What is the purpose of analysis of variance ANOVA )?
ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance. It's a statistical test that was developed by Ronald Fisher in 1918 and has been in use ever since. Put simply, ANOVA tells you if there are any statistical differences between the means of three or more independent groups. One-way ANOVA is the most basic form.
Why ANOVA is called analysis of variance instead of analysis of means?
It may seem odd that the technique is called "Analysis of Variance" rather than "Analysis of Means." As you will see, the name is appropriate because inferences about means are made by analyzing variance. ANOVA is used to test general rather than specific differences among means. This can be seen best by example.
Is ANOVA for mean or variance?
ANOVA stands for analysis of variance. It is used to compare the mean between several groups. We use a test of variance (Fisher) for ANOVA.
Which test is used in analysis of variance?
An ANOVA test is a type of statistical test used to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between two or more categorical groups by testing for differences of means using variance.
Why would we use Analysis of Variance to compare groups rather than multiple t-tests?
Why would we use analysis of variance to compare groups, rather than multiple t-tests? Correta - We retain statistical power. 2. You research the growth rates of plants with three different types of light source.
What is ANOVA simple explanation?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical technique that is used to check if the means of two or more groups are significantly different from each other. ANOVA checks the impact of one or more factors by comparing the means of different samples.
When should I use ANOVA?
Use a one-way ANOVA when you have collected data about one categorical independent variable and one quantitative dependent variable. The independent variable should have at least three levels (i.e. at least three different groups or categories).
How do you find ANOVA Analysis of Variance?
Steps for Using ANOVAStep 1: Compute the Variance Between. First, the sum of squares (SS) between is computed: ... Step 2: Compute the Variance Within. Again, first compute the sum of squares within. ... Step 3: Compute the Ratio of Variance Between and Variance Within. This is called the F-ratio.
What type of data are best Analysed in ANOVA?
A common use of the method is the analysis of experimental data. so experimental type of data are best analyzedby ANOVA.
What are the four assumptions of ANOVA?
The factorial ANOVA has a several assumptions that need to be fulfilled – (1) interval data of the dependent variable, (2) normality, (3) homoscedasticity, and (4) no multicollinearity.
Why is ANOVA better than multiple t tests?
Two-way anova would be better than multiple t-tests for two reasons: (a) the within-cell variation will likely be smaller in the two-way design (since the t-test ignores the 2nd factor and interaction as sources of variation for the DV); and (b) the two-way design allows for test of interaction of the two factors ( ...
What are the assumptions of analysis of variance?
When we model data using 1-way fixed-effects ANOVA, we make 4 assumptions: (1) individual observations are mutually independent; (2) the data adhere to an additive statistical model comprising fixed effects and random errors; (3) the random errors are normally distributed; and (4) the random errors have homogenous ...
What are the assumptions of analysis of variance?
When we model data using 1-way fixed-effects ANOVA, we make 4 assumptions: (1) individual observations are mutually independent; (2) the data adhere to an additive statistical model comprising fixed effects and random errors; (3) the random errors are normally distributed; and (4) the random errors have homogenous ...
What is the difference between ANOVA and t-test?
The t-test is a method that determines whether two populations are statistically different from each other, whereas ANOVA determines whether three or more populations are statistically different from each other.
What is the difference between ANOVA and chi square?
The chi-square is used to investigate whether the distribution of classes and is compatible with a distribution model (often equal distribution, but not always), while ANOVA is used to investigate whether differences in means between samples are significant or not.
Why is ANOVA better than multiple t tests?
Two-way anova would be better than multiple t-tests for two reasons: (a) the within-cell variation will likely be smaller in the two-way design (since the t-test ignores the 2nd factor and interaction as sources of variation for the DV); and (b) the two-way design allows for test of interaction of the two factors ( ...
What is ANOVA in statistics?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models. It is one of the significant aspects of statistics. The statistics students should be aware of the analysis of variance. But most of the statistics students find it challenging to understand analysis of variance. But it is not that difficult.
Why do statisticians use ANOVA?
On the other hand, random factors don’t have this feature. The analyst uses the ANOVA to determine the influence that the independent variable has on the dependent variable. With the use of Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), we test the differences between two or more means. Most of the statisticians have an opinion that it should be known as “Analysis of Means.” We use it to test the general rather than to find the difference among means. With the help of this tool, the researchers are able to conduct many tests simultaneously.
What Does the Analysis of Variance Reveal?
In the initial stage of the ANOVA test, analyze factors that affect a given data set. When the initial stage finishes, then the analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors. It helps them to contribute to the data set with consistency measurably. Then the analyst performs the f-test that helps to generate the additional data that align with the proper regression model. The analysis of methods also allows you to compare more than two groups simultaneously to test whether the relationship exists between them or not.
How to use ANOVA in Excel?
To use ANOVA in Excel, you have to install the Data Analysis Toolpak and the data that you have to analyze.
Why do we use ANOVA?
You would use ANOVA to understand how your different groups react, with a null hypothesis for the test that means the various groups are equal .
What is one way ANOVA?
One way ANOVA is the unidirectional ANOVA. In this ANOVA, there are sole response variables as compared with the two-way ANOVA. It evaluates the impact of a sole factor. And this factor is determined that the samples are the same or not. Besides, it is also used to determine that there is any statistically significant difference between the mean of three or more independent groups.
How to determine variability of samples?
You can determine the variability of the samples and within samples with the results of ANOVA. If the tested group doesn’t have any difference, then it is called the null hypothesis, and the result of F-ratio statistics will also be close to 1. There is also the fluctuation in its sampling. And this sampling is likely to follow the Fisher F distribution. It is also a group of distribution functions. It has two characteristic numbers, i.e., numerator degrees of freedom and the denominator degrees of freedom.
Why is ANOVA one way?
It is called a one-way ANOVA because there is only one variable (type of sport played) that is being used to divide participants into different groups.
What is an ANOVA?
Analysis of Variance, or ANOVA for short, is a statistical test that looks for significant differences between means on a particular measure. For example, say you are interested in studying the education level of athletes in a community, so you survey people on various teams.
What is an ANOVA test?
Analysis of Variance, or ANOVA for short, is a statistical test that looks for significant differences between means on a particular measure. For example, say you are interested in studying the education level of athletes in a community, so you survey people on various teams. You start to wonder, however, if the education level is different among the different teams. You could use an ANOVA to determine if the mean education level is different among the softball team versus the rugby team versus the Ultimate Frisbee team.
What software is used to calculate the F statistic?
Statistical software can be used to calculate the F statistic and determine whether it is significant or not. All types of ANOVA follow the basic principles outlined above. However, as the number of groups and the interaction effects increase, the sources of variation will become more complex.
What are the different types of ANOVA?
There are four basic types of ANOVA models: one-way between groups, one-way repeated measures, two-way between groups, and two-way repeated measures. Statistical software programs can be used to make conducting an ANOVA easier and more efficient.
What is the significance of the F statistic?
If there is significantly greater between group variation than within group variation (in other words, when the F statistic is larger), then it is likely that the difference between the groups is statistically significant. Statistical software can be used to calculate the F statistic and determine whether it is significant or not.
What is the term for how much each group mean deviates from the overall mean?
Next, how much each group mean deviates from the overall mean is calculated. This is called between group variation.
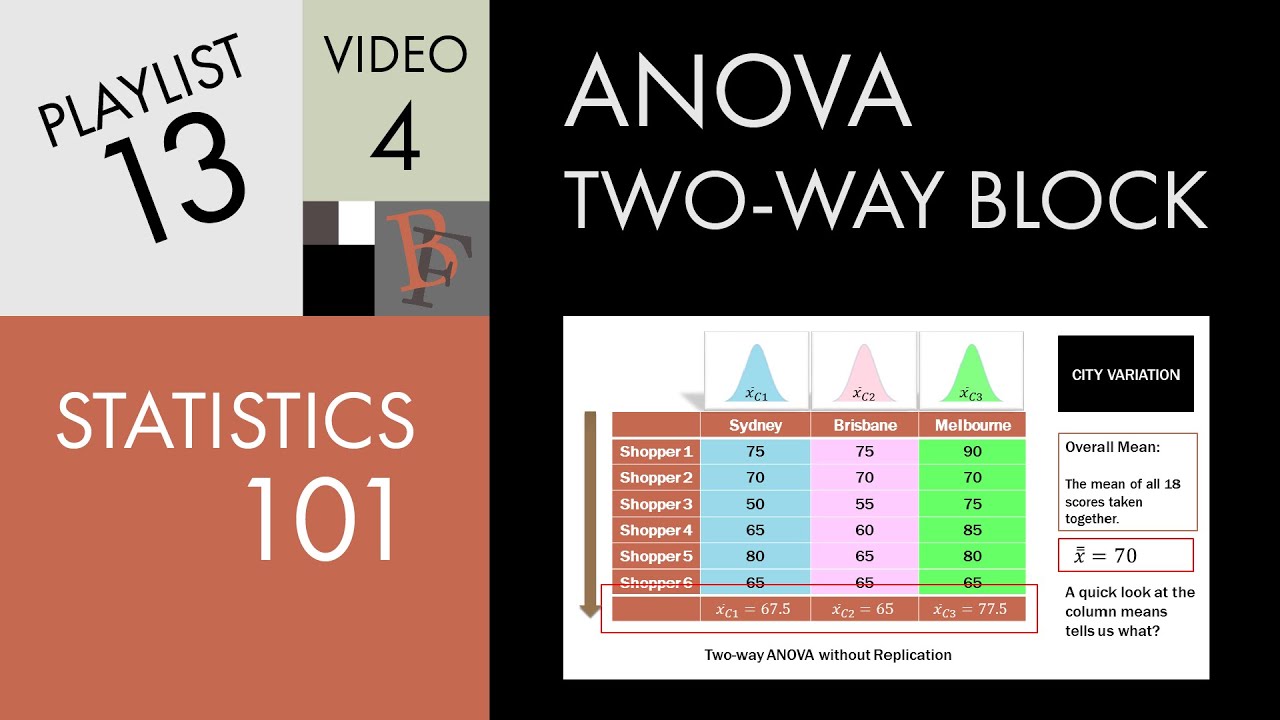
What is the grand mean in ANOVA?
Grand Mean. Mean is a simple or arithmetic average of a range of values . There are two kinds of means that we use in ANOVA calculations, which are separate sample means and the grand mean . The grand mean is the mean of sample means or the mean of all observations combined, irrespective of the sample.
How to measure within group variability?
We can measure Within-group variability by looking at how much each value in each sample differs from its respective sample mean. So first, we’ll take the squared deviation of each value from its respective sample mean and add them up. This is the sum of squares for within-group variability.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis?
Thus, they can be considered as a part of a larger set of the population. On the other hand, the alternate hypothesis is valid when at least one of the sample means is different from the rest of the sample means. In mathematical form, they can be represented as:
What does it mean when a null hypothesis states that all the samples are equal?
In other words, the null hypothesis states that all the sample means are equal or the factor did not have any significant effect on the results. Whereas, the alternate hypothesis states that at least one of the sample means is different from another. But we still can’t tell which one specifically. For that, we will use other methods that we will discuss later in this article.
How to do a MANOVA in Excel 2013?
Steps to perform MANOVA in Excel 2013: Step 1: Download the ‘RealStats’ add-in from the link mentioned above. Step 2: Press “control+m” to open RealStats window. Step 3: Select “Analysis of variance”. Step 4: Select “MANOVA: single factor”. Step 5: Type an Input Range into the Input Range box.
Why does the F distribution not have negative values?
Unlike the z and t-distributions, the F-distribution does not have any negative values because between and within-group variability are always positive due to squaring each deviation.
Which statistic measures if the means of different samples are significantly different or not?
The statistic which measures if the means of different samples are significantly different or not is called the F-Ratio. Lower the F-Ratio , more similar are the sample means. In that case, we cannot reject the null hypothesis.
Why do we use ANOVA?from qualtrics.com
You would use ANOVA to help you understand how your different groups respond, with a null hypothesis for the test that the means of the different groups are equal.
What does the ANOVA test mean?from analyticssteps.com
The ANOVA, which stands for the Analysis of Variance test, is a tool in statistics that is concerned with comparing the means of two groups of data sets and to what extent they differ.
What Does “One-Way” or “Two-Way Mean?from statisticshowto.com
One-way or two-way refers to the number of independent variables (IVs) in your Analysis of Variance test.
What is MANOVA?from statisticshowto.com
MANOVA is just an ANOVA with several dependent variables. It’s similar to many other tests and experiments in that it’s purpose is to find out if the response variable (i.e. your dependent variable) is changed by manipulating the independent variable. The test helps to answer many research questions, including:
What is Factorial ANOVA?from statisticshowto.com
A factorial ANOVA is an Analysis of Variance test with more than one independent variable, or “ factor “ . It can also refer to more than one Level of Independent Variable. For example, an experiment with a treatment group and a control group has one factor (the treatment) but two levels (the treatment and the control). The terms “two-way” and “three-way” refer to the number of factors or the number of levels in your test. Four-way ANOVA and above are rarely used because the results of the test are complex and difficult to interpret.
How to run an ANOVA in Qualtrics?from qualtrics.com
You can run an ANOVA test through the Qualtrics Crosstabs featuretoo . Here’s how: Ensure your “banner” (column) variable has 3+ groups and your “stub” (rows) variable has numbers (like Age) or numeric recodes (like “Very Satisfied” = 7) Select “Overall stat test of averages”. You’ll see a basic ANOVA p-value.
What is repeated measures ANOVA?from statisticshowto.com
Repeated measures ANOVA is similar to a simple multivariate design. In both tests, the same participants are measured over and over. However, with repeated measures the same characteristic is measured with a different condition. For example, blood pressure is measured over the condition “time”. For simple multivariate design it is the characteristic that changes. For example, you could measure blood pressure, heart rate and respiration rate over time.
How is ANOVA used in comparative analysis?
ANOVA is used in the analysis of comparative experiments, those in which only the difference in outcomes is of interest. The statistical significance of the experiment is determined by a ratio of two variances. This ratio is independent of several possible alterations to the experimental observations: Adding a constant to all observations does not alter significance. Multiplying all observations by a constant does not alter significance. So ANOVA statistical significance result is independent of constant bias and scaling errors as well as the units used in expressing observations. In the era of mechanical calculation it was common to subtract a constant from all observations (when equivalent to dropping leading digits) to simplify data entry. This is an example of data coding .
How to use analysis of variance?
The analysis of variance can be used to describe otherwise complex relations among variables. A dog show provides an example. A dog show is not a random sampling of the breed: it is typically limited to dogs that are adult, pure-bred, and exemplary. A histogram of dog weights from a show might plausibly be rather complex, like the yellow-orange distribution shown in the illustrations. Suppose we wanted to predict the weight of a dog based on a certain set of characteristics of each dog. One way to do that is to explain the distribution of weights by dividing the dog population into groups based on those characteristics. A successful grouping will split dogs such that (a) each group has a low variance of dog weights (meaning the group is relatively homogeneous) and (b) the mean of each group is distinct (if two groups have the same mean, then it isn't reasonable to conclude that the groups are, in fact, separate in any meaningful way).
What are the antecedents of the analysis of variance?
These include hypothesis testing, the partitioning of sums of squares, experimental techniques and the additive model. Laplace was performing hypothesis testing in the 1770s. Around 1800, Laplace and Gauss developed the least-squares method for combining observations, which improved upon methods then used in astronomy and geodesy. It also initiated much study of the contributions to sums of squares. Laplace knew how to estimate a variance from a residual (rather than a total) sum of squares. By 1827, Laplace was using least squares methods to address ANOVA problems regarding measurements of atmospheric tides. Before 1800, astronomers had isolated observational errors resulting from reaction times (the " personal equation ") and had developed methods of reducing the errors. The experimental methods used in the study of the personal equation were later accepted by the emerging field of psychology which developed strong (full factorial) experimental methods to which randomization and blinding were soon added. An eloquent non-mathematical explanation of the additive effects model was available in 1885.
Why is power analysis important in ANOVA?
Power analysis is often applied in the context of ANOVA in order to assess the probability of successfully rejecting the null hypothesis if we assume a certain ANOVA design, effect size in the population, sample size and significance level. Power analysis can assist in study design by determining what sample size would be required in order to have a reasonable chance of rejecting the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
Analysis of variance ( ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the t -test beyond two means.
When is a factor ANOVA used?
Factorial ANOVA is used when there is more than one factor. Repeated measures ANOVA is used when the same subjects are used for each factor (e.g., in a longitudinal study ). Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is used when there is more than one response variable.
How many classes of models are there in variance analysis?
There are three classes of models used in the analysis of variance, and these are outlined here.
How is ANOVA used in comparative analysis?from en.wikipedia.org
ANOVA is used in the analysis of comparative experiments, those in which only the difference in outcomes is of interest. The statistical significance of the experiment is determined by a ratio of two variances. This ratio is independent of several possible alterations to the experimental observations: Adding a constant to all observations does not alter significance. Multiplying all observations by a constant does not alter significance. So ANOVA statistical significance result is independent of constant bias and scaling errors as well as the units used in expressing observations. In the era of mechanical calculation it was common to subtract a constant from all observations (when equivalent to dropping leading digits) to simplify data entry. This is an example of data coding .
What is ANOVA test?from en.wikipedia.org
ANOVA is (in part) a test of statistical significance. The American Psychological Association (and many other organisations) holds the view that simply reporting statistical significance is insufficient and that reporting confidence bounds is preferred.
What Does the Analysis of Variance Reveal?from investopedia.com
The ANOVA test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency. The analyst utilizes the ANOVA test results in an f-test to generate additional data that aligns with the proposed regression models.
What is normal model based ANOVA?from en.wikipedia.org
The normal-model based ANOVA analysis assumes the independence, normality and homogeneity of variances of the residuals. The randomization-based analysis assumes only the homogeneity of the variances of the residuals (as a consequence of unit-treatment additivity) and uses the randomization procedure of the experiment. Both these analyses require homoscedasticity, as an assumption for the normal-model analysis and as a consequence of randomization and additivity for the randomization-based analysis.
What is the simplest experiment suitable for ANOVA analysis?from en.wikipedia.org
The simplest experiment suitable for ANOVA analysis is the completely randomized experiment with a single factor. More complex experiments with a single factor involve constraints on randomization and include completely randomized blocks and Latin squares (and variants: Graeco-Latin squares, etc.). The more complex experiments share many of the complexities of multiple factors. A relatively complete discussion of the analysis (models, data summaries, ANOVA table) of the completely randomized experiment is available .
How to calculate ANOVA?from en.wikipedia.org
The calculations of ANOVA can be characterized as computing a number of means and variances, dividing two variances and comparing the ratio to a handbook value to determine statistical significance. Calculating a treatment effect is then trivial: "the effect of any treatment is estimated by taking the difference between the mean of the observations which receive the treatment and the general mean".
What is the F statistic in ANOVA?from investopedia.com
The result of the ANOVA formula, the F statistic (also called the F-ratio), allows for the analysis of multiple groups of data to determine the variability between samples and within samples.
Why do we use ANOVA?
You would use ANOVA to help you understand how your different groups respond, with a null hypothesis for the test that the means of the different groups are equal.
What is an ANOVA test?
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) tells you if there are any statistical differences between the means of three or more independent groups. What is ANOVA? ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance. It’s a statistical test that was developed by Ronald Fisher in 1918 and has been in use ever since.
How to run an ANOVA in Qualtrics?
You can run an ANOVA test through the Qualtrics Crosstabs featuretoo . Here’s how: Ensure your “banner” (column) variable has 3+ groups and your “stub” (rows) variable has numbers (like Age) or numeric recodes (like “Very Satisfied” = 7) Select “Overall stat test of averages”. You’ll see a basic ANOVA p-value.
What is one way ANOVA?
The one-way ANOVA tests for an overall relationship between the two variables, and the pairwise tests test each possible pair of groups to see if one group tends to have higher values than the other. How to run an ANOVA test through Stats iQ.
What is the difference between a factorial and a one way ANOVA?
Two-way ANOVA does the same thing, but with more than one independent variable, while a factorial ANOVA extends the number of independent variables even further .
Can you run ANOVA with R?
You can also run ANOVA using any number of popular stats software packages and systems, such as R, SPSS or Minitab. A more recent development is to use automated tools such as Stats iQ from Qualtrics, which make statistical analysis more accessible and straightforward than ever before. Stats iQ and ANOVA.
Does Stats IQ show a pairwise test?
Rather, it tests for a general tendency of one group to have larger values than the other. Additionally, while Stats iQ does not show results of pairwise tests for any group with less than four values, those groups are included in calculating the degrees of freedom for the other pairwise tests.
What is ANOVA in data analysis?from researchgate.net
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an extremely important method in exploratory and confirmatory data analysis . Unfortunately, in complex problems (e.g., split-plot designs), it is not always easy to set up an appropriate ANOVA. We propose a hierarchical analysis that automatically gives the correct ANOVA comparisons even in complex scenarios. The inferences for all means and variances are performed under a model with a separate batch of effects for each row of the ANOVA table. We connect to classical ANOVA by working with finite-sample variance components: fixed and random effects models are characterized by inferences about existing levels of a factor and new levels, respectively. We also introduce a new graphical display showing inferences about the standard deviations of each batch of effects. We illustrate with two examples from our applied data analysis, first illustrating the usefulness of our hierarchical computations and displays, and second showing how the ideas of ANOVA are helpful in understanding a previously fit hierarchical model.
What is Bayesian hierarchical model?from researchgate.net
The article is about algorithms for learning Bayesian hierarchical models, the computational complexity of which scales linearly with the number of observations and the number of parameters in the model. It focuses on crossed random effect and nested multilevel models, which are used ubiquitously in applied sciences, and illustrates the methodology on two challenging real data analyses on predicting electoral results and real estate prices respectively. The posterior dependence in both classes is sparse: in crossed random effects models it resembles a random graph, whereas in nested multilevel models it is tree-structured. For each class we develop a framework for scalable computation based on collapsed Gibbs sampling and belief propagation respectively. We provide a number of negative (for crossed) and positive (for nested) results for the scalability (or lack thereof) of methods based on sparse linear algebra, which are relevant also to Laplace approximation methods for such models. Our numerical experiments compare with off-the-shelf variational approximations and Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. Our theoretical results, although partial, are useful in suggesting interesting methodologies and lead to conclusions that our numerics suggest to hold well beyond the scope of the underlying assumptions.
What are the principles of ANOVA?from researchgate.net
These principles are then used to understand the implications of analyzing unbalanced data, and to propose some corrections in the calculations. For instance, by determining the equivalent degrees of freedom of each factor, it is possible to mitigate the effect of non-orthogonality of unbalanced data on the results. In addition, unwanted correlation effects between factors in multi-factor analyses can also be compensated with correction factors in the calculation of the sums of squares, while at the same time the law of total variance can be preserved. Different examples of unbalanced data reported in the literature were presented in order to illustrate the use of the proposed analysis, and to highlight the differences in the results obtained with respect to conventional calculation methods. In addition, unbalanced simulated data obtained from a pre-defined model were used to evidence the effect of confounding between main effects and interactions, and to show the benefit of the proposed approach to reduce the risk of reaching erroneous conclusions in these situations. The proposed ANOVA calculations were implemented in MS-Excel (ForsChem Actinium XL).
What is a meta-analysis?from researchgate.net
This meta-analysis is an investigation into anomalous perception (i.e., conscious identification of information without any conventional sensorial means). The technique used for eliciting an effect is the ganzfeld condition (a form of sensory homogenization that eliminates distracting peripheral noise). The database consists of peer-reviewed studies published between January 1974 and June 2020 inclusive. The overall effect size will be estimated using a frequentist and a Bayesian random-effect model. Moderators analyses will be used to examine the influence of level of experience of participants, the type of task and the peer-review level. Publication bias will be estimated by using four different tests. Trend analysis will be conducted with a cumulative meta-analysis and a meta-regression model with Year of publication as covariate.
Why is Bayesian approach important?from researchgate.net
The objective of the paper is to use Bayesian approach to estimate variances components of two-full factorial experiment. Bayesian approach such as Monte Carlo simulations, using R2WinBUGS was used to obtain posterior distribution of parameters of interest. Deviance information criterion has been applied to select the best priors. In two factors full factorial experiment, the posterior estimates of the experimental error variance, mains effect and interaction error variance, coefficient of variation, and the predicted means of mains effect and interaction were obtained and compared with those under the frequentist method. Remarkable difference between mean based Bayesian estimates of variance components and the frequentist approach was found. Half-t prior distribution was the best candidate for Bayesian posterior estimate for two factors full factorial. Bayesian approach can be useful in industrial experiment and engineering to perform industrial experiments performance and investigation.
Is ANOVA a linear regression?from jstor.org
In this sense, ANOVA is indeed a special case of linear regression, but only if. hierarchical models are used. In fact, the batching of effects in a hierarchical model. has an exact counterpart in the rows of the analysis of variance table.
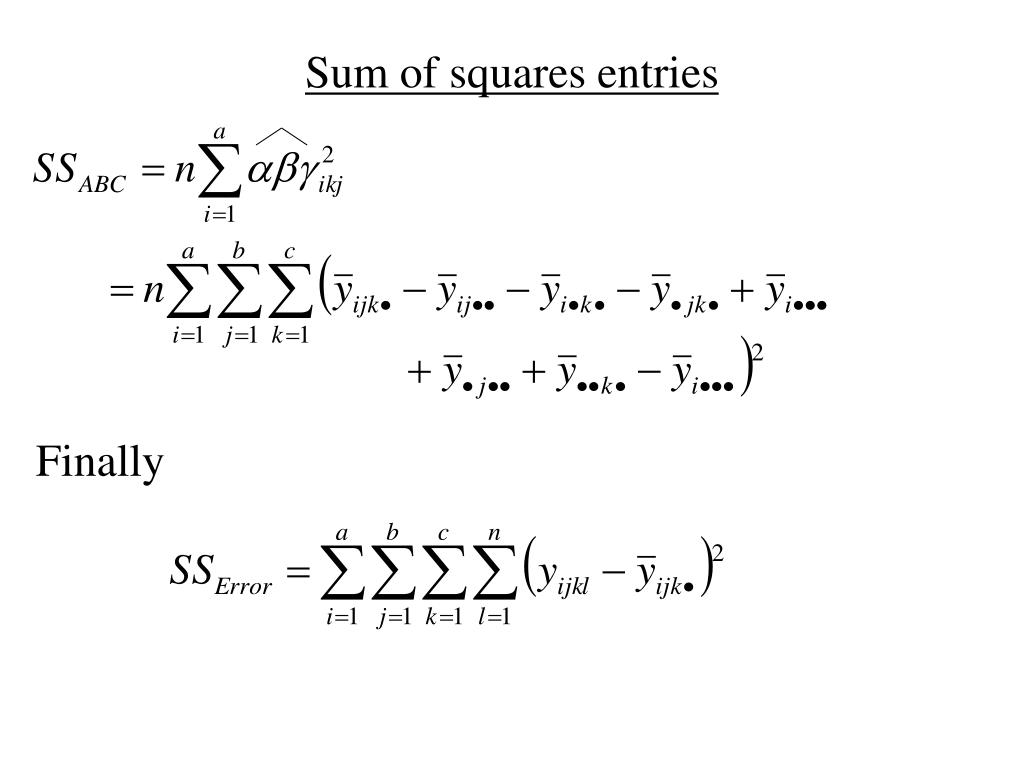
The Formula For Anova Is
- F=MSTMSEwhere:F=ANOVA coefficientMST=Mean sum of squares due to treatmentMSE=Mean…
What Does The Analysis of Variance Reveal?
- The ANOVA test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency. The analyst utilizes the ANOVA test results in an f-test to generate additional data that aligns with the proposed regressionmodels. The ANOVA test all…
Example of How to Use Anova
- A researcher might, for example, test students from multiple colleges to see if students from one of the colleges consistently outperform students from the other colleges. In a business application, an R&D researcher might test two different processes of creating a product to see if one process is better than the other in terms of cost efficiency. The type of ANOVA test used de…
One-Way Anova Versus Two-Way Anova
- There are two main types of ANOVA: one-way (or unidirectional) and two-way. There also variations of ANOVA. For example, MANOVA (multivariate ANOVA) differs from ANOVA as the former tests for multiple dependent variables simultaneously while the latter assesses only one dependent variable at a time. One-way or two-way refers to the number of independent variable…