
What is the process of beta oxidation?
Beta- oxidation is a metabolic process whereby fatty acids are broken down into acetyl-CoA. There are four reactions in the process, and these reactions repeat until the entire fatty acid chain has been converted into individual acetyl-CoA molecules. Each of these molecules is then processed for energy.
What does beta oxidation produce?
What are the products of beta oxidation? The products of beta-oxidation are FADH2, NADH, H+, and acetyl-CoA. One of each of these molecules is produced for each round of beta-oxidation a fatty acid...
What is beta oxidation?
Beta oxidation, also referred to as β-oxidation, is a process of breaking down unsaturated fatty acids with the help of enzymatic action. More simply, beta oxidation is also known as the process of breaking down long chain fatty acids that is essential for the body to absorb these types of fatty acids.
Where does beta oxidation occur?
Oxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body; the mitochondria, in which only Beta-oxidation occurs; the peroxisome, where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur; and omega-oxidation, which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Is fatty acid oxidation the same as beta oxidation?
An overview of fatty acid oxidation is provided in Figure 1. Fatty acid β-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids are broken down to produce energy. Fatty acids primarily enter a cell via fatty acid protein transporters on the cell surface. Once inside, FACS adds a CoA group to the fatty acid.
Why is the oxidation of fatty acids called β-oxidation of fatty acids quizlet?
Why is fatty acid oxidation often called B-oxidation? The major reaction site is the beta-carbon or #3 carbon from the thioester carbon. The bond between the α (C2) and β carbon (C3) of the fatty acid is broken during each round of the cycle. steps of TCA cycle.
Why is β-oxidation also called the fatty acid spiral chain?
Because each shortened fatty acyl-CoA cycles back to the beginning of the pathway, β-oxidation is sometimes referred to as the fatty acid spiral. The fate of the acetyl-CoA obtained from fatty acid oxidation depends on the needs of an organism.
What is fatty acid oxidation called?
The process of fatty acid oxidation, called beta oxidation, is fairly simple.
Where does beta oxidation of fatty acids occur in the cell?
the mitochondriaOxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body; the mitochondria, in which only Beta-oxidation occurs; the peroxisome, where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur; and omega-oxidation, which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Why is beta oxidation important quizlet?
Because the acyl group will generate energy within the mitochondrial matrix (which the purpose of beta oxidation) this step is important for the generation of energy from lipids.
What is beta oxidation explain it?
Beta oxidation is a metabolic process involving multiple steps by which fatty acid molecules are broken down to produce energy. More specifically, beta oxidation consists in breaking down long fatty acids that have been converted to acyl-CoA chains into progressively smaller fatty acyl-CoA chains.
Why do fatty acids need to be activated before they can be catabolized by β-oxidation?
Once the triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids they must be activated before they can enter into the mitochondria and proceed on with beta-oxidation. This is done by Acyl-CoA synthetase to yield fatty acyl-CoA. After the fatty acid has been acylated it is now ready to enter into the mitochondria.
Is beta oxidation anabolic or catabolic?
Answer and Explanation: Beta-oxidation is a catabolic process where fatty acids are broken down to produce acetyl CoA.
Is lipolysis the same as beta oxidation?
Lipolysis. To obtain energy from fat, triglycerides must first be broken down by hydrolysis into their two principal components, fatty acids and glycerol. This process, called lipolysis, takes place in the cytoplasm. The resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β-oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle ...
Where is the beta carbon on a fatty acid?
The first carbon following the carboxyl carbon is the alpha carbon. The second carbon following the carboxyl carbon is the beta carbon. The last carbon in the chain, farthest from the carboxyl group, is the omega carbon.
What is beta oxidation of fatty acids PDF?
Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria and/or peroxisomes to generate acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle. Fatty acids are oxidized by most of the tissues in the body.
What is de novo synthesis of fatty acids?
De novo fatty-acid synthesis involves two key enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty-acid synthase (FASN). ACC carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA. The malonyl-CoA product is further converted by FASN to long-chain fatty acids.
What is called fatty acid?
Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Fatty acid molecules are usually joined together in groups of three, forming a molecule called a triglyceride.
Where can gluconeogenesis occur?
Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidneys. Gluconeogenesis supplies the needs for plasma glucose between meals. Gluconeogenesis is stimulated by the diabetogenic hormones (glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine, and cortisol). Gluconeogenic substrates include glycerol, lactate, propionate, and certain amino acids.
What are the products of fatty acid oxidation?
The products are acetyl-CoA and a fatty acyl-CoA that has been shortened by two carbon atoms.
What changes in the rate of fatty acid oxidation?
The rate of fatty acid oxidation changes in response to the hormonal and nutritional state of the animal. The rate of fatty acid oxidation is high during fasting but low within the fed animal.
What is the function of fatty acids in metabolism?
Therefore, Fatty acid metabolism consists of catabolic processes that generate energy and anabolic processes that make biologically important molecules (phospholipids, triglycerides, second messengers, ketone bodies, and local hormones). Fatty acids are a family of molecules and these are classified within the lipid macronutrient class.
Why do unsaturated fatty acids complicate the picture a bit?
Unsaturated fatty acids complicate the picture a bit, primarily because they have cis bonds, for the most part, if they are of biological origin and these must be converted to the relevant trans intermediate made in step 1. Sometimes the bond must be moved down the chain, as well, in order to be positioned properly.
What is the process of beta oxidation?
Beta-oxidation occurs in cycle and each cycle consists of sequence of four enzymatic reaction: An oxidation step that produce FADH 2. A hydration step. A second oxidation step that produce NADH+ H +. A thiolytic cleavage that release a molecule of acetyl coA.
Where does oxidation occur?
Oxidation of fatty acid (FA) releases large amount of energy. Oxidation of fatty acid occurs in mitochondria cell lacking mitochondria (e.g. RBC) and brain cell (due to blood brain barrier) cannot oxidize FA to release energy. Most of the fatty acids are oxidized by beta-oxidation.
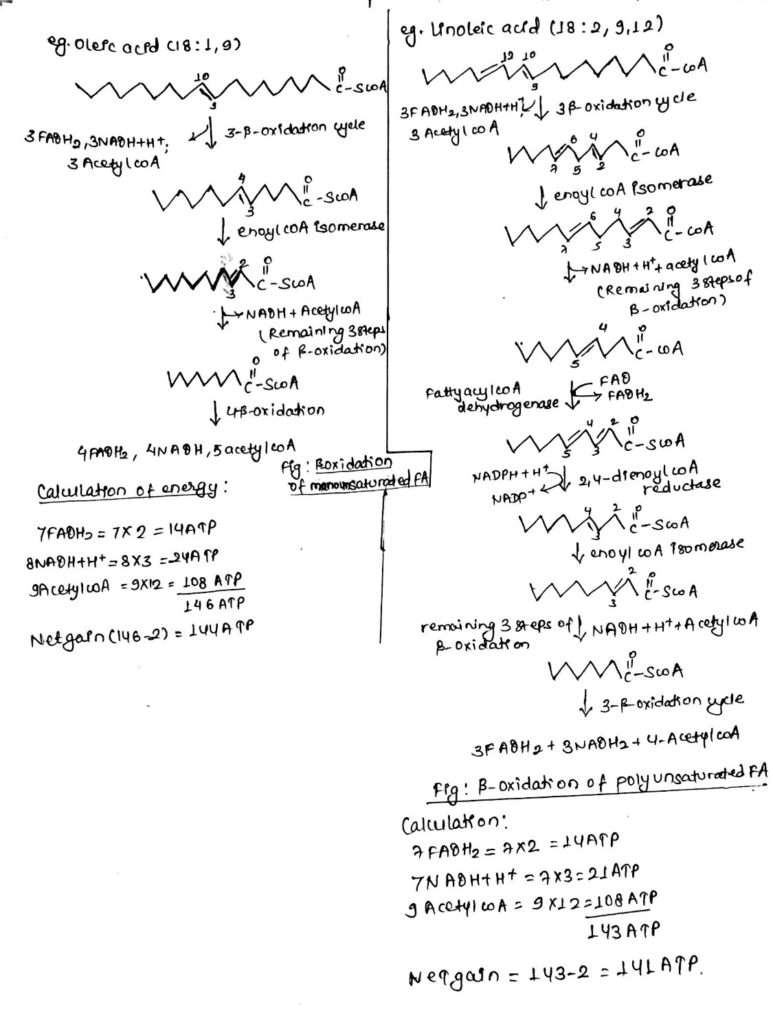
What enzyme is used to oxidize poly unsaturated fatty acids?
similarly, due to presence of two or more double bonds, beta oxidation of poly unsaturated fatty acid requires two additional enzymes- enoyl coA isomerase and 2, 4- dienoyl coA reductase.
Is monounsaturated fatty acid a double bond?
monounsaturated fatty acid consists of a double bond. Beta oxidation of monounsaturated fatty acid involves most of the reactions same as found in beta oxidation of saturated fatty acid. However, an extra enzyme enoyl coA isomerase is needed. similarly, due to presence of two or more double bonds, beta oxidation of poly unsaturated fatty acid ...
