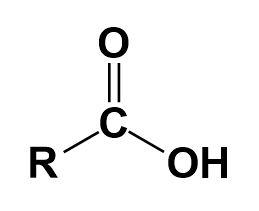
What is the difference between an ester and a ketone?
An ester is a molecule that has a carbonyl and alkoxy group bonded together. A ketone is a more acidic molecule. An ester is a less acidic molecule. Ketones have more reactivity while esters have less reactivity. The oxidation of alcohols and hydrocarbons can produce a ketone as can the hydration of alkynes.
What is the acidity of ketone?
The hydrogen atoms attached with the alkyl or aryl group is acidic. Due to the presence of this acidic hydrogen, ketones are acidic in nature. But the acidity of ketone is not as much as in any acids (pka of ketone is 17 to 21). Let’s focus on the following topics on the acidity of ketone.
Why do ketones have a high reactivity?
The ketones are molecules which do have high reactivity and can easily react with other substances. This is due to the very polar nature of the carbonyl group which in turn gives the molecule a partial positive charge. This means that other substances are often attracted to the molecule with which they then readily react.
What is a ketone?
Definition: A ketone is a molecule in which a carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom to make a carbonyl group and carbons are bonded to this carbonyl. The ketones are molecules which do have high reactivity and can easily react with other substances.
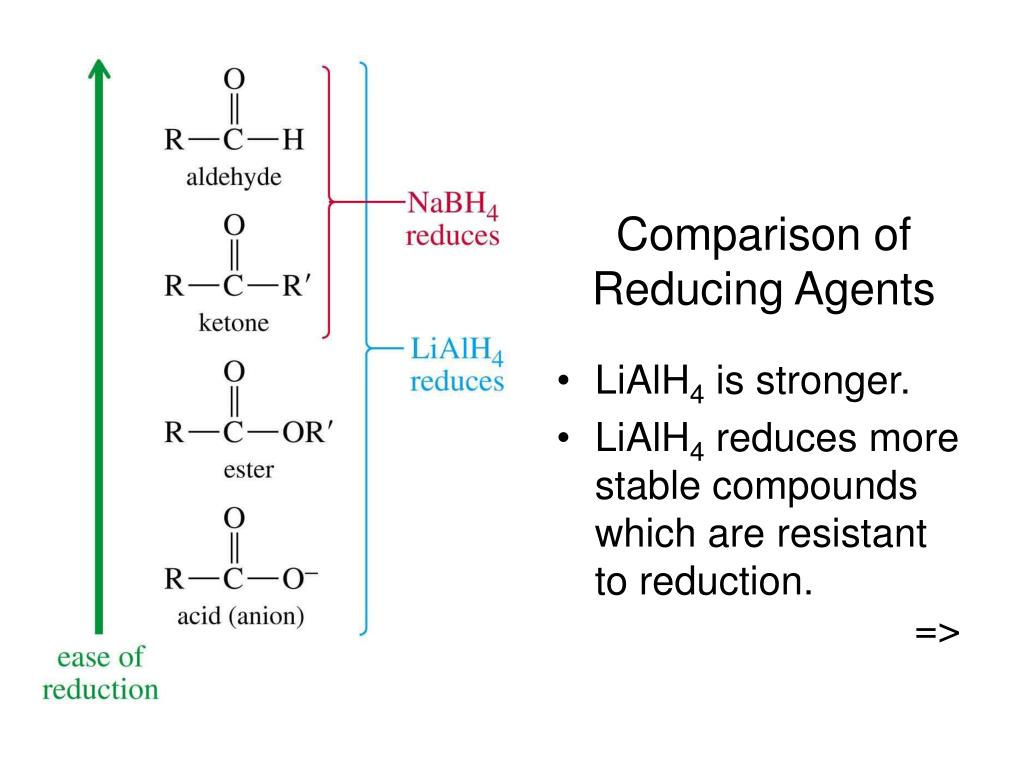
Why is an ester more basic than a ketone?
The alkoxy group can stabilize the positive charge by mesomeric effect and the third resonance form makes full sense. That's why esters are more basic than ketones. The fact that, in a protonated carboxylic acid, the first and third resonance forms are equivalent gives an extra of stabilization.
Are ketones more acidic than carboxylic acids?
Carboxylic acids generally have pKas in the range of 3 - 5, and therefore are weaker acids than hydronium ion (H3O+), but they are stronger acids than other organic acids, such as alcohols (16 - 20), aldehydes and ketones (18 - 22), alkynes (25), benzene (35) or alkanes (50).
Are ketones more acidic than ethers?
However, it is less acidic than that of carbonyl compounds such as ketones. Ethers cannot form hydrogen bonds with each other. This results in lower boiling points because there are no strong interaction forces between its molecules.
Why is alpha hydrogen of ketone more acidic than ester?
The alpha-hydrogen of ketones (pKa = 20) is more acidic as compared to the alpha-hydrogens of esters (pKa = 25). The reason for this is that the ester functional group has free lone pairs on the oxygen which can participate in resonance with carbonyl group.
Why are esters less acidic than aldehydes and ketones?
In the ester, there is also a resonance donation from the alkoxy group towards the carbonyl that competes with the stabilisation of the enolate charge. This makes the ester enolate less stable than those of aldehydes and ketones so esters are even less acidic.
What makes a ketone acidic?
Ketones are those compounds, in which two alkyl or aryl groups are attached with the carbonyl carbon. The hydrogen atoms attached with the alkyl or aryl group is acidic. Due to the presence of this acidic hydrogen, ketones are acidic in nature.
What is the difference between ketone and ester?
A ketone is a molecule that has a carbonyl bonded to carbons. An ester is a molecule that has a carbonyl and alkoxy group bonded together.
What is difference between ketone and ether?
The main difference between ether and ketone is that the functional group of ether is composed of two carbon atoms bonded to the same oxygen atom whereas the functional group of ketone is composed of an oxygen atom bonded to a carbon atom via a double bond.
Are ketones more acidic than alcohols?
Alcohols in general are more acidic than ketones because in aldehydes/ketones, you lose an alpha H to make a carbanion, which is more unstable than a negative charge residing on a more electronegative O in alcohols. First ketones are not acidic.
Which is more acidic ketone or aldehyde?
Which is more acidic aldehyde or ketone? Compared with the alkyl groups of ketones, aldehydes are more acidic (lower pKa) than ketones due to the lower electron donating effect of protons.
Which is more acidic carboxylic acid or ester?
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than esters because acidic strength depends upon the stability of the conjugate base. Carboxylic acids have a more stable conjugate base than esters.
Why is the alpha hydrogen more acidic?
In a carbonyl group, the oxygen is extremely electronegative and it attracts the electron cloud towards itself developing a partial positive charge on the α-carbon. To reduce the positive charge, α-carbon looses its hydrogen readily and makes it acidic in nature.
Are ketones more acidic than aldehydes?
In most academic courses you'd learn that aldehydes are more acidic (lower pKa) than ketones due to the lower electron donating effect of the proton compared to the alkyl group of the ketone.
Are alcohols more acidic than carboxylic acids?
A carboxylic acid is, therefore, a much stronger acid than the corresponding alcohol, because, when it loses its proton, a more stable ion results. Some atoms or groups, when attached to a carbon, are electron-withdrawing, as compared with a hydrogen atom in the same position.
Are ketones acidic basic or neutral?
Ketones are also weak bases, undergoing protonation on the carbonyl oxygen in the presence of Brønsted acids.
Which is more acidic alcohol or ketone?
Alcohols in general are more acidic than ketones because in aldehydes/ketones, you lose an alpha H to make a carbanion, which is more unstable than a negative charge residing on a more electronegative O in alcohols. First ketones are not acidic.
Which resonance structure removes the positive charge from the carbonyl carbon?
Both the ketone and ester have a resonance structure that places positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, however you can also draw a third resonance structure for the ester that removes some of the positive charge from the carbonyl carbon and places it on the ester oxygen.
Does Martin's resonance approach yield the correct order of reactivity?
While the resonance approach may not be rigorous, it does yield the correct order of reactivity and allows the user to make predictions while only using pencil and paper.
Is ester carbonyl positive or negative?
This makes the ester carbonyl carbon less positive (more negative, more nucleophilic, less prone to attack by a nucleophile) than the ketone carbonyl carbon (more positive, less nucleophilic, more prone to attack by a nucleophile).
Is carbonyl a nucleophile?
The este r carbonyl carbon is a stronger nucleophile and less prone to nucleophilic attack than the carbonyl carbon in a keto ne. I think you are trying to understand why the carbonyl in a ketone typically reacts faster with a nucleophile than the carbonyl in an ester. Look at the resonance structures drawn below.
Is ester a nucleophile?
I guess the ester is a weaker nucleophile because it does have an additional oxygen atom, unlike the ketone, that is pulling electrons from the C-O double bond towards the carbon atom (this happens vice versa too of course with the ester oxygen). This lowers the ionic character of the C-O double bond ...
Is LUMO more accessible than ester?
So the LUMO of the ketone will be more accessible compared to the ester (smaller energy difference). Another important fact is, that the ester is much more rigid than the ketone as it has one low lying MO that spans the O = C − O moiety (MO20), which is obviously not present (as it cannot be) in the ketone (MO18).
Is ester more rigid than ketone?
Another important fact is, that the ester is much more rigid than the ketone as it has one low lying MO that spans the O = C − O moiety (MO20), which is obviously not present (as it cannot be) in the ketone ( MO18). You can also see, that the π contribution of carbon in the ketone is lower.
What is the difference between ester and ketone?
A ketone has a molecular structure that includes a carbonyl bonded to carbons while an ester has a molecular structure in which a carbonyl is bonded to an alkoxy group.
Which has more reactivity, esters or ketones?
Ketones have more reactivity while esters have less reactivity.
What is Ester?
An ester is a molecule which has a carbonyl group and is a molecule in which the hydroxyl has been replaced by a group that is known as an alkoxy (an oxygen atom and an alkyl group).
Why do ketones have a high reactivity?
This is due to the very polar nature of the carbonyl group which in turn gives the molecule a partial positive charge. This means that other substances are often attracted to the molecule with which they then readily react. In fact, nucleophilic addition and oxidation and reduction reactions are common.
What are the molecules that can be used as solvents?
Both ketones and esters are molecules that can be used as solvents in certain situations.
What are some examples of ketones?
There are many examples of ketones including acetone, phenylethanone, and propanone. Ketones form the basis for the production of many useful products in industry. For example, they are often used to make various solvents such as acetone that is widely used as a nail polish remover due to its properties as an excellent solvent. Ketones can also be used to strip paints and lacquers and even to make explosives and are often used in the tanning industry.
How are esters formed?
Formation: Esters can be formed from alcohols, carboxylic acids and certain of the inorganic acids such as nitric acid or phosphoric acid. The process in which carboxylic acid reacts with water in the presence of some type of acid in the presence of heat to form an ester is known as esterification.
Why are ketones acidic?
Ketones are acidic compound (pka =20). To explain the acidity of ketone, the definition of acid-base (Bronsted-Lowry Scheme) will be remembered that an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. After dissociation of an acid, conjugate base and H+ ion will be generated.
Are ketones acidic in water?
The pka value of water and ketone is 16 and 20 respectively. Pka value indicates water as more acidic than ketone (substance having lower pka is more acidic).
Are ketones more acidic than carboxylic acids?
No, ketones are not more acidic than carboxylic acid. The pka value of ketone and carboxylic acid is 20 and 3-5 respectively.
Are ketones more acidic than esters?
Yes, ketones are more acidic than ester. Pka value confirms the more acidic nature of ketone with respect to ester. The pka value of ketone and ester is nearly equals to 20 and 25 respectively.
Are ketones more acidic than aldehydes?
No, ketones are less acidic than an aldehyde. Pka of an aldehyde and ketone is 17 and 20 respectively. As lower pka value indicates more acidity, aldehyde is more acidic with respect to ketone.
Why are ketones more acidic than alkanes?
The C-H bond of a ketone is more acidic than the C-H bond of an alkane because the pka value of ketone and alkene is approximately 20 and 50 respectively.
Why are esters more acidic than ketones?from chemistry.stackexchange.com
Esters are more acidic than ketones, because the resonance between the two oxygen atoms gives less opportunity for the delocalization of the electron pair on the alpha carbon in esters contrary to what happens in ketones. But, in esters, when the resonance happens between the two oxygen atoms, the oxygen atom gains a positive charge which is highly ...
What is the difference between ester and ketone?from differencebetween.net
A ketone has a molecular structure that includes a carbonyl bonded to carbons while an ester has a molecular structure in which a carbonyl is bonded to an alkoxy group.
What is Ester?from differencebetween.net
An ester is a molecule which has a carbonyl group and is a molecule in which the hydroxyl has been replaced by a group that is known as an alkoxy (an oxygen atom and an alkyl group).
What are ketones used for?from differencebetween.net
Ketones have many uses including as solvents such as nail polish removers and paint and lacquer removers, and they can be used to produce explosives and in the tanning industry. Esters also have several uses including as solvents, dyes, as additives in gasoline and to make Mylar film and Plexiglas.
Why do ketones have a high reactivity?from differencebetween.net
This is due to the very polar nature of the carbonyl group which in turn gives the molecule a partial positive charge. This means that other substances are often attracted to the molecule with which they then readily react. In fact, nucleophilic addition and oxidation and reduction reactions are common.
What are some examples of ketones?from differencebetween.net
There are many examples of ketones including acetone, phenylethanone, and propanone. Ketones form the basis for the production of many useful products in industry. For example, they are often used to make various solvents such as acetone that is widely used as a nail polish remover due to its properties as an excellent solvent. Ketones can also be used to strip paints and lacquers and even to make explosives and are often used in the tanning industry.
How are esters formed?from differencebetween.net
Formation: Esters can be formed from alcohols, carboxylic acids and certain of the inorganic acids such as nitric acid or phosphoric acid. The process in which carboxylic acid reacts with water in the presence of some type of acid in the presence of heat to form an ester is known as esterification.