
Why is emphysema a serious health problem?
What happen in emphysema is described as follows:
- As the soft, fragile tissues between alveoli are damaged – air pockets develop in the lung.
- Then air is easier to get trapped in the spaces of destroyed lung tissue, causing airflow limitation. ...
- Over time the lung enlarges slowly and you’re more difficult to take a breath (now your breathing requires more effort).
How bad is emphysema?
“It burned your lungs when you walked in the house ... The cat needed a dental [cleaning]. It had really bad teeth. She said she didn’t have the money. I did a fundraiser for her. And she never showed up.” Garcia, who works with Blackheart Trappers ...
What are the risk factors of emphysema?
traditionally defined by a low percent of forced vital capacity exhaled in the first second (FEV 1 /FVC), and cigarette smoking is the greatest environmental risk factor. Only a minority of smokers develop COPD, and genetic factors are thought to account ...
Are emphysema and COPD the same thing?
Are Emphysema and COPD the Same Thing? Although emphysema and COPD may be used interchangeably, they do not have the same meaning. Emphysema is a type of COPD. COPD is a term that may be used in reference to various lung diseases, such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis or bronchiectasis.
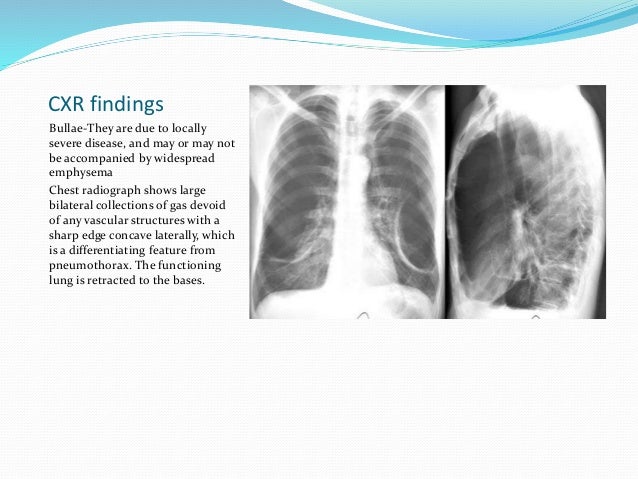
Is emphysema obstructive or restrictive?
The most common causes of obstructive lung disease are: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Asthma. Bronchiectasis.
Why is COPD considered obstructive?
Overview. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production and wheezing.
What happens to airways during emphysema?
Emphysema, the fourth leading cause of death in the United States, affects the walls of the millions of tiny air sacs in the lungs, which become inflamed and lose elasticity, causing the bronchioles to collapse.
Does smoking cause obstructive or restrictive?
Causes of Obstructive Lung Disease The primary risk factor for this condition, according to the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, is smoking. More than 75% of individuals with COPD either currently smoke or they used to.
What is the difference between COPD and emphysema?
The main difference between emphysema and COPD is that emphysema is a progressive lung disease caused by over-inflation of the alveoli (air sacs in the lungs), and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is an umbrella term used to describe a group of lung conditions (emphysema is one of them) which are ...
Why does air get trapped in emphysema?
When emphysema develops, the alveoli and lung tissue are destroyed. With this damage, the alveoli cannot support the bronchial tubes. The tubes collapse and cause an “obstruction” (a blockage), which traps air inside the lungs.
Why does airway resistance increase in emphysema?
Emphysema, by reducing the elastic recoil of the lung through parenchymal destruction and increase in alveolar size, as well as reducing the elastic load applied to the airways through destruction of alveolar attachments, also contributes to the airflow limitation characteristic of smokers.
Why are airways narrowed in COPD?
In a lung with COPD, the airways are narrowed because: the lung tissue is damaged so there is less pull on the airways. mucus blocks part of the airway. the airway lining becomes inflamed and swollen.
What is the cause of shortness of breath?
Emphysema is a progressive, destructive lung disease in which the walls between the tiny air sacs are damaged. As a result, the lungs lose their elasticity causing exhalation, or breathing out, to become more and more difficult. Air remains trapped in the overinflated lungs, leading to progressive shortness of breath.
Why do people with COPD lose weight?
However, most weight loss in COPD patients is due to the increased metabolic demand of respiratory muscles that are overworked because of emphysema damage.
How to treat COPD?
Surgical Treatment for COPD 1 Lung Volume Reduction Surgery involves removing parts of the lung that are most affected by COPD. Removal of lung tissue seems counterintuitive, but it allows the remaining, healthy parts of the lung function more efficiently. 2 Bullectomy involves the removal of bullae from the lungs. Bullae are large air sacs in the lungs that form when a large number of alveoli are destroyed by COPD. These air sacs interfere with breathing.
What happens if you have a frequent exacerbation?
People with frequent exacerbations (2 or more a year), have a more rapid deterioration in lung function, more frequent hospitalizations, and higher mortality. There are many medical options for treating emphysema/COPD.
How long does steroid therapy last for COPD?
Steroids. Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications. The only role for systemic steroid therapy in COPD is for 5-10 days during an acute exacerbation. Longer term treatment with systemic steroids in COPD has not been shown to have any benefit and can carry significant risks.
What is the purpose of bronchodilators?
Bronchodilators relax the muscles of the bronchi, the major air passageway in the lungs. This allows air to get in and out easier. These medications are available in pill or liquid form (taken orally), or as an aerosol spray (inhaled).
Is asthma a reversible disease?
COPD and asthma are both obstructive lung diseases marked by shortness of breath but asthma is by definition reversible while with COPD the airflow obstruction is either irreversible or only partly reversible. The mainstay of therapy in asthma is inhaled corticosteroids while in COPD it is long acting bronchodilators.
What are the symptoms of emphysema?
See your doctor if any of these symptoms arise: Shortness of breath, especially during light exercise or climbing steps. Ongoing feeling of not being able to get enough air. Long-term cough or “smoker’s cough”.
How do you know if you have emphysema?
Often times, symptoms may not be noticed until 50 percent or more of the lung tissue has been destroyed.
What happens to the alveoli when you exhale?
When you exhale, the alveoli shrink, forcing carbon dioxide out of the body. When emphysema develops, the alveoli and lung tissue are destroyed. With this damage, the alveoli cannot support the bronchial tubes. The tubes collapse and cause an “obstruction” (a blockage), which traps air inside the lungs.
What is the name of the disease that develops after smoking?
Emphysema is a disease of the lungs that usually develops after many years of smoking. Along with asthma and chronic bronchitis, emphysema belongs to a group of lung diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Why do you need an ECG for shortness of breath?
It is especially helpful in determining if a patient needs extra oxygen. Electrocardiogram (ECG): ECGs check heart function and are used to rule out heart disease as a cause of shortness of breath. You might also talk to your doctor about whether testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is appropriate for you.
Why do lungs have barrel chested?
The tubes collapse and cause an “obstruction” (a blockage), which trap s air inside the lungs. Too much air trapped in the lungs can give some patients a barrel-chested appearance. Also, because there are fewer alveoli, less oxygen will be able to move into the bloodstream.
What is the best test for emphysema?
This means that air is being trapped in your lungs. Other tests include: X-rays: X-rays are generally not useful for detecting early stages of emphysema.
What causes emphysema in the lungs?
Rarely, emphysema is caused by an inherited deficiency of a protein that protects the elastic structures in the lungs. This condition is called called alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency.
What are the risks of emphysema?
Factors that increase your risk of developing emphysema include: 1 Smoking. Emphysema is most likely to develop in cigarette smokers; however, cigar and pipe smokers also are susceptible. The risk for all types of smokers increases with the number of years and amount of tobacco smoked. 2 Age. Although the lung damage that occurs in emphysema develops gradually, most people with tobacco-related emphysema begin to experience symptoms of the disease between the ages of 40 and 60. 3 Passive smoking. This means breathing in the smoke from someone else's cigarette, pipe or cigar. Being around secondhand smoke increases your risk of emphysema. 4 Occupational exposure to fumes or dust. If you breathe fumes from certain chemicals or dust from grain, cotton, wood or mining products, you're more likely to develop emphysema. This risk is even greater if you smoke. 5 Exposure to indoor and outdoor pollution. Breathing indoor pollutants (such as fumes from heating fuel), as well as outdoor pollutants (such as car exhaust).
What are the two conditions that make up chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
This leads to a persistent cough and further reduces the air that gets down into your lungs. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two conditions that make up chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Our picks for Emphysema.
What is the cause of shortness of breath?
What is emphysema ? Emphysema is a lung condition that causes shortness of breath and a cough. The air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are damaged. Over time, the inner walls of the air sacs weaken and the lining of the alveoli becomes damaged. This causes a smaller number of larger air spaces instead of normal small ones.
Why do I cough when I have emphysema?
This means that less oxygen can be transferred from the air you breathe in into your bloodstream. Most people with emphysema also have a condition called chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis causes inflammation in the tubes (called bronchi) that carry the air to and from your lungs. This leads to a persistent cough and further reduces ...
How do you know if you have emphysema?
The main symptoms of emphysema are shortness of breath and a cough, which usually begin gradually. As the shortness of breath and the cough become progressively worse, you will find you will become increasingly less active until even usual daily domestic tasks become very difficult.
How many people in the US have emphysema?
Emphysema affects about 14 million people in the USA. This includes about 14 out of every 100 white male smokers and 3 out of every 100 white male non-smokers. Slightly fewer female smokers and African Americans are affected. In the UK it is thought that around 1.2 million people have COPD.
Which emphysema affects the upper lobes of the lungs?
paraseptal emphysema. centrilobular emphysema, which affects mainly the upper lobes and is most common in people who smoke. panlobular em physema, which affects both the paraseptal and centrilobular areas of the lungs. During diagnosis, a CT scan can show which type of emphysema is present.
What is the best medicine for emphysema?
The main medications for emphysema are inhaled bronchodilators, which can help relieve symptoms. They relax and open the airways, making it easier for a person to breathe. The inhaler delivers the following bronchodilators: beta-agonists, which relax bronchial smooth muscle and help clear mucus.
What is the name of the condition where the air sacs in the lungs become damaged and stretched?
Types. Diagnosis. Prevention. Summary. Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In this condition, the air sacs in the lungs become damaged and stretched. This results in a chronic cough and difficulty breathing.
What is the name of the disease where the air sacs and alveoli become larger?
Emphysema is a type of COPD. With emphysema , lung tissue loses elasticity, and the air sacs and alveoli in the lungs become larger. The walls of the air sacs break down or are destroyed, narrowed, collapsed, stretched, or over-inflated.
Why do people with COPD never smoke?
of people with COPD have never smoked. Other causes appear to be genetic factors, such as an alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and exposure to environmental irritants , including secondhand smoke, workplace pollutants, air pollution, and biomass fuels.
How long does it take for emphysema to progress?
The outlook for a person with emphysema will depend on individual factors and how well they manage their condition. It takes several years to progress to the final stages of COPD or emphysema, but lifestyle factors play a role.
What is the global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease?
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease sets out the stages of COPD. Generally, the stages are based on a combination of airflow limitation, symptoms, and exacerbations. A doctor can use a breathing test to measure lung capacity. The test measures the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1).
Why is emphysema the most preventable respiratory disease?
Emphysema is one of the most preventable respiratory illnesses because it is so strongly linked to smoking. Air pollutants, an alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and respiratory infections can also play a role, but smoking is considered the number one cause.
What is the term for the destruction of the alveoli?
Emphysema. Emphysema is one of the diseases that comprises COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Emphysema develops over time and involves the gradual damage of lung tissue, specifically the destruction of the alveoli (tiny air sacs).
How does emphysema affect the lungs?
Emphysema destroys the walls between the alveoli. This leaves the lungs less able to absorb oxygen into the bloodstream and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Lung tissue also loses its resilience, which prevents it from stretching and contracting properly.
How to stop emphysema from getting worse?
Don't smoke. If you smoke, quitting is the most important thing you can do to stop emphysema from getting worse. Participate in pulmonary rehabilitation. Pulmonary rehabilitation is a form of physical therapy.
Why is oxygen important for emphysema?
As emphysema becomes more severe, the oxygen level in your blood may become dangerously low. If this happens, breathing in extra oxygen can help you live longer. And it can help you avoid problems that can occur when your body isn't getting enough oxygen on its own.
What is the name of the disease that makes it hard to breathe?
April 28, 2015. Emphysema is a respiratory disease that makes it hard to breathe. Normally, when you take a breath, air travels from your nose and mouth through your windpipe and into the bronchi. These are small air passages that branch off into each lung. The bronchi branch further into thousands of smaller, thinner tubes ...
What is the name of the small round air sacs that absorb oxygen from the air?
The bronchi branch further into thousands of smaller, thinner tubes that end in grape-like clusters of small, round air sacs called alveoli. Tiny blood vessels absorb oxygen from the air through the walls of the alveoli and deliver it to cells throughout the body. Carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction.
What to do if you have emphysema?
Get vaccinated. If you have emphysema, ask your doctor about vaccinations against influenza (flu) and pneumococcal pneumonia. These vaccinations can help to prevent life-threatening respiratory infections in people with lung disease.
What is the best medicine for emphysema?
Corticosteroids are powerful drugs that curb inflammation and help open airways. They are available in inhalers and as pills. Antibiotics are used to treat lung infections caused by bacteria. People with emphysema often need antibiotics for respiratory infections.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary emphysema?
Other symptoms may include: Anxiety. Depression. Extreme tiredness (fatigue) Heart problems. Over-inflation of the lungs. Sleep problems. Weight loss. The symptoms of pulmonary emphysema may look like other lung conditions or health problems.
What is the condition that causes airflow blockage?
Pulmonary emphysema is a chronic lung condition. It’s often part of COPD, a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing problems. It develops very slowly over time. It’s most often caused by smoking.
What is the cause of lung holes?
Damage to the air sacs can't be fixed. It causes permanent holes in the lower lung tissue. Pulmonary emphysema is part of a group of lung diseases called COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). COPD lung diseases cause airflow blockage and breathing problems. The 2 most common conditions of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
What is the condition where the air sacs collapse?
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition in which the air sacs (alveoli) may be: Collapsed. Destroyed. Narrowed. Overinflated. Stretched. Overinflation of the air sacs is a result of a breakdown of the alveoli walls. It causes a decrease in respiratory function and breathlessness. Damage to the air sacs can't be fixed.
How to repair a damaged lung?
There is no way to repair or regrow the damaged lung tissue. Treatment may include: A pulmonary rehab program. This may include breathing exercises to strengthen the muscles you use for breathing, and exercises for the rest of your body. Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
What is pulmonary function?
Along with a complete health history and physical exam, your healthcare provider may request pulmonary function tests. These tests help measure the lungs’ ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. The tests are often done with special machines into which you breathe.
Can pulmonary emphysema be repaired?
There is no way to repair or regrow the damaged lung tissue. The goal of treatment for people with pulmonary emphysema is to live more comfortably, control symptoms, and prevent the disease from getting worse. A key part of treatment is to quit smoking.
What is COPD in medical terms?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an umbrella term given to a group of chronic lung diseases that make it harder to breathe air out of the lungs. These diseases include emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and sometimes asthma.
How can COPD be prevented?
COPD can usually be prevented by maintaining healthy habits. However, it remains the third leading cause of death in the United States. COPD affects around 30 million people throughout the country. In addition to quitting smoking or never picking up the habit, you can protect your lungs by avoiding pollutants.
How does electronic cigarettes affect the lungs?
Little is known about how electronic cigarettes, also called e-cigarettes, exactly affect the lungs and whether they contribute to COPD or other lung diseases.
What happens when the alveoli are stretched?
As alveoli become permanently stretched and their walls rupture, the lungs will have trouble taking in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide. This forces the heart and lungs to work harder and decreases the oxygen available to other organs and tissues, causing further damage.
What is the treatment for bronchodilators?
Other treatments include supplemental oxygen therapy. In rare cases, lung volume reduction surgery or even a lung transplant may be required.
Can you have COPD and not have emphysema?
However, it’s possible to be diagnosed with COPD and not have emphysema. A person can receive a COPD diagnosis while only having chronic bronchitis, for instance. Emphysema is usually the direct result of years of smoking cigarettes. Its symptoms tend to affect people who are middle-aged or older.
Does smoking cause bronchitis?
This results in damage to the tiny air sacs in the lungs called alveoli. This damage occurs in people with emphysema. Inflammation caused by smoking can lead to chronic bronchitis and damage the breathing tubes and bronchi, even though the alveoli may not yet be damaged permanently.

Overview
Causes
- The main cause of emphysema is long-term exposure to airborne irritants, including: 1. Tobacco smoke 2. Marijuana smoke 3. Air pollution 4. Chemical fumes and dust Rarely, emphysema is caused by an inherited deficiency of a protein that protects the elastic structures in the lungs. It'…
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology
Effects
Symptoms
- Emphysema is a disease of the lungs that usually develops after many years of smoking. Both chronic bronchitis and emphysema belong to a group of lung diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Once it develops, emphysema cant be reversed. This is why not smoking or stopping smoking is very important.