The fed funds rate is a range because the Federal Reserve cannot mandate a set number. Instead, it sets the target rate as a guide for banks to follow. Thus, the volume-weighted median of overnight banking transactions become the effective federal funds rate.
How to calculate federal funds rate?
federal funds target rate = real interest rate + current inflation rate + 0.5 * inflation rate gap + 0.5 * output gap. So plugging in the numbers from our example, thats: 1% + 4% + 0.5 * 2% + 0.5 * (-0.18%) = 5.91%. Use our Taylor rule calculator to avoid all of these laborious computations!
What is the current effective fed funds rate?
The U.S. federal funds effective rate was drastically lowered between February and April 2020. It dropped from 1.58 percent in February that year, down to 0.65 in March, and further down to 0.05 in April.
What is the daily fed funds rate?
The fed funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions (banks and credit unions) lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight, on an uncollateralized basis. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times a year to determine the federal funds target rate. The current federal funds rate as of April 08, 2022 is 0.33%.
What does the federal funds rate refer to?
The federal funds rate refers to the interest rate that banks charge other banks for lending to them excess cash from their reserve balances on an overnight basis. By law, banks must maintain a reserve equal to a certain percentage of their deposits in an account at a Federal Reserve bank.

Is the Fed funds rate a range?
The Federal Open Markets Committee (FOMC) sets the federal funds rate—also known as the federal funds target rate or the fed funds rate—to guide overnight lending among U.S. banks. It's set as a range between an upper and lower limit. The federal funds rate is currently 3% to 3.25%.
Why is the Fed Funds rate so important?
The federal funds rate is one of the most important interest rates in the U.S. economy. That's because it affects monetary and financial conditions, which in turn have a bearing on critical aspects of the broader economy including employment, growth, and inflation.
How does the Federal Reserve keep the federal funds within the target range?
The two tools used to keep the FFR in the target rate range are: Interest on reserve balances (IORB): The Fed pays interest on the reserves that banks keep with it. Overnight reverse repurchases (ON RRP): The Fed sells securities to banks that aren't eligible for interest on reserve balances.
What does a higher fed funds rate mean?
The fed funds rate is determined by the money supply, which is controlled by the Fed via buying and selling U.S. Treasury securities. 1. Higher money supply leads to higher inflation, pushing down the federal funds rate.
What happens when fed funds rate increases?
This key interest rate impacts how much commercial banks charge each other for short-term loans. A higher fed funds rate means more expensive borrowing costs, which can reduce demand among banks and other financial institutions to borrow money.
What is the difference between fed funds rate and interest rate?
The fed funds rate is the interest rate that depository institutions—banks, savings and loans, and credit unions—charge each other for overnight loans. The discount rate is the interest rate that Federal Reserve Banks charge when they make collateralized loans—usually overnight—to depository institutions.
Why is the federal funds rate so influential on other interest rates?
Why is the Federal Funds Rate so influential on other interest rates? The Federal Funds Rate is influential because it determines at what interest rate banks borrow money. How does the Federal Funds Rate affect consumers looking to take out a loan? The Federal Funds Rate is the rate at which banks borrow money.
Why is the federal funds rate often lower than the discount rate?
The discount rate is typically set higher than the federal funds rate target, usually by 100 basis points (1 percentage point), because the central bank prefers that banks borrow from each other so that they continually monitor each other for credit risk and liquidity.
What is the current fed funds target rate?
3.00-3.25Fed Funds RateThis weekMonth agoFed Funds Rate (Current target rate 3.00-3.25)3.253.25
How does fed funds rate affect economy?
By increasing the federal funds rate, the Federal Reserve is effectively attempting to shrink the supply of money available for making purchases. This, in turn, makes money more expensive to obtain. Conversely, when the Federal Reserve decreases the federal funds rate, it increases the money supply.
How does federal funds rate affect inflation?
When inflation is too high, the Federal Reserve typically raises interest rates to slow the economy and bring inflation down. When inflation is too low, the Federal Reserve typically lowers interest rates to stimulate the economy and move inflation higher.
How does the Fed funds rate affect other interest rates?
The federal funds rate influences the prime rate, which influences all other interest rates, such as the rates on mortgages and personal loans. But if interest rates fall, the same home for the same purchase price will result in lower monthly payments and less total interest paid over the life of the mortgage.
Why is the federal funds rate so influential on other interest rates quizlet?
Why is the Federal Funds Rate so influential on other interest rates? The Federal Funds Rate is influential because it determines at what interest rate banks borrow money.
How does the Fed funds rate affect Treasury yields?
An increase in fed funds (short-term) tends to flatten the curve because the yield curve reflects nominal interest rates: higher nominal = higher real interest rate + lower inflation.
How does the federal funds rate affect other interest rates?
Set by the Federal Reserve, the federal funds rate is the interest banks charge each other to borrow money overnight. Changes in the federal funds rate influence the interest rates on loans, credit cards, and bank accounts. The federal funds rate is the key tool the Fed uses to stimulate or slow down the economy.
What happens when the federal funds rate decreases?
If the Fed wants the federal funds rate to decrease, then it buys government securities from a group of banks. As a result, those banks end up holding fewer securities and more cash reserves, which they then lend out in the federal funds market to other banks.
What Is The Federal Funds Rate?
Understanding The Federal Funds Rate
- The federal funds rate refers to the interest rate that banks charge other institutions for lending excess cash to them from their reserve balances on an overnight basis. By law, banks must maintain a reserve equal to a certain percentage of their deposits in an account at a Federal Reserve bank. The amount of money a bank must keep in its Fed account is known as a reserve …
Special Considerations
- The FOMC cannot force banks to charge the exact federal funds rate. Rather, the FOMC sets a target rate as a guidepost. The actual interest rate a lending bank will charge is determined through negotiations between the two banks. The weighted average of interest rates across all transactions of this type is known as the effective federal funds rate.2 While the FOMC can't ma…
Impact of The Federal Funds Rate
- The federal funds rate is one of the most important interest rates in the U.S. economy. That's because it affects monetary and financial conditions, which in turn have a bearing on critical aspects of the broader economy including employment, growth, and inflation. The rate also influences short-term interest rates, albeit indirectly, for everythin...
Overview
In the United States, the federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions (banks and credit unions) lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight on an uncollateralized basis. Reserve balances are amounts held at the Federal Reserve to maintain depository institutions' reserve requirements. Institutions with surplus balances in their accounts lend those b…
Mechanism
Financial institutions are obligated by law to hold liquid assets that can be used to cover sustained net cash outflows. Among these assets are the deposits that the institutions maintain, directly or indirectly, with a Federal Reserve Bank. An institution that is below its required liquidity can address this temporarily by borrowing from institutions that have Federal Reserve deposits in excess of the requirement. The interest rate that a borrowing bank pays to a lending bank to bor…
Applications
Interbank borrowing is essentially a way for banks to quickly raise money. For example, a bank may want to finance a major industrial effort but may not have the time to wait for deposits or interest (on loan payments) to come in. In such cases the bank will quickly raise this amount from other banks at an interest rate equal to or higher than the Federal funds rate.
Raising the federal funds rate will dissuade banks from taking out such inter-bank loans, which i…
Comparison with LIBOR
Though the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR), the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) and the federal funds rate are concerned with the same action, i.e. interbank loans, they are distinct from one another, as follows:
• The target federal funds rate is a target interest rate that is set by the FOMC for implementing U.S. monetary policies.
Predictions by the market
Considering the wide impact a change in the federal funds rate can have on the value of the dollar and the amount of lending going to new economic activity, the Federal Reserve is closely watched by the market. The prices of Option contracts on fed funds futures (traded on the Chicago Board of Trade) can be used to infer the market's expectations of future Fed policy changes. Based on CME Group 30-Day Fed Fund futures prices, which have long been used to express the market's …
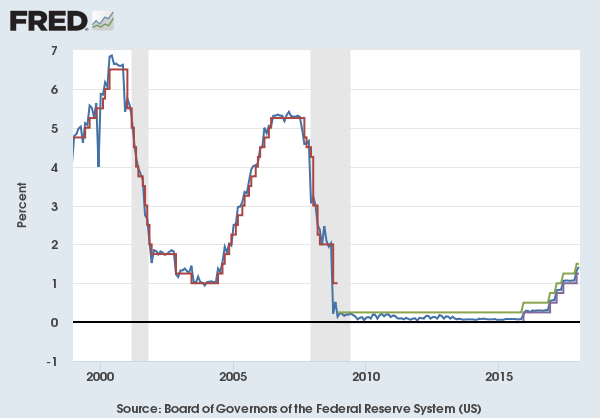
Historical rates
The last full cycle of rate increases occurred between June 2004 and June 2006 as rates steadily rose from 1.00% to 5.25%. The target rate remained at 5.25% for over a year, until the Federal Reserve began lowering rates in September 2007. The last cycle of easing monetary policy through the rate was conducted from September 2007 to December 2008 as the target rate fell from 5.25% to …
Explanation of federal funds rate decisions
When the FOMC wishes to reduce interest rates they will increase the supply of money by buying government securities. When additional supply is added and everything else remains constant, the price of borrowed funds – the federal funds rate – falls. Conversely, when the Committee wishes to increase the federal funds rate, they will instruct the Desk Manager to sell government securities, thereby taking the money they earn on the proceeds of those sales out of circulation …
International effects
A low federal funds rate makes investments in developing countries such as China or Mexico more attractive. A high federal funds rate makes investments outside the United States less attractive. The long period of a very low federal funds rate from 2009 forward resulted in an increase in investment in developing countries. As the United States began to return to a higher rate in the end of 2015 investments in the United States became more attractive and the rate of investmen…