
How to configure BGP?
To configure the BGP peer sessions:
- Run the show interfaces terse command to verify that the physical router has a logical tunnel ( lt) interface. ...
- On Logical System A, configure the interface encapsulation, peer-unit number, and DLCI to reach Logical System E. ...
- On Logical System A, configure the network address for the link to Peer E, and configure a loopback interface. ...
How does BGP select the best routing path?
- Choose the route with the highest weight.
- If weight is not set, choose the route with the highest local preference.
- Choose routes that this router originated.
- Choose the path with the shortest Autonomous System path.
- Choose the path with the lowest origin code (i is lowest, e is next, ? ...
What is BGP used for?
Where bgp is used? Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used to Exchange routing information for the internet and is the protocol used between ISP which are different ASes. The protocol can connect together any internetwork of autonomous system using an arbitrary topology.
What are BGP routes?
BGP is the standard routing protocol commonly used in the Internet to exchange routing and reachability information between two or more networks. When used in the context of Azure Virtual Networks, BGP enables the Azure VPN Gateways and your on-premises VPN devices, called BGP peers or neighbors, to exchange "routes" that will inform both gateways on the availability and reachability for those prefixes to go through the gateways or routers involved.

What is the benefit of using BGP?
BGP offers network stability that guarantees routers can quickly adapt to send packets through another reconnection if one internet path goes down. BGP makes routing decisions based on paths, rules or network policies configured by a network administrator.
Why do we use BGP instead of OSPF?
BGP and OSPF are two of the most common routing protocols. While BGP excels with dynamic routing for large networks, OSPF offers more efficient path choice and convergence speed.
Why we use BGP instead of IGP?
BGP is used to carry customer prefixes in the Service Provider networks, and IGP protocols are used for the infrastructure device reachability. So, IGP is used for Transport, Underlay purposes but BGP is used for Service Layer, which means the Overlay mechanism.
Why was BGP created?
Curiously enough, BGP was conceived as an interim solution to overcome the infeasibility of using the existing Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) with the increase in complexity for connectivity between Administrative Domains.
Why BGP is used in MPLS?
BGP carries routing information for the network and MPLS labels, whereas MPLS transports the data traffic. Figure 1 shows a typical scenario. The service provider backbone comprises two types of routers: Provider edge routers (PE routers)
What port does BGP use?
port 179BGP peers are established by manual configuration between routing devices to create a TCP session on port 179. A BGP-enabled device periodically sends keepalive messages to maintain the connection.
Is MPLS IGP or EGP?
Yes, you still need to run IGP. IGP is a foundation of any MPLS network.
Is BGP IGP or EGP?
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is one of a family of IP Routing protocols, and is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) designed to distribute routing information between ASs. EGPs are all vector routing protocols.
What is the difference between IGP and BGP?
BGP is used to carry customer prefixes in the Service Provider networks, and IGP protocols are used for the infrastructure device reachability. So, IGP is used for Transport, Underlay purposes but BGP is used for Service Layer, which means the Overlay mechanism.
Who maintains BGP?
The definition of this Extended Community Attribute is documented in RFC 4360. The IANA administers the registry for BGP Extended Communities Types.
Why is BGP slow protocol?
Keep in mind, though, BGP is a “slow to converge” protocol. Routing changes on the Internet occur all the time. If BGP had to react to every change, it would flood the Internet with routing updates that could slow traffic all over the globe. So, BGP plays a waiting game to give routes time to settle down.
How many BGP routes are on the Internet?
There are 735,386 active IPv4 BGP routes and 64,665 active IPv6 BGP routes as per AT&T Looking glass service (Picture 6).
Where is BGP routing used most?
the InternetBorder Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the routing protocol for the Internet. Much like the post office processing mail, BGP picks the most efficient routes for delivering Internet traffic.
What is the difference between RIP OSPF and BGP?
OSPF and RIP are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) and distribute routing information within an autonomous system, whereas BGP is a Exterior Gateway Protocol. The routes learned via the dynamic routing protocols are applied to the kernel routing table.
Why is OSPF not scalable?
In theory, OSPF topology is limited by the number of links that can be advertised in the Router LSA as each router gets only one Router LSA and it cant be bigger than 64K which is the biggest an IP packet can be. The same constraint applies to the Network LSA also.
Which routing protocol is best and why?
Many network engineers believe that EIGRP is the best choice for a routing protocol on private networks because it offers the best balance between speed, scalability and ease of management.
What is BGP protocol?
BGP is the protocol that tells data requests what path they need to take to reach the server. If, for example, you log in to Facebook or open the app to pull up your feed, BGP is what guides your data packet along the fastest route to retrieve that data for you from Facebook’s servers.
What is BGP metaphor?
Several very apt metaphors have been used in recent articles to explain BGP. People have likened it to everything from an air traffic controller to a constantly evolving map of the internet. It’s even been called “the duct tape of the internet.” And they’re all right.
How Do BGP and DNS Work Together?
Part of the way BGP works is that it advertises viable routes for data. If BGP stops working, those routes can’t be found and disappear from the internet, so the data has nowhere to go.
What is BGP in Cloudflare?
Cloudflare describes BGP as “ the postal service of the internet ,” in that it chooses the fastest and most efficient route for your requests to reach their intended server. BGP looks at all the available routes your data could take, then chooses what it sees as the best one.
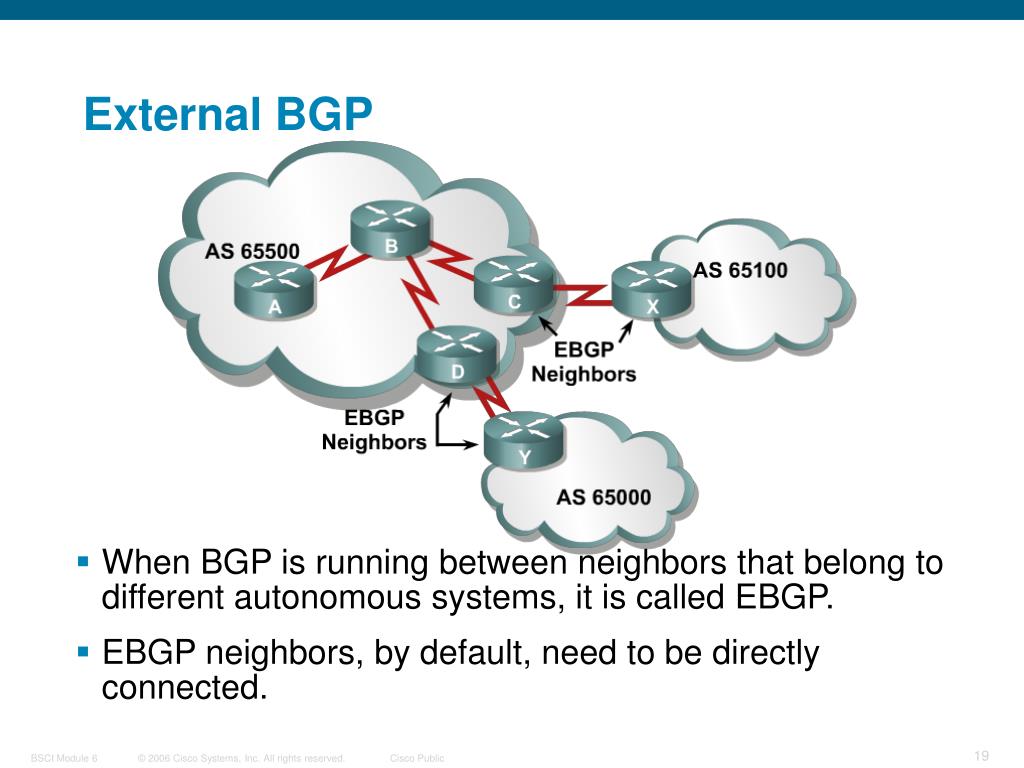
What is external BGP?
External BGP (eBGP): The protocol used by the internet at large. In our post office metaphor, this is akin to international shipping.
When did BGP update get bad?
According to Cloudflare, a bad BGP update in 2004 by Turkish ISP TTNet temporarily advertised TTNet as the best destination for all traffic on the internet. That resulted in connection problems for an entire day until the issue was sorted out.
Can BGP update go wrong?
Autonomous systems run BGP updates without incident all the time. But when they go wrong, they can go very wrong. In their article, Clark explains that since BGP is designed to spread from system to system quickly, an error can have a ripple effect like the one we saw at Facebook.
What is an AS in BGP?
If we continue to think of BGP as the Postal Service of the Internet, ASes are like individual post office branches. A town may have hundreds of mailboxes, but the mail in those boxes must go through the local postal branch before being routed to another destination. The internal routers within an AS are like mailboxes. They forward their outbound transmissions to the AS, which then uses BGP routing to get these transmissions to their destinations.
What is BGP in mail?
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the postal service of the Internet. When someone drops a letter into a mailbox, the postal service processes that piece of mail and chooses a fast, efficient route to deliver that letter to its recipient. Similarly, when someone submits data across the Internet, BGP is responsible for looking at all ...
Who operates BGP autonomous systems?
ASes typically belong to Internet service providers (ISPs) or other large organizations, such as tech companies, universities, government agencies, and scientific institutions. Each AS wishing to exchange routing information must have a registered autonomous system number (ASN). Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns ASNs to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), which then assigns them to ISPs and networks. ASNs are 16 bit numbers between one and 65534 and 32 bit numbers between 131072 and 4294967294. As of 2018, there are approximately 64,000 ASNs in use worldwide. These ASNs are only required for external BGP.
What is the difference between external BGP and internal BGP?
It should be noted that using internal BGP is NOT a requirement for using external BGP. Autonomous systems can choose from a number of internal protocols to connect the routers on their internal network.
What is BGP in Argentina?
When a user in Singapore loads a website with origin servers in Argentina, BGP is the protocol that enables that communication to happen quickly and efficiently.
Is RPKI enough to protect BGP?
But RPKI’s existence alone is not enough. If large networks do not deploy RPKI, they can spread large-scale hijacking attacks. Currently, over 50% of the top Internet providers support RPKI to some extent, but a larger majority is needed to fully secure BGP. Network operators can protect their networks by implementing RPKI and using network alerting technology like Cloudflare Route Leak Detection. This feature helps prevent BGP hijacking attacks by letting customers know when unauthorized parties are advertising their prefixes.
Can autonomous systems use BGP?
Autonomous systems can also use an internal version of BGP to route through their internal networks, which is known as internal BGP, or iBGP for short. It should be noted that using internal BGP is NOT a requirement for using external BGP.
Why do operators use BGP?
However, in large transit 3 networks, and very complex terminal networks, 4 the operator of the network uses BGP policy to provide security and apply business logic to the traffic that is flowing through their network. Because that policy can be quite complex, the management of BGP policy can be quite complex as well.
Why use BGP in Calico?
To summarize, we use BGP to advertise the end points in a Calico network because it is: Simple. Industry current best practice. The only protocol that will sufficiently scale. The use of an IGP for infrastructure routing is dependent on the interconnect fabric that is chosen for your Calico installation.
What is an IGP in a network?
In a network made up of an incomplete graph of routers, 1 the routers need to know the topology of the network, so that they can send traffic across the network of routers to reach the intended destination. This is where an IGP, such as IS–IS or OSPF is used.
How many routers can BGP support?
To meet this requirement (among others) BGP was developed. It can scale up to hundreds of routers in a network, and tens of thousands if a technology called BGP route reflection is used. It can also advertise millions of routes and manage that via a very flexible policy infrastructure, if needed.
How many end points can an IGP advertise?
This number is a bit more flexible, but usually tops out at thousands or low tens of thousands of end points. Many large network operators get nervous when the number of routes in an IGP extends beyond five or six thousand.
Is BGP a viable option?
5. In short, BGP is the only viable option for this component of routing in a Calico network.
Is BGP more complex than OSPF?
Actually, that’s not quite correct. If anything, because BGP is not really interested in the full topology, in its most simple application, BGP is simpler to configure, run, and troubleshoot than OSPF or IS–IS. The protocol itself is pretty simple. However, in large transit 3 networks, and very complex terminal networks, 4 the operator of the network uses BGP policy to provide security and apply business logic to the traffic that is flowing through their network. Because that policy can be quite complex, the management of BGP policy can be quite complex as well. If the policy is simple, or if there is no policy, BGP configuration is usually just telling a BGP router who its other peers are.
Types of BGP
Internal BGP − Internal BGP (IBGP) is a BGP connection between BGP speakers in the same AS.
Message Types
Open Message − This is a message that is sent to establish the session after the different autonomous system successfully makes the connection. This message contains the information related to the autonomous system like the version of BGP using, Hold time, BGP identifier (IP address), AS number and some optional parameters.
Need of BGP
BGP has an advantage as it gives us much more control over what routes we advertise and over what advertisements we accept from our neighbours.
What is an IGP router?
Service providers therefore need to use an IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) for the routing within their administrative domain. It's usually OSPF or IS-IS which is used.
What does R1 do with OSPF?
R1 then sends out link-local multicast hello messages looking for other OSPF routers that it can form an adjacency with.
Does IGP work for all routers?
You saw before when we just had the one service provider that an IGP would work for everything. But we're going to run into a problem as the network grows and we've got multiple different service providers. IGP's such as OSPF and IS-IS are not designed to support routing on the Internet. It's not feasible to control routing for the entire planet on a physical hop by physical hop basis. We can't have every service provider knowing about all the different individual routers in the whole world - obviously that's not going to work! So a different model needs to be used. And that's where BGP, the Border Gateway Protocol, comes in.
What is MP-BGP?
The multiprotocol version of BGP is used to carry MPLS VPN information between all provider edge (PE) routers within a VPN community. MP-BGP is defined in RFC 2858. It introduces a new BGP capabilities advertisement to determine whether a BGP peer supports MP-BGP.
Which is better, BGP or transit AS?
BGP is better option in transit AS, it mean that you can allow your packets packet to move through from one AS to other AS, for Example LAN to an ISP.
What is the best routing protocol?
As a routing protocol BGP is best choice in following environment: 1 BGP is normally use for connecting different AS’s, in an environment where your autonomous system have multiple links to other AS’s. 2 BGP is better option in transit AS, it mean that you can allow your packets packet to move through from one AS to other AS, for Example LAN to an ISP. 3 BGP is build for controlling the large networks, it will work great if you have a large amount of traffic and traffic needs high degree of control. 4 The multiprotocol version of BGP is used to carry MPLS VPN information between all provider edge (PE) routers within a VPN community. MP-BGP is defined in RFC 2858. It introduces a new BGP capabilities advertisement to determine whether a BGP peer supports MP-BGP. 5 You can handle the Policy-based routing w ith BGP among different AS. There two types of BGP that are IBGP and EBGP, you can use the IBGP in internal or in single AS, while EBGP is used among different AS.
Can policy based routing be used in different AS?
You can handle the Policy-based routing w ith BGP among different AS. There two types of BGP that are IBGP and EBGP, you can use the IBGP in internal or in single AS, while EBGP is used among different AS.
What Exactly Is BGP Anyway?
How Do BGP and DNS Work Together?
- BGP is what makes data routing on the internet possible, which makes it the glue—or the duct tape—that holds the internet together. Part of the way BGP works is that it advertises viable routes for data. If BGP stops working, those routes can’t be found and disappear from the internet, so the data has nowhere to go. That’s part of what happened at ...
How BGP Can Mess Up The Internet
- Multiple factors can affect the route your data takes through the internet’s map. Cost can be one, as some providers charge for access to their systems. The changing nature of the internet itself is another. Autonomous systems and websites can move or be removed entirely from the map of the internet. They can also change or add service providers—an example might be a college switchi…
Fixing The Bugs
- According to Cloudflare, a bad BGP update in 2004 by Turkish ISP TTNet temporarily advertised TTNet as the best destination for all traffic on the internet. That resulted in connection problems for an entire day until the issue was sorted out. Incidents like these point to certain weaknesses in BGP, namely that the autonomous systems that make up the internet at large will implicitly trust …