There are several reasons why vaginal delivery of a breech baby is so hazardous. For starters breech presentation makes the basic mechanics of vaginal delivery much more difficult. The baby's head is the largest part of their body so it is the most difficult to push through the birth canal.
Do breech babies have complications when they grow up?
One such region is the spinal cord, which ends up bearing the highest pressure when the baby is in the breech position. This results in higher chances of deformities in the spinal cord, muscle coordination problems, or further complications in the child’s growth.
Why are breech births dangerous?
The danger of breech birth is mostly due to the fact that the largest part of a baby is its head. When the breech baby's pelvis or hips deliver first, the woman's pelvis may not be large enough for the head to be delivered also. This can result in a baby getting stuck in the birth canal, which can cause injury or death.
What causes a breech birth?
- if the pregnant woman has a history of several pregnancies
- if a woman is pregnant with multiples
- if a woman has a history of delivering prematurely
- if a woman has placenta previa
- if the uterus contains either too little or too much amniotic fluid
- if the woman’s uterus has an abnormal shape or other problems such as fibroids
What happens during a breech vaginal birth?
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby’s feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby’s head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early ...

How long does it take for a baby to be breech?
How will I know if my baby is breech? A baby is not considered breech until around 35 or 36 weeks. In normal pregnancies, a baby usually turns head-down to get into position in preparation for birth. It’s normal for babies to be head-down or even sideways before 35 weeks.
What percentage of pregnancies are breech?
About 3-4 percent of all pregnancies. Trusted Source. will result in the baby being breech. A breech pregnancy occurs when the baby (or babies!) is positioned head-up in the woman’s uterus, so the feet are pointed toward the birth canal. In a “normal” pregnancy, the baby will automatically turn inside the womb into a head-down position ...
How to help a breech baby?
Another popular method for women with breech babies is inverting their bodies to encourage the baby to flip. Women use different methods, like standing on their hands in a swimming pool, propping up their hips with pillows, or even using the stairs to help elevate their pelvis.
What does it mean when a woman has a premature birth?
if the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid, meaning the baby has extra room to move around in or not enough fluid to move around in. if the woman has an abnormally shaped uterus or has other complications, such as fibroids in the uterus. if a woman has placenta previa.
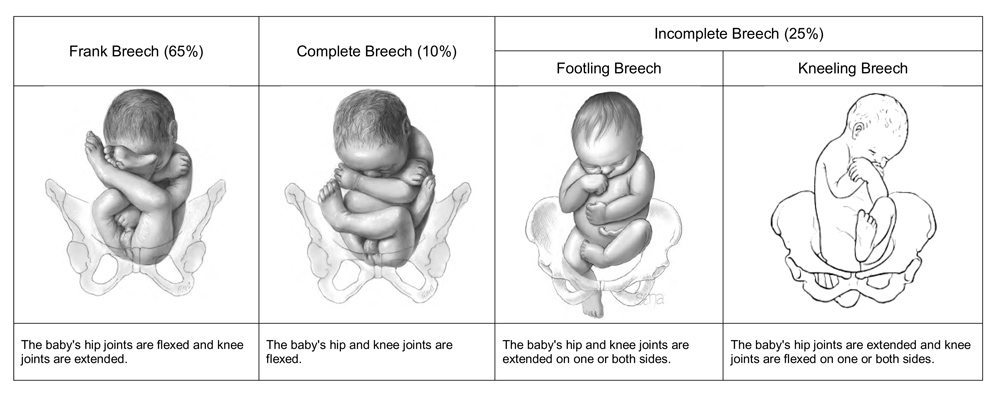
What are the different types of breech?
There are three different types of breech pregnancies: frank, complete, and footling breech, depending on how the baby is positioned in the uterus. With all types of breech pregnancies, the baby is positioned with its bottom toward the birth canal instead of the head. Doctors can’t say exactly why breech pregnancies occur, ...
How to tell if a baby is breech?
Your doctor will be able to tell if your baby is breech by feeling your baby’s position through your stomach. They will also most likely confirm that the baby is breech using an ultrasound in the office and in the hospital before you deliver.
How long does it take for an ev to work?
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, most doctors will suggest an EV between 36 and 38 weeks of pregnancy.
What is breech delivery?
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor. Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
How are breech babies born?
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen. 3
How many babies are breech at 28 weeks?
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. 2 However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech. 1
What are the complications of ECV?
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor. 3
What happens if the umbilical cord is pinched?
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. 2 There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
When should a baby be breech?
However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
Can a breech fetus be delivered?
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, ces arean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
What are the clinical conditions associated with breech presentation?
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4][5]These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
What is a breech presentation?
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
What are the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation?
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6][7]
What is the recurrence rate after a breech delivery?
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10% , and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
How to diagnose breech presentation?
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
What is the gestational age for breech?
One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
Who is responsible for breech delivery?
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12][13][14]
Abstract
The increased risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality associated with vaginal delivery of the fetus in breech presentation has attracted the attention of obstetricians and midwives for centuries.
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.

Types of Breech Presentation
Signs of Breech
- There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation. Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.2 A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination i…
Risk Factors
- Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor.2However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation. These can include:1 1. Previous pregnancies 2. Multiple fetuses in the uterus 3. An abnormally shaped uterus 4. Uterine fibroids, which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years …
Treatment
- Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.3 In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus.1However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with ce…
Complications
- During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow.2There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation. Complications associated with ce...
Summary
- In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word from Verywell
- Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time. At the end of your pregna…