In the further 6% of individuals the spinal cord can extend to the L2-L3 interspace. Therefore a lumbar puncture is generally performed at or below the L3-L4 interspace. As a general anatomical rule, the line drawn between the posterior iliac crests often corresponds closely to the level of L3-L4.
What is a lumbar puncture?
Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine.
Why is a spinal tap usually done between L3 and L4?
If the spinal cord (and consequently, the CSF) runs until the first lumbar vertebra, then why is a spinal tap usually done between L3 and L4? It’s done at that level because CSF can be drawn from there without risk of injury to the spinal cord.
Is a lumbar puncture (LP) Safe?
In experienced hands, a lumbar puncture is a relatively safe procedure. Proper positioning of the patient is extremely important. The patient is asked to lie on their side, with their back toward the examiner and then curl into a ball.
How is the interspace selected for a lumbar puncture?
The interspace is selected after palpation of the spinous processes at each lumbar level. Once the area for needle insertion has been ascertained, the examiner puts on a mask and sterile gloves – this decreases the risk of infection.
At what level lumbar puncture is done and why?
In approximately 94% of individuals the spinal cord terminates at the level of the L1 vertebrae. In the further 6% of individuals the spinal cord can extend to the L2-L3 interspace. Therefore a lumbar puncture is generally performed at or below the L3-L4 interspace.
Where is the ideal location for lumbar puncture?
It's performed in your lower back, in the lumbar region. During a lumbar puncture, a needle is inserted into the space between two lumbar bones (vertebrae) to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. This is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord to protect them from injury.
What spinal level is the safest place to perform a spinal tap?
A needle is placed in the subarachnoid space at the level of the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebra to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid.
Why is it important to insert the needle at the vertebral level of L3 as opposed to higher levels?
In spinal anesthesia, a needle is generally inserted to the L3-4 intervertebral space or under in order to minimize the danger of spinal cord damage by the needle. Therefore, it is very important to precisely measure the vertebral level. Tuffier's line is a transverse line connecting the tops of the iliac crests.
How do you know if its L3 or L4?
Wearing nonsterile gloves, locate the L3-L4 interspace by palpating the right and left posterior superior iliac crests and moving the fingers medially toward the spine (see the image below). Palpate that interspace (L3-L4), the interspace above (L2-L3), and the interspace below (L4-L5) to find the widest space.
Why is the lumbar puncture performed in the lower lumbar area of the vertebral column?
A lumbar puncture (LP) or spinal tap may be done to diagnose or treat a condition. For this procedure, your healthcare provider inserts a hollow needle into the space surrounding the spinal column (subarachnoid space) in the lower back to withdraw some cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or inject medicine.
At what level is a spinal tap performed to prevent damage to the spinal cord quizlet?
Because the spinal cord ends at the bottom of L1 or the top of L2, L4 is a safe level for inserting a needle. Remember, in the lumbar region, spinal nerves exit below the vertebra with the same number.
Why Is spinal tap performed below L2?
The spinal cord continues below L2 down into the sacrum as many separate strands of nerve pathways, the cordae equina, bathed in CSF. Putting a needle into the spaces between the strands to collect fluid is much safer than taking the risk of hitting the solid cord higher up the spine.
Where is the needle usually inserted to avoid spinal cord damage?
In lumbar puncture (LP), a needle is inserted into the lumbar subarachnoid space to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for laboratory testing, to measure CSF pressure, and sometimes to give intrathecal diagnostic or therapeutic agents.
Where in the vertebral column is a lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine.
Why is a lumbar puncture done in the median plane?
A 22-gauge spinal needle is most commonly used in adults. Hold the needle between both the thumbs and index fingers, insert a spinal needle with a stylet in the midline and within the median plane. Staying in the median plane will help avoid damage to the nerve roots.
What is lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture = spinal tap is quite stressful, but if expertly done causes not much pain, docs nowadays first numb the skin where the puncture is taking place. The aim is to obtain cerebro-spinal fluid, so a needle is advanced into the spinal space:
What is the L4 and L5 disc?
We don’t know if your L4 and L5 disc problem is a bulging disc, herniated disc or spinal stenosis. Although it really doesn’t matter if you want to end the pain. Most disc abnormalities are treated medically with pain management. These treatments can include chiropractic, physical therapy, surgery and/or pain drugs.
Why is it important to avoid a spinal cord puncture?
Short answer: because traditionally it is considered an easy space to identify, and safely below the level where the spinal cord ends. The detailed answer, of course, is not so simple. The important point is that you want to avoid skewering the spinal cord with your lumbar puncture (LP) needle, as this could lead to permanent neurological damage. ...
What is the sac of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord sits in a sac of fluid (the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, that you are aiming to sample with your LP). It ends - in the average adult at around L1 - by breaking up into a loose ‘whisk’ of nerve roots, called the cauda equina (Latin for ‘horse’s tail’).
What is the name of the nerve that ends at L1?
It ends - in the average adult at around L1 - by breaking up into a loose ‘whisk’ of nerve roots, called the cauda equina (Latin for ‘. Short answer: because traditionally it is considered an easy space to identify, and safely below the level where the spinal cord ends. The detailed answer, of course, is not so simple.
Can you skewer your spinal cord with a lumbar puncture needle?
The detailed answer, of course, is not so simple. The important point is that you want to avoid skewering the spinal cord with your lumbar puncture (LP) needle, as this could lead to permanent neurological damage.
Is lumbar puncture painful?
The procedure is extremely painful and that seems like a logical solution. I'm sure the answer is complex - I'm just curious. A lumbar puncture = spinal tap is quite stressful, but if expertly done causes not much pain, docs nowadays first numb the skin where the puncture is taking place.
What position is a lumbar puncture performed in?
A lumbar puncture can be performed in two positions: Lateral recumbent. Patient on his or her side with head propped up on a single pillow to keep spine straight. Knees & torso flexed to optimise interlaminar foramen of vertebrae. Ask or use assistant to draw patient’s legs up to their chest.
Where do you place your thumbs for lumbar puncture?
Anatomy in lumbar puncture (LP) Place palms of hands over PSIS so that superior edge is under your index finger. Your thumbs will connect at, or point to, the approximate location of the L4 vertebrae.
How to advance needle in umbilicus?
Advance needle slowly in direction of umbilicus with bevel facing upwards (towards the ceiling) if patient in lateral position. Advance slowly through spinous ligament resistance until you feel some give (sometimes described as a “pop”) with change in resistance as needle enters subarachnoid space.
How long to wait to do LP for subarachnoid haemorrhage?
Check for allergies to latex, betadine, lignocaine or other medications. If doing the LP for possible subarachnoid haemorrhage, ensure 12 hours have passed since the onset of symptoms. Document informed consent (written if possible) Infection, bleeding, failure, pain.
Where to place hands over PSIS?
Place palms of hands over PSIS so that superior edge is under your index finger. Your thumbs will connect at, or point to, the approximate location of the L4 vertebrae. Skin; supraspinous ligaments; interspinous ligaments; ligamentum flavum; epidural space; dura; subarachnoid membrane into subarachnoid space.
Can you inject lignocaine into a spinal canal?
Always check for entrance to blood vessel prior to injection of lignocaine & never inject into spinal canal. Wait a few minutes for lignocaine to work. During this time do a final check of your equipment and make sure you have an assistant to help with bottles. Insert spinal needle.
What is the purpose of lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture can also be used to detect whether someone has 'Stage 1' or 'Stage 2' Trypanosoma brucei.
Why do we need a lumbar puncture?
The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine.
What does it mean when your CSF is low?
Decreased CSF pressure can indicate complete subarachnoid blockage, leakage of spinal fluid, severe dehydration, hyperosmolality, or circulatory collapse.
What is a hypodermic needle?
A hypodermic needle is used to access the subarachnoid space and collect fluid. Fluid may be sent for biochemical, microbiological, and cytological analysis. Using ultrasound to landmark may increase success. Lumbar puncture was first introduced in 1891 by the German physician Heinrich Quincke .
What is the position of the patient during lumbar puncture?
The person is usually placed on their side (left more commonly than right). The patient bends the neck so the chin is close to the chest, hunches the back, and brings knees toward the chest. This approximates a fetal position as much as possible.
What is the presence of white blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid?
The presence of white blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid is called pleocytosis. A small number of monocytes can be normal; the presence of granulocytes is always an abnormal finding. A large number of granulocytes often heralds bacterial meningitis. White cells can also indicate reaction to repeated lumbar punctures, reactions to prior injections of medicines or dyes, central nervous system hemorrhage, leukemia, recent epileptic seizure, or a metastatic tumor. When peripheral blood contaminates the withdrawn CSF, a common procedural complication, white blood cells will be present along with erythrocytes, and their ratio will be the same as that in the peripheral blood.
Why is it difficult to assess when a needle passes through the ligamentum flavum?
Therefore, it is difficult to assess when the needle passes through them into the subarachnoid space because the characteristic "pop" or "give" may be subtle or nonexistent in the pediatric lumbar puncture.
What is lumbar puncture?
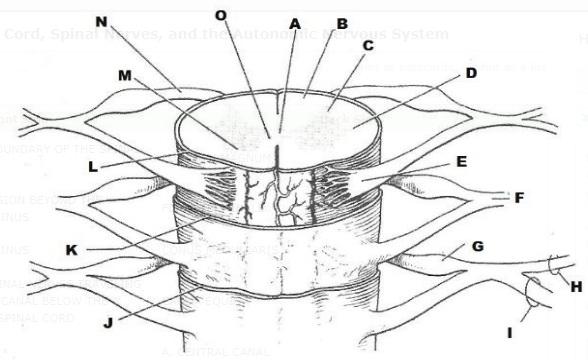
A lumbar puncture is a puncture into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for clinical investigation, to remove excess fluid or to inject medication. Anatomy. The three coverings of the brain and spinal cord, known as the meninges, are separated by small spaces. The outer meninx, the dura mater, is the ...
How long should a patient stay flat after lumbar puncture?
The patient should remain flat for six to 12 hours because headache, which is common after lumbar puncture, is aggravated by sitting up.
What holds the spinal cord together?
The spinal vertebrae are held together by ligaments. Those penetrated in a lumbar puncture are the interspinous ligaments (which bind adjacent spinous processes together) and the ligamentum flavum (which binds adjacent vertebral laminae together and, in so doing, lines the posterior wall of the spinal canal).
How long should I drink after a lumbar puncture?
This must be maintained for up to 24 hours afterwards, depending on the patient’s condition and local policy procedures. Patients should be well-hydrated for myelograms and standard lumbar punctures, and should be encouraged to drink well before and after the procedures. CSF findings.
Why is there turbidity in CSF?
Lumbar punctures are carried out to isolate the organism involved in meningitis, and to give intrathecal antibiotics. Fresh blood may be visible in CSF because of bleeding at the puncture site.
Which layer of the brain is the delicate and vascular pia mater?
The innermost third layer, which rests on the brain surface, is the delicate and vascular pia mater (Fig 1). Cerebrospinal fluid. The CSF in the subarachnoid space is produced in the third and fourth ventricles of the brain and then passes via canals to the subarachnoid space.
Is it safe to put a needle in the sacrum?
The spinal cord continues below L2 down into the sacrum as many separate strands of nerve pathways, the cordae equina, bathed in CSF. Putting a needle into the spaces between the strands to collect fluid is much safer than taking the risk of hitting the solid cord higher up the spine.
What is lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture is a procedure that is used to examine the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The cerebrospinal fluid is the fluid which circulates around the brain and membranes around the brain and spinal cord (the meninges).
What interspace is a lumbar puncture?
Therefore a lumbar puncture is generally performed at or below the L3-L4 interspace. As a general anatomical rule, the line drawn between the posterior iliac crests often corresponds closely to the level of L3-L4.
How long before lumbar puncture needle?
The lumbar puncture needle is typically a 20 – 22 gauge needle and it is inserted into the target area and slowly advanced. The bevel of the needle is maintained in ...
Is lumbar puncture surgery safe?
To begin with the procedure is usually carefully explained to the patient, including the risks and benefits. In experienced hands, a lumbar puncture is a relatively safe procedure. Proper positioning of the patient is extremely important.
How to perform lumbar puncture?
Lumbar puncture may be performed with the child lying on their side or sitting up. Position back and bottom close to edge of bed. Aim for maximum flexion of spine (curl into foetal position), but avoid over-flexing neck, especially in infants, as this may cause respiratory compromise.
When should lumbar puncture be performed?
Key points. A lumbar puncture (LP) should only be performed after a thorough neurological examination and once all contraindications have been considered. Careful preparation, adequate analgesia and an experienced assistant are critical to success.
What to do if CSF is not flowing?
If CSF is not flowing: replace the stylet and advance (or withdraw and reposition) the needle slightly, then re-check for CSF. it is possible to reposition and reangle needle multiple times, each time reviewing patient and needle position. multiple attempts may lead to local swelling and bruising.
What needle should I use for a headache?
Use a 22 or 25 gauge bevelled spinal needle with stylet (the use of needles without a stylet has an associated rare risk of spinal epidermoid tumours) Consider using 25 gauge pencil point needles for older children/adolescents to reduce the risk of headache; evidence is not convincing in younger children.

Overview
Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine. Examples of these conditions include meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage. It may also be used therapeutically in some conditions. Increased intr…
Medical uses
The reason for a lumbar puncture may be to make a diagnosis or to treat a disease.
The chief diagnostic indications of lumbar puncture are for collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Analysis of CSF may exclude infectious, inflammatory, and neoplastic diseases affecting the central nervous system. The most common purpose is in suspected meningitis, since there is no other reliable tool with which meningitis, a life-threatening but highly treatable condition, can be …
Contraindications
Lumbar puncture should not be performed in the following situations:
• Idiopathic (unidentified cause) increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
• Bleeding diathesis (relative)
• Infections
Adverse effects
Post spinal headache with nausea is the most common complication; it often responds to pain medications and infusion of fluids. It was long taught that this complication can be prevented by strict maintenance of a supine posture for two hours after the successful puncture; this has not been borne out in modern studies involving large numbers of people. Doing the procedure with the person on their side might decrease the risk. Intravenous caffeine injection is often quite effecti…
Technique
The brain and spinal cord are enveloped by a layer of cerebrospinal fluid, 125–150 ml in total (in adults) which acts as a shock absorber and provides a medium for the transfer of nutrients and waste products. The majority is produced by the choroid plexus in the brain and circulates from there to other areas, before being reabsorbed into the circulation (predominantly by the arachnoid granulations).
Interpretation
Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid generally includes a cell count and determination of the glucose and protein concentrations. The other analytical studies of cerebrospinal fluid are conducted according to the diagnostic suspicion.
Increased CSF pressure can indicate congestive heart failure, cerebral edema, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hypo-osmolality resulting from hemodialysis, meningeal inflammation, purulent me…
History
The first technique for accessing the dural space was described by the London physician Walter Essex Wynter. In 1889 he developed a crude cut down with cannulation in four patients with tuberculous meningitis. The main purpose was the treatment of raised intracranial pressure rather than for diagnosis. The technique for needle lumbar puncture was then introduced by the German physician Heinrich Quincke, who credits Wynter with the earlier discovery; he first reported his ex…
Further reading
• Ellenby, MS; Tegtmeyer, K; Lai, S; Braner, DA (28 September 2006). "Lumbar puncture". Videos in clinical medicine. The New England Journal of Medicine. 355 (13): e12. doi:10.1056/NEJMvcm054952. PMID 17005943.