Why does Zr 4+ ion exist? Ions exist when electrons are lost in the outer shell in order to stabilize electronic configurations. An example of a stable atom would be noble gases. Zirconium losing four electrons (represented as Zr 4+ ) is considered stable like the noble gas argon.
Full Answer
What element is Zr in the periodic table?
Apr 10, 2020 · Why does Zr 4+ ion exist? Ions exist when electrons are lost in the outer shell in order to stabilize electronic configurations. An example of a stable atom would be noble gases. Zirconium losing four electrons (represented as Zr 4+ ) is considered stable like the noble gas argon. Click to see full answer.
What is the molecular formula for Zr OH 4?
May 02, 2012 · Zr has atomic number 40 , so it need to lose 4 electrons to gain noble gas configuration of the noble gas Kr
What is Zr used for in a nuclear reactor?
Zirconium cation (4+) Please visit the Zirconium element page for information specific to the chemical element of the periodic table. PubChem CID. 115139. Structure. Find Similar Structures. Molecular Formula. Zr+4. Synonyms.
What does ZR stand for?
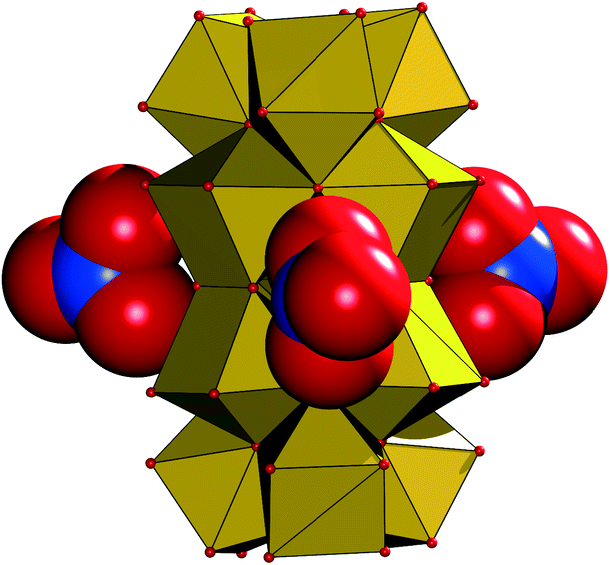
As no hydrolysis reaction occurred during the simulation time of 10 ps, the target of this study was the evaluation of the structure and dynamics of the monomeric hydrated zirconium(IV) ion. The ion forms three hydration shells. In the first hydration shell the ion is 8-fold coordinated with a maximum probability of the Zr–O distance at 2.25 Å.
See more
Zirconium is predominantly in the +4 oxidation state in its compounds. Some less stable compounds, however, are known in which the oxidation state is +3. (The most important respect in which zirconium differs from titanium is that lower oxidation states are of minor importance.) The increased size of the atoms makes the oxides more basic and the aqueous chemistry …

How many ions does Zr have?
| PubChem CID | 115139 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | Zr+4 |
| Synonyms | Zirconium cation (4+) zirconium(4+) Zirconium Ion UNII-91WHB38Z4C 91WHB38Z4C More... |
| Molecular Weight | 91.22 |
| Dates | Modify 2022-04-09 Create 2005-08-01 |
Is Zr an atom or ion?
What is special about zirconium?
How many electrons are in a 4d orbital of Zr?
What is the charge of Zr?
What is Zr in the periodic table?
Is Zr toxic?
Is zirconium a rare metal?
Is zirconium Reactive or nonreactive?
What is the electron configuration for HF?
How many 4d electrons would be predicted in the ground state for the following elements a zirconium?
How many valence electrons does Zr have?
What is Zr in the periodic table?
Zirconium (Zr), chemical element, metal of Group 4 (IVb) of the periodic table, used as a structural material for nuclear reactors. Element Properties.
Why is zirconium used in nuclear energy?
Zirconium, obscure before the late 1940s, became a significant engineering material for nuclear energy applications because it is highly transparent to neutrons. The element was identified (1789) in zircon, ZrSiO 4 (zirconium orthosilicate), from its oxide by the German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth, ...
Why is hafnium removed from zirconium?
Hafnium, present in all zirconium ores, must be scrupulously removed from the metal intended for reactor uses because hafnium strongly absorbs thermal neutrons. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
What is zirconium used for?
Zirconium is also used as an alloying agent in the production of some magnesium alloys and as an additive in the manufacture of certain steels.
How much hafnium is in zirconium?
For some purposes separation of the two elements is not important: zirconium containing about 1 percent of hafnium is as acceptable as pure zirconium.
Why is zirconium a passive gas?
At normal temperatures in air, zirconium is passive because of the formation of a protective film of oxide or nitride.
What is the temperature of zirconium?
Zirconium absorbs oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen in astonishing amounts. At about 800 °C (1,500 °F) it combines chemically with oxygen to yield the oxide, ZrO 2. Zirconium reduces such refractory crucible materials as the oxides of magnesium, beryllium, and thorium.
Who discovered zirconium?
In the Middle Ages colourless gemstones of zircon were thought to be an inferior kind of diamond, but that was shown to be wrong when a German chemist, Martin Klaproth (1743-1817), analysed one in 1789 and discovered zirconium. Klaproth was unable to isolate the metal itself. That was achieved in 1824 by the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius but there was little use for it or its chemical compounds, and so it languished for a century or more.
When was zirconium first made?
Totally pure zirconium was only produced in 1925 by the Dutch chemists Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer by the decomposition of zirconium tetraiodide (ZrI 4 ). These days the metal is produced in bulk by heating zirconium tetrachloride (ZrCl 4) with magnesium. Glossary. Atomic radius, non-bonded.
What is zirconium oxide used for?
It is used to make crucibles that will withstand heat-shock, furnace linings, foundry bricks, abrasives and by the glass and ceramics industries.
Where is zirconium mined?
More than 1.5 million tonnes of zircon are mined each year, mainly in Australia and South Africa. Most baddeleyite is mined in Brazil. Zirconium metal is produced commercially by first converting zircon to zirconium chloride, and then reducing the chloride with magnesium.
Who failed to isolate the pure metal?
Klaproth failed to isolate the pure metal itself, and Humphry Davy also failed when he tried electrolysis in 1808. It was not until 1824 that the element was isolated, when the Swedish chemist Jöns Berzelius heated potassium hexafluorozirconate (K 2 ZrF 6) with potassium metal and obtained some zirconium as a black powder.
Is zirconium a superconductor?
With niobium, zirconium is superconductive at low temperatures and is used to make superconducting magnets. Zirconium metal is protected by a thin oxide layer making it exceptionally resistant to corrosion by acids, alkalis and seawater. For this reason it is extensively used by the chemical industry.
Is zirconium a good material for nuclear power?
Zir conium does not absorb neutrons, making it an ideal material for use in nuclear power stations. More than 90% of zirconium is used in this way. Nuclear reactors can have more than 100,000 metres of zirconium alloy tubing. With niobium, zirconium is superconductive at low temperatures and is used to make superconducting magnets.
How many electrons are needed to form C4+ions?
To form C4+ions , four electrons are to be removed from carbon, which require a high value of ionization energy. It is not available under ordinary conditions.
Which compound is preferred for acylation reactions?
Out of Acet.yl chloride and acetic anhydride, acetic anhydride is preferred for acylation reactions. Explain why?
Is fluorine more electronegative than chlorine?
Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine even then, p-flurobenzoic acid is weaker acid than p-chlorobenzoic acid explain ?
Do carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophillc substitution reactions?
Carbonyl compounds do not undergo nucleophillc substitution reactions.why?
