
What causes a positive Babinski sign?
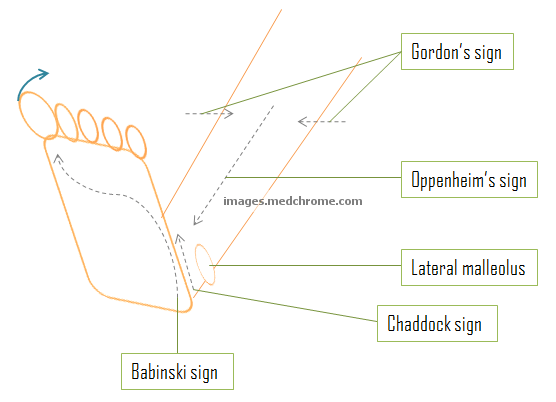
- Chaddock reflex. Your doctor will use a blunt instrument like the opposite end of a reflex hammer and run it along the outer edge of the top of the foot ...
- Gordon reflex. Your doctor will ask the child to lie down face up. ...
- Oppenheim reflex. Your doctor will run a firm tool along the tibia — the bone that you can feel on the front of your calf.
Is Babinski positive or negative?
The Babinski reflex is known by a number of other names: the plantar response (because the sole is the plantar surface of the foot), the toe or big toe sign or phenomenon, the Babinski phenomenon or sign. (It is wrong to say that the Babinski reflex is positive or negative; it is present or absent).
What does a positive Babinski sign mean?
In adults or children over 2 years old, a positive Babinski sign happens when the big toe bends up and back to the top of the foot and the other toes fan out. This can mean that you may have an underlying nervous system or brain condition that's causing your reflexes to react abnormally.
What is a positive Babinski sign?
Positive Babinski sign occurs when stimulation of lateral plantar aspect of the foot leads to extension (dorsiflexion or upward movement) of the big toe (hallux). Also, there may be fanning of the other toes. This suggests that there is been spread of the sensory input beyond the S1 myotome to L4 and L5.
What is the Babinski reflex test?
The Babinski reflex test is done as part of the routine neurological exam and is utilized to determine the integrity of the cortical spinal tract. The presence of a Babinski sign suggests damage to the cortical spinal tract. Because the cortical spinal tract fiber tracts run from the brain, through the brainstem and into the spinal cord, lesions of the central nervous system (CNS) often affect the integrity of the cortical spinal tract. Thus, the presence or absence of the Babinski reflex can provide very useful information on the presence or absence of pathology affecting the central nervous system. Babinski reflex is especially important in the setting where there is suspicion of spinal cord injury or stroke, as it may be an early indicator of the presence of these emergency conditions 12).
What does it mean when a child has a Babinski reflex?
When the Babinski reflex is present in a child older than 2 years or in an adult, it is often a sign of a central nervous system disorder. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
What is the Babinski sign?
Positive Babinski sign occurs when stimulation of lateral plantar aspect of the foot leads to extension (dorsiflexion or upward movement) of the big toe (hallux). Also, there may be fanning of the other toes. This suggests that there is been spread of the sensory input beyond the S1 myotome to L4 and L5.
Where does the Babinski sign originate?
The remainder originates from primary sensory areas, the parietal cortex, and the operculum. Damage anywhere along the cortical spinal tract can result in the presence of a Babinski sign.
Where does nociceptive input travel?
Nociceptive input travels up the tibial and sciatic nerve to the S1 region of the spine and synapse with anterior horn cells. The motor response which leads to the plantar flexion is mediated through the S1 root and tibial nerve. The toes curl down and inward. Sometimes there is no response to stimulation.
When is Babinski's normal?
In infants with at cortical spinal tract which is not fully myelinated the presence of a Babinski sign in the absence of other neurological deficits is considered normal up to 24 months of age. Babinski’s may be present when a patient is asleep.
Who created the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex (plantar reflex) was described by the neurologist Joseph Babinski in 1899 1). According to Dr. Joseph Babinski, plantar stimulation by stroking the lateral sole of the foot to the base of 5th toe and arcing toward the base of the big toe produce a downward deflection (or plantar flexion) of the great toe in those ...
What is the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex is easy to elicit without sophisticated equipment. Also, it requires little active patient participation, so it can be performed in patients who are otherwise unable to cooperate with the neurological exam.[1][2][3] The Babinski reflex (plantar reflex) was described by the neurologist Joseph Babinski in 1899.
Who invented the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex was described by the neurologist Joseph Babinski in 1899. Since that time, it has been incorporated into the standard neurological examination. The Babinski reflex is easy to elicit without sophisticated equipment.
When is Babinski's normal?
In infants with at CST which is not fully myelinated the presence of a Babinski sign in the absence of other neurological deficits is considered normal up to 24 months of age. Babinski’s may be present when a patient is asleep. [4][5] Indications.
Where does nociceptive input travel?
Nociceptive input travels up the tibial and sciatic nerve to the S1 region of the spine and synapse with anterior horn cells. The motor response which leads to the plantar flexion is mediated through the S1 root and tibial nerve. The toes curl down and inward. Sometimes there is no response to stimulation.
Can a Babinski reflex test be performed in patients who are otherwise unable to cooperate with the neurological exam?
Since it is a reflex, it does not require active patient participation and therefore can be performed in patients who are otherwise unable to cooperate with the neurological exam. This activity describes the technique for performing the Babinski reflex test and how to interpret the results.
Who was the first person to describe the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex (plantar reflex) was described by the neurologist Joseph Babinski in 1899. Since that time, it has been incorporated into the standard neurological examination.
Is Babinski reflex easy to elicit?
Since that time, it has been incorporated into the standard neurological examination. The Babinski reflex is easy to elicit without sophisticated equipment. Also, it requires little active patient participation, so it can be performed in patients who are otherwise unable to cooperate with the neurological exam. [1][2][3]
How old is Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex, or plantar reflex, is a foot reflex that happens naturally in babies and young children until they’re about 6 months to 2 years old. This reflex is usually tested by doctors by stroking the sole of the foot.
What age does the Babinski reflex occur?
Conditions that can affect the Babinski sign. The Babinski reflex indicates typical neurological function in children under 1–2 years old. If the Babinski reflex, or a positive Babinski sign, happens in children over 2 or in adults.
How long can a baby hold the Babinski reflex?
In a child under 2 years old born with intellectual disabilities or other mental conditions, the Babinski reflex may be held for an abnormally long period of time. In a child under 1–2 years old born with any condition that causes spasticity (muscle spasms and stiffness), the Babinski reflex may seem weak as the doctor strokes ...
How long does it take for Babinski reflex to disappear?
As a result, the Babinski reflex and other common reflexes seen in infancy disappear. The Babinski reflex may be normal in children up to 2 years old. It can sometimes end after 12 months. If the Babinski sign is still noticeable beyond that, it likely indicates neurological problems.
What is the Babinski sign?
The Babinski sign has since become an essential tool used by doctors and pediatricians. They use it to make sure that both adult and child brain activity, neurological responses, and nerve activity are normal and don’t indicate any underlying abnormalities in the brain or the nervous system.
What reflex test is used to test a baby's reflex?
This reflex is often tested beside other natural reflexes that babies have during infancy. Other reflex tests include the: root reflex, in which the doctor rubs a finger on the corner of the baby’s mouth to see if the baby reflexively moves their head toward the direction of stroking to look for a nipple or bottle to feed on. ...
Do Babinski reflexes disappear?
Babies don’t have full control over their nervous systems, so these reflexes are common and indicate healthy neurological function. As children grow, they get better control over their nervous systems. As a result, the Babinski reflex and other common reflexes seen in infancy disappear.
What is the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex is sometimes also referred to as the plantar reflex, extensor plantar reflex, or the Babinski sign. Since its discovery, testing the Babinski reflex has become a common part of newborn and infant examinations throughout the world. It can easily be tested in a newborn simply by stimulating the bottom of the foot.
When to be concerned about Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex only a concern after a child is two years old, when it is not displayed in infancy, or when it appears differently on each foot. In rare cases, your baby or older child may have an abnormal Babinski reflex; adults may have issues with their Babinski reflex as well.
How to test Babinski sign?
It can easily be tested in a newborn simply by stimulating the bottom of the foot. A positive Babinski sign in a new born is where the big toe extends upward and the rest of the toes flare out. A baby sometimes exhibits a reflex where the toes curl downwards instead of fanning out when the side of the heel is stroked.
What reflexes are stimulated when the bottom of a baby's foot is touched?
One of the most fascinating reflexes is the Babinski reflex, or plantar reflex, which is stimulated when the bottom of your baby’s foot is touched. If you gently stroke the sole of your newborn’s foot, you’ll probably notice that their big toe extends upward and the rest of their toes flare out.
What reflex is used to stimulate feeding?
Sucking Reflex . Another reflex that aids in feeding, the sucking reflex is stimulated anytime you place an object in your baby’s mouth. Whether it’s a breast, bottle, pacifier, or even your finger, your baby will begin to suck.
How long does it take for a baby to get out of the Moro reflex?
The Moro reflex is usually outgrown by four months.
What happens when you hold a baby upright?
If you hold your baby upright on a solid surface, you may notice that your baby begins to take a few steps. It’s pretty amazing, but doesn’t mean that your newborn is ready to walk. It’s just a reflex, but some experts believe it prepares your little one for their future adventures in walking.
How to check for Babinski reflex?
To check for the Babinski reflex, a doctor will use a blunt object, such as a tongue depressor. Before the test, they will make sure that the person is in a relaxed and comfortable state. They may warn the person about the sensation of the test, which may vary from ticklish to uncomfortable and unpleasant.
What happens if you have a Babinski reflex?
If the Babinski reflex is present, the big toe will move upward as the other toes fan outward. Although it took some time for the reflex to gain recognition, it is now one of the most important. Trusted Source. signs in clinical neurology. Doctors still use the Babinski reflex as a standard part of neurological testing.
How many babies have the Babinski reflex?
A study in the International Journal of Physiology found that the Babinski reflex occurs in about 62–75% of newborns. As newborns generally do not yet have a fully developed nervous system, the reflex is not necessarily a sign of a neurological condition.
What age do Babinski reflexes occur?
Doctors consider a Babinski reflex response that appears in adults or children over the age of 2 years to be an abnormal reflex response. It may be a sign of an underlying neurological condition or nervous system disorder.
What age can you get a Babinski test?
Doctors will still move on to other testing to help continue their diagnosis. An annual general checkup for adults and children over the age of 2 years may include a Babinski reflex test, along with other reflex tests. Anyone uncertain about their results should see a doctor for a diagnosis.
When should Babinski reflex be absent?
The reflex may be present in infants without any underlying conditions. After the age of 2 years , though, the Babinski reflex should be absent. A positive result in adults or children over the age of 2 years may be a sign of an underlying issue in the central nervous system.
When does reflex response disappear?
Trusted Source. of age. In some cases, the reflex response disappears earlier — potentially as early as 1 year of age.
What is Babinski reflex?
Babinski reflex. Babinski reflex is one of the normal reflexes in infants. Reflexes are responses that occur when the body receives a certain stimulus. The Babinski reflex occurs after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked. The big toe then moves upward or toward the top surface of the foot. The other toes fan out.
What does it mean when a child has a Babinski reflex?
When the Babinski reflex is present in a child older than 2 years or in an adult, it is often a sign of a central nervous system disorder. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. Disorders may include:
