Active transport is important because it allows the cell to move substances against the concentration gradient. What is the purpose of active transport? Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. Active transport powered by adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of i…
Why does active transport require the use of ATP?
The utilization of energy by a cell is required in order to transport substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient. Active transport systems perform precisely this function, burning energy (typically in the form of ATP) in order to maintain the proper concentrations of ions and molecules in living organisms.
What are facts about active transport?
Fun Facts about Active Transport
- Moving molecules through the cell membrane takes them through any of the 3 main protein ports. ...
- We mentioned on type of active transport, but there are actually two others. ...
- Sodium-Potassium pump, there is the Exocytosis, and the Endocytosis.
Why does active transport need energy?
Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid, the cell must use energy to move the substance.
What is the importance of active transport in living organisms?
Active transport is a very important process enabling cells to accumulate molecules or ions from the environment against the concentration gradient.Conversely, contents of cells heavily loaded with electrolytes or metabolic products can be excreted against the concentration gradient.

Why is active transport important example?
Active transport always leads to accumulation of molecules are ions towards one side of the membrane. This mode of transportation in plants is carried out by membrane proteins and transports the substance from the lower concentration to higher concentration.
Why is active transport important a level?
Active transport is important in: Reabsorption of useful molecules and ions into the blood after filtration into the kidney tubules. Absorption of some products of digestion from the digestive tract. Loading sugar from the photosynthesising cells of leaves into the phloem tissue for transport around the plant.
Why is active transport important GCSE?
For plants to take up mineral ions, ions are moved into root hairs, where they are in a higher concentration than in the dilute solutions in the soil. Active transport then occurs across the root so that the plant takes in the ions it needs from the soil around it.
What is active transport in biology?
Active transport is the process of moving molecules across a cellular membrane through the use of cellular energy.
Where is active transport used in the body?
The process of active transport takes place in humans during digestion of food in the ileum (small intestine). Once food has been absorbed by the villi after some time the concentration of food molecules inside the villi increases at this point no more food can diffuse in.
What is needed for active transport?
Active transport requires assistance from carrier proteins, which change conformation when ATP hydrolysis occurs.
What is active transport GCSE biology?
Active transport is the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
Why does the active transport require energy?
Active transport requires energy to move substances across a plasma membrane , often because the substances are moving from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, or because of their large size.
What is active transport in physiology?
Active transport is an energy-driven process where membrane proteins transport molecules across cells, mainly classified as either primary or secondary, based on how energy is coupled to fuel these mechanisms.
Why is active transport important to albatrosses?
Active transport is also used in marine birds and reptiles, because they consume large amounts of salt when they drink water, and as the kidneys cannot get rid of it all, they have salt glands which use active transport.
Why does active transport of molecules across a membrane require ATP?
To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell must use energy. Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells.
How is ATP used in active transport a level biology?
Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. The primary active transport system uses ATP to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second substance is moved out of the cell.
What Are the Benefits of Active Transportation?
Active transportation offers the promise of improving the health of our people and the places they live.
How does active transportation work?
Active transportation works for all kinds of communities, from small rural towns to urban centers. With the creation of walking and bicycling networks linking home, work, school, shopping, transit and recreation destinations at a fraction of the cost of comparable roads, these gains will grow rapidly.
How did the interstate highway system affect the rise of obesity?
The building of the interstate highway system between 1956 and 1991 contributed to a steady decline in walking and biking as our communities were designed around the automobile. The resulting lack of transportation choices continues to contribute to troubling levels of physical inactivity that are a key factor in the rise of many chronic diseases and America’s obesity epidemic.
How much does obesity cost?
Two-thirds of American adults, and nearly one-third of children, are now considered overweight or obese, with obesity-related health care costs now estimated at $160 billion per year. Investments in active transportation networks will help to combat the obesity epidemic by making it easier to build routine physical activity into our daily lives.
How can we build out the neglected part of our transportation networks?
Through cost-effective investments, we can build out the neglected part of our transportation networks by creating “active transportation systems” that connect homes, workplaces, schools, shops and recreation. For pennies on the dollar, we can create seamless networks of trails, sidewalks and cycle tracks that can give all Americans the choice of mobility without driving, especially when connected to public transportation.
What is the MAP-21 program?
In June 2012, the U.S. Congress passed a federal transportation bill, “Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century” (MAP-21) that reduced dedicated federal funding for active transportation by at least 30 percent, consolidated three core programs that support active transportation into a single Transportation Alternatives program, and changed the rules to grant states more control over whether and how to fund active transportation.
What is the Fast Act?
The Federal Government and Active Transportation. With the recent passage of the federal transportation reauthorization bill (the “FAST Act”), active transportation saw a marginal increase in funding—a victory in a contentious political climate, but at a level insufficient to meet growing demand.
What is the Difference Between Active Transport and Passive Transport?
Active transport moves substances from a region of lower concentration to a higher concentration, i. e., against the concentration gradient. There is an energy requirement for this process, as it does not occur naturally in the absence of active forces.
How does folding of the cell membrane work?
The folding of the cell membrane is accomplished in a mechanism similar to the antiport transport of potassium and sodium ions. Molecules of ATP bind to proteins in the cell membrane, causing them to change their shape. The conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of the cell membrane until a vesicle is created.
What is the name of the channel that binds to the molecule it is supposed to transport?
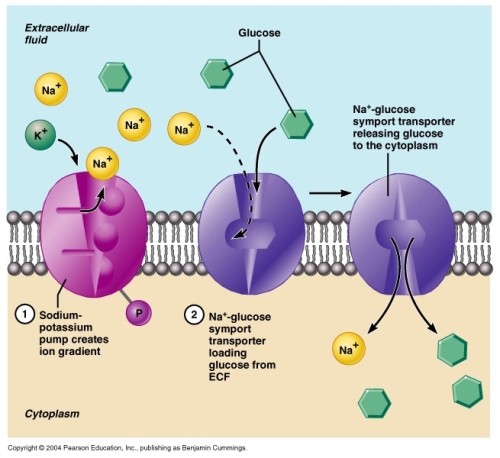
For example, one type of active transport channel in the cell membrane will bind to the molecule it is supposed to transport – such as a sodium ion – and hold onto it until a molecule of ATP comes along and binds to the protein. The energy stored in ATP then allows the channel to change shape, spitting the sodium ion out on the opposite side of the cell membrane. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called “primary” active transport.
How does active transport occur?
In exocytosis, a cell moves something outside of itself in large quantities by wrapping it in a membrane called a vesicle and “spitting out” the vesicle. In endocytosis, a cell “eats” something by wrapping and re-forming its membrane around the substance or item.
Why are antiport pumps so efficient?
These pumps are extremely efficient because many of them can use one ATP molecule to fuel these two different tasks. One important type of antiport pump is the sodium-potassium pump, which is discussed in more detail under “Examples of Active Transport.”.
Why is sodium important in the body?
It represents an important method of sugar transport in the body, required to provide energy for cellular respiration. The natural diffusion of sodium ions inside the cell facilitates the movement of glucose into the cell. Glucose can be carried into the cell with the sodium without the transport protein expending ATP.
What is the energy stored in ATP?
The energy stored in ATP then allows the channel to change shape, spitting the sodium ion out on the opposite side of the cell membrane. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called “primary” active transport. Another type of active transport is “secondary” active transport. In this type of active transport, ...
Why is facilitated diffusion important?
Facilitated diffusion is needed to move substances that are too large to move through the spaces between the phospholipids of the cell membrane.Facilitated diffusion also allows for the passage of ionic, hydrophilic, and/or polar molecules that can't diffusion on their own ...
How does active transport work?
Most cells maintain a large concentration difference of potassium, sodium, and calcium ions. This gradient concentration difference is produced by active transport. Active transport pushes substances against a concentration gradient. This means that the substances move from a lower to a higher concentration. In order to counter the forces of diffusion and osmosis, work must be done. Thus, active transport requires the use of energy in the form of ATP. An example of active transport in the body is the sodium-potassium pump, which helps the heart function properly.
What is facilitated transport?
Active and facilitated transport are both means of moving substances into and out of the cell. Unlike passive diffusion, active and facilitated transport both utilize a protein through which substances travel. Facilitated diffusion is like passive diffusion in that substances move down a concentration gradient.
How does active transport produce a concentration difference?
Most cells maintain a large concentration difference of potassium, sodium, and calcium ions. This gradient concentration difference is produced by active transport. Active transport pushes substances against a concentration gradient. This means that the substances move from a lower to a higher concentration.
What is a certified educator?
Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What Is Active Transportation?
What Are The Benefits of Active Transportation?
- Active transportation offers the promise of improving the health of our people and the places they live. 1. Healthy People: America faces an obesity crisis, with more than two-thirds of American adults either overweight or obese. By making walking and biking safe and convenient, we can make it much easier for people to build routine physical activi...
The Federal Government and Active Transportation
- With the recent passage of the federal transportation reauthorization bill (the “FAST Act”), active transportation saw a marginal increase in funding—a victory in a contentious political climate, but at a level insufficient to meet growing demand. The recent Congressional debate spawned new champions for active transportation, but also revealed that unfortunately there are still decision-…
Making The Case
- It Doesn't Have to Be This Way
By designing our communities to prioritize the rapid movement of automobiles, we have created places where it is difficult—even dangerous—for people to walk or bicycle. Creating a more balanced transportation system through cost-effective investments in active transportation syst… - The Case for Active Transportation: Healthy Places
Whether a place is a small town, urban or suburban, increased public investment in active transportation is an essential ingredient in creating an economically healthy, vibrant 21st century community.