory products are removed from the body mainly in the urine. Ammonia, which is very toxic in humans, is converted to urea, which is nontoxic, very soluble, ...
What enzyme is converted to glucose in the liver?
In the fasting state in the liver, malate can be converted to glucose or to oxaloacetate, which is transaminated to regenerate the aspartate required for reaction 3. Arginine is cleaved to form urea and regenerate ornithine. Enzyme: arginase, which is located primarily in the liver and is inhibited by ornithine.
Which enzyme condenses citrulline and aspartate to form arginosuccinate?
Argininosuccinate synthetase: Condenses citrulline with aspartate to form arginosuccinate. This reaction occurs in the cytosol and requires one ATP.
Which enzyme cleaves arginine into one molecule of urea and ornithine in?
Arginase: Cleaves arginine into one molecule of urea and ornithine in the cytosol. The ornithine is then transported back into the mitochondria for entry back into the cycle.
What cycle is used to excrete NH4+?
The urea cycle allows for the excretion of NH4+ by transforming ammonia into urea, which is then excreted by the kidneys.
Why does urea cycle occur only in liver?
The urea cycle is partly cytoplasmic and partly mitochondrial. Only the liver possesses all the enzymes required to synthesize urea from ammonia, and this pathway is strictly located in periportal hepatocytes.
What is the site of urea cycle?
The urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys.
Where does urea synthesis occur?
Urea synthesis takes place in the liver via a cyclic pathway. The key compound is ornithine, on which the urea molecule is 'built'; intermediates in the process include citrulline and arginine.
Where do urea cycle occur Mcq?
Urea is exclusively produced in liver and then transported through the blood to the kidneys for the excretion through urine. Urea is formed from the NH4, CO2 and alpha-amino nitrogen of aspartate which requires ATP. Enzymes which catalyzes the urea cycle are present in the mitochondria and cytosol of liver cell.

Overview
Urea cycle disorders
Urea cycle disorders are rare and affect about one in 35,000 people in the United States. Genetic defects in the enzymes involved in the cycle can occur, which usually manifest within a few days after birth. The recently born child will typically experience varying bouts of vomiting and periods of lethargy. Ultimately, the infant may go into a coma and develop brain damage. New-borns with UCD are at a much higher risk of complications or death due to untimely screening tests and misdiagn…
Function
Amino acid catabolism results in waste ammonia. All animals need a way to excrete this product. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic organisms, excrete ammonia without converting it. Organisms that cannot easily and safely remove nitrogen as ammonia convert it to a less toxic substance, such as urea, via the urea cycle, which occurs mainly in the liver. Urea produced by the liver is then released into the bloodstream, where it travels to the kidneys and is ultimately excrete…
Reactions
The entire process converts two amino groups, one from NH 4 and one from aspartate, and a carbon atom from HCO 3, to the relatively nontoxic excretion product urea. This occurs at the cost of four "high-energy" phosphate bonds (3 ATP hydrolyzed to 2 ADP and one AMP). The conversion from ammonia to urea happens in five main steps. The first is needed for ammonia to enter the cycle …
Products of the urea cycle
As stated above many vertebrates use the urea cycle to create urea out of ammonium so that the ammonium does not damage the body. Though this is helpful, there are other effects of the urea cycle. For example: consumption of two ATP, production of urea, generation of H , the combining of HCO−3 and NH+4 to forms where it can be regenerated, and finally the consumption of NH+4.
Regulation
The synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate and the urea cycle are dependent on the presence of N-acetylglutamic acid (NAcGlu), which allosterically activates CPS1. NAcGlu is an obligate activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Synthesis of NAcGlu by N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is stimulated by both Arg, allosteric stimulator of NAGS, and Glu, a product in the transamination reactions and one of NAGS's substrates, both of which are elevated when free amino acids are el…
Link with the citric acid cycle
The urea cycle and the citric acid cycle are independent cycles but are linked. One of the nitrogen atoms in the urea cycle is obtained from the transamination of oxaloacetate to aspartate. The fumarate that is produced in step three is also an intermediate in the citric acid cycle and is returned to that cycle.
Additional images
• Urea cycle.
• Urea cycle colored.
Steps in The Urea Cycle
- The urea cycle is a series of five reactions catalyzed by several key enzymes. The first two steps in the cycle take place in the mitochondrial matrix and the rest of the steps take place in the cytosol. Thus the urea cycle spans two cellular compartments of the liver cell. 1. In the first step of the Krebs-Henseleit cycle, ammonia produced in the ...
Significance of The Urea Cycle
- The main purpose of the urea cycle is to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body. About 10 to 20 g of ammonia is removed from the body of a healthy adult every day. A dysfunctional urea cycle would mean excess amount of ammonia in the body, which can lead to hyperammonemia and related diseases. The deficiency of one or more of the key enzymes catalyzing various reaction…
Diagnosis of Urea Cycle Defects
- A blood aminogram is routinely used in the diagnosis of urea cycle disorders. The concentration of the nitrogen-carrying amino acids, glutamine and alanine, in plasma is elevated in the case of OTC deficiency. In babies, elevated levels of orotic acid in the urine may be an indicator of OTC deficiency. Increased levels of blood citrulline and argininosuccinate are also seen in cases of ci…
References
Further Reading