
The reason WHY we use after-tax cost of debt in calculating the WACC
Weighted average cost of capital
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. The WACC is commonly referred to as the firm’s cost of capital. Importantly, it is dictated by the external market and not by management.
What is the difference between WACC and cost of capital?
Jan 13, 2020 · The reason WHY we use after-tax cost of debt in calculating the WACC because we are interested in maximizing the value of the firm ' s stock, and the stock price depends on after-tax cash flows NOT before-tax cash flows. That is why we adjust the interest rate downward due to debt ' s preferential tax treatment. Click to see full answer.
What happens to WACC when you increase debt?
This is why Rd (1 – corporate tax rate) is used to calculate the after-tax cost of debt.2 . Does WACC use after-tax cost of debt? WACC is the average after-tax cost of a company’s various capital sources, including common stock, preferred stock, bonds, and any other long-term debt.
How to use WACC to value a company?
Dec 04, 2021 · Yield to maturity equals the internal rate of return of the debt, i.e. it is the discount rate that causes the debt cash flows (i.e. coupon and principal payments) to equal the market price of the debt. To calculate the after-tax cost of debt, subtract a company’s effective tax rate from 1, and multiply the difference by its cost of debt.
Is a high WACC good or bad?
Mar 24, 2020 · The reason WHY we use after-tax cost of debt in calculating the WACC because we are interested in maximizing the value of the firm ' s stock, and the stock price depends on after-tax cash flows NOT before-tax cash flows. That is why we adjust the interest rate downward due to debt ' s preferential tax treatment. One may also ask, what does after tax cost …
Does WACC use after-tax cost of debt?
After-tax cost of debt is the net cost of debt determined by adjusting the gross cost of debt for its tax benefits. It equals pre-tax cost of debt multiplied by (1 – tax rate). It is the cost of debt that is included in calculation of weighted average cost of capital (WACC).Apr 9, 2019
Why do we use the weighted after-tax cost of debt but we do not do the same for cost of equities?
Why do we use aftertax figure for cost of debt but not for cost of equity? -Interest expense is tax-deductible. There is no difference between pretax and aftertax equity costs. How do you determine the appropriate cost of debt for a company?
What is the after-tax equation for the WACC?
0:072:14WACC Example 1 finding after tax WACC - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe need to use after-tax cost of debt not pre-tax cost of debt. Which is pre-tax cost of debtMoreWe need to use after-tax cost of debt not pre-tax cost of debt. Which is pre-tax cost of debt multiplied by one minus tax rate therefore after-tax Wak is weight of debt multiplied.
Why is after-tax cost of debt more relevant?
The after-tax cost of debt is more relevant because it is the actual cost of debt to the company.
What is after-tax cost of debt?
The after-tax cost of debt is the initial cost of debt, adjusted for the effects of the incremental income tax rate. To calculate it, subtract the company's incremental tax rate from 100% and then multiply the result by the interest rate on the debt.Jan 12, 2022
How is WACC pre-tax calculated from post tax WACC?
0:011:19WACC Example 1 finding pre tax WACC - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlus weight of equity multiplied by cost of equity consequently pre-tax Wak is market value of debtMorePlus weight of equity multiplied by cost of equity consequently pre-tax Wak is market value of debt divided by both market value of debt plus.
What is cost of debt in WACC?
The cost of debt is the return that a company provides to its debtholders and creditors. When debtholders invest in a company, they are entering an agreement wherein they are paid periodically or on a fixed schedule. Bond agreements or indentures set up the schedule.
How do you find before tax cost of debt?
If you want to know your pre-tax cost of debt, you use the above method and the following formula cost of debt formula:Total interest / total debt = cost of debt.Effective interest rate * (1 – tax rate)Total interest / total debt = cost of debt.Effective interest rate * (1 – tax rate)Sep 17, 2020
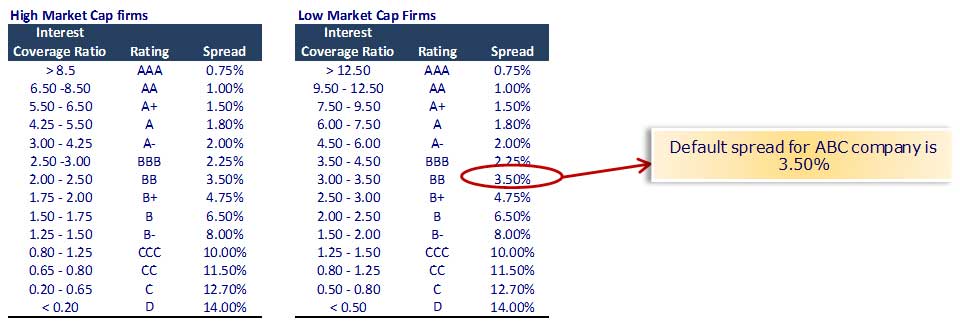
What is premium in lending?
The premium acts as compensation for the additional risk of default with a corporate lender. The size of the premium (default spread) will reflect the debt investor’s perception of the default risk. The higher the perceived risk is, the higher is the demanded premium.
What is the cost of debt?
The cost of debt is the return that a company provides to its debtholders and creditors. When debtholders invest in a company, they are entering an agreement wherein they are paid periodically or on a fixed schedule. Bond agreements or indentures set up the schedule.
Why are stock shares and equity used interchangeably?
due to the set payment schedule (interest payments will not go down during a bad year) but also produce smaller returns (interest payments will not go up during a good year). Due to the added security, required debt returns are lower than those for stock returns.
What is default rate?
Default Rate The default rate is the rate of all loans issued by a lender or financial institution that is left unpaid by the borrower and declared to be. Market Risk Premium.
What is the difference between corporate bonds and Treasury bonds?
Corporate bonds differ from Treasury bonds (government-issued) in the sense that they carry significantly greater default risk. A default happens when a firm fails to pay an interest payment to a bondholder. No matter how financially stable a firm appears, the risk of default is always a possibility.
What is call option?
Call Option A call option, commonly referred to as a "call," is a form of a derivatives contract that gives the call option buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock or other financial instrument at a specific price - the strike price of the option - within a specified time frame. if applicable, and any other relevant factors.
Is debt financing a tax deductible expense?
It provides the additional benefit that interest payments are tax-deductible ( tax shield. Tax Shield A Tax Shield is an allowable deduction from taxable income that results in a reduction of taxes owed.
What sources does Investopedia use?
These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.
Is debt interest tax deductible?
Payments on debt interest are typically tax-deductible, so the acquisition of debt financing can actually lower a company's total tax burden. 1 . The most common utilization of this method is in the calculation of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Does after tax affect the first loan?
Clearly, the after-tax calculation does not affect the original decision to pursue the first loan, as it is still the cheapest option. When comparing the cost of the loan to the cost of equity capital, however, the incorporation of the tax rate can make a world of difference.
Is the first loan cheaper?
Using the pretax definition of cost of capital, it is clear that the first loan is the cheaper option because of its lower interest rate. Depending on the context of the calculation, however, businesses often look at the after-tax cost of debt capital to gauge its impact on the budget more accurately. Payments on debt interest are typically ...
What is the WACC for Walmart in 2021?
Let's calculate the WACC for retail giant Walmart (WMT). In April 2021, the risk-free rate as represented by the annual return on a 20-year treasury bond was 2.21%. 1 Walmart's beta was 0.48 as of April 14, 2021. Meanwhile, the average long-term return of the market is roughly 8%. Using the CAPM, Walmart's cost of equity is 4.99%.
What is the WACC formula?
The WACC formula includes the weighted average cost of equity plus the weighted average cost of debt. Note that, generally, the cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity given that interest expenses are tax-deductible.
How much is Walmart's market cap in 2021?
The market cap for Walmart was $394 billion as of April 14, 2021. The long term debt stood at $44 billion as of the end of fiscal year 2021 and its average cost of debt was 3.9%. 2. The WACC for Walmart is as follows: V = E + D = $394 billion + $44 billion = $438 billion.
What is WACC in finance?
WACC is the average after-tax cost of a company’s various capital sources, including common stock , preferred stock, bonds, and any other long-term debt. In other words, WACC is the average rate a company expects to pay to finance its assets. Companies often run their business using the capital they raise through various sources.
What does lower WACC mean?
Generally, the lower the WACC the better. A lower WACC represents lower risk for a company's operations. The debt portion of the WACC formula represents the cost of capital for company-issued debt. It accounts for interest a company pays on the issued bonds or commercial loans taken from the bank.
Why is WACC not suitable for risky projects?
The WACC is also not suitable for accessing risky projects because to reflect the higher risk the cost of capital will be higher.
What is weighted average cost of capital?
Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is used by analysts and investors to assess an investor's returns on an investment in a company. As the majority of businesses run on borrowed funds, the cost of capital becomes an important parameter in assessing a firm’s potential for net profitability. WACC measures a company’s cost to borrow money, ...
WACC Formula and Calculation
After-Tax Cost of Debt
- One of the chief advantages of debt financing is that interest payments can often be deducted from an organization's taxes, while returns for equity traders, dividends or rising stock prices, o...
Things to Know Before You Refinance Your Mortgage
- To calculate the cost of capital, the cost of equity and cost of debt must be weighted after which added collectively. The cost of capital is mostly calculated utilizing the weighted average cost of capital. The capital asset pricing model, however, can be used on any inventory, even if the company does not pay dividends. The principle suggests the price of equity relies on the invento…