Glycolysis Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO + H. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and N…Glycolysis
What are the five steps of glycolysis?
The Energy-Requiring Phase of Glycolysis
- In the first step of glycolysis, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose, creating glucose-6-phosphate.
- During step two of glycolysis, glucose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase.
- A second ATP molecule is used to phosphorylate fructose-6-phosphate, producing fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
Which is true about glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates. However, glycolysis doesn't require oxygen, and many anaerobic organisms—organisms that do not use oxygen—also have this pathway. Click to see full answer. Hereof, what happens simple glycolysis?
What are the steps of glycolysis?
What are the irreversible steps of glycolysis?
- Hexokinase
- Pyruvate kinase
- Phosphofructokinase
What is the pathway of glycolysis?
Like all biochemical reactions, glycolysis follows a pathway, i.e., a series of chemical reactions each of which is catalyzed by a separate enzyme. Glycolytic pathway is the first step in respiration, where glucose, the respiratory substrate, is oxidized to a simpler organic compound.

Why glycolysis is called?
In glycolysis also known as EMP pathway ,glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in almost all living organism. In anaerobic organism, it is the only process in respiration.
What does glycolysis mean literally?
“breakdown of sugarGlycolysis, which literally means “breakdown of sugar," is a catabolic process in which six-carbon sugars (hexoses) are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis.
What is glycolysis also called?
The scheme of glycolysis was given by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas. Hence it is also known as the EMP pathway.
Who named glycolysis?
Glycolysis is also called as EMP pathway. It was named after the discoverers Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas. It is the common process involved in the aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What is the difference between glycolysis and glycolysis?
Glycolysis – It is an anaerobic process, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. In glycolysis, partial oxidation of glucose occurs, which yields two molecules of pyruvic acid....Also Read:GlycolysisOverview of cellular respirationDifference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic RespirationCytoplasm
What is glycolysis in a sentence?
How to use glycolysis in a sentence. Meyer and Balk's collaboration found that the plants do produce more proteins for use in glycolysis, an inefficient method of splitting apart sugars to make ATP that's found in all cells.
Which best describes what glycolysis is?
Glycolysis is the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid (also called pyruvate). The glycolysis process is a multi-step metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of animal cells, plant cells, and the cells of microorganisms.
Is glycolysis short term or long term?
Physiologically, glycolysis produces energy at a high rate but for a short duration. Biopsies of animal muscle indicate two types of tissue; the two types have different metabolic activities.
What is the opposite of glycolysis?
Gluconeogenesis means new synthesis of glucose. It is the reverse of glycolysis. The body makes glucose in the liver (and also in the kidney).
Why is glycolysis the oldest?
The many steps in the process of aerobic cellular respiration can be divided into three stages. The first stage, glycolysis, produces ATP without oxygen. Because this part of the cellular respiration pathway is universal, biologists consider it the oldest segment.
What does the word glycolysis mean quizlet?
Glycolysis - definition. The breakdown of one molecule of glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (2 x 3C) with a small net yield of ATP (2 molecules of ATP)
What is glycolysis kid friendly?
Glycolysis means ''glucose splitting'' and that is just what happens during this first step of cellular respiration. A glucose molecule hanging out in a cell is split in half to make two smaller molecules of a chemical called pyruvate. During this splitting some energy—two molecules of ATP—is made.
Why is glycolysis considered ancient?
Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. It takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve since it is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth.
What is glycolysis used for?
Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that is used by all cells for the oxidation of glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) and intermediates for use in other metabolic pathways.
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms.
What is the substrate of trise phosphate isomerase?
Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
How is phosphoenolpyruvate transferred to ADP?
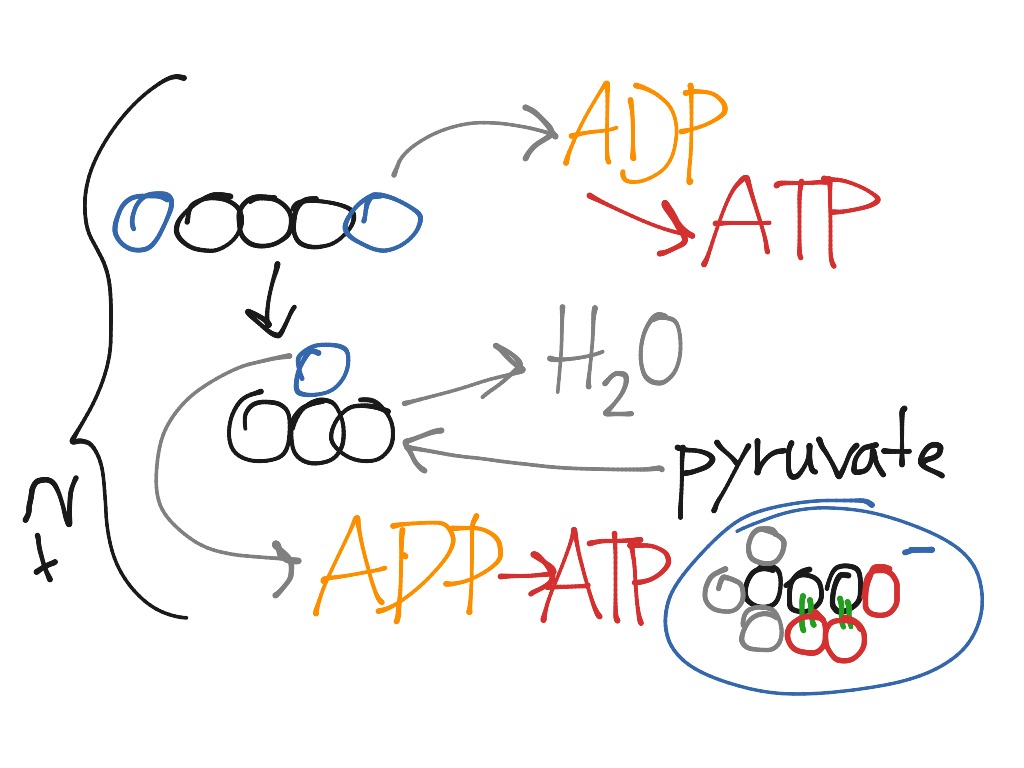
A phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP to form pyruvate and ATP by the action of pyruvate kinase. Two molecules of pyruvate and ATP are obtained as the end products.
How many molecules of phosphoglycerate are in ATP?
Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
What is the primary step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration. In the absence of oxygen, the cells take small amounts of ATP through the process of fermentation. This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and is known as the EMP pathway ...
How is a phosphate group added to glucose?
A phosphate group is added to glucose in the cell cytoplasm, by the action of enzyme hexokinase. In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,6-phosphate.
Which enzyme is responsible for the phosphoglycerate molecule?
The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
What is the process of breaking large molecules into smaller units?
Catabolism is a series of processes which break large molecules into smaller units. Anabolism is assembly of small units into larger molecules.
What is the process of catabolism and anabolism?
For the function, multiplication and division of cells, metabolism is required. The process of both catabolism and anabolism is generally termed as Metabolism .
What is the function of PFK2?
PFK2 (Phosphofructokinase 2) catalyse the synthesis of F2,6-BP. In glycolysis as fructose 6 phosphate is formed some goes for synthesis of F2,6-BP. And this F2,6 -BP activate PFK1.
What is the first step in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis is the first part of cellular respiration. During glycolysis, the Oxidation of glucose begins, and some electrons are transferred to NAD: Additionally, a small amount of energy is transferred to ATP. Glycolysis converts a single glucose molecule, which contains six carbon atoms, Into two molecules of pyruvate, each of which has three carbon atoms. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
What is the first step in lipid synthesis?
Glycolysis is the initial step in the conversion of glucose to lipid, and glycolysis can under this condition be viewed at an anabolic reaction; the first step in lipid synthesis from glucose.
What is the molecule that controls the energy state of the cell?
The molecule that controls that choice is phosphofructokinase (PFK-1). PFK-1 represents the committed step in glycolysis. It is directly responsive to the energy state of the cell, that is to say that the enzyme is up-regulated by AMP (indicating low cellular energy) and down-regulated by ATP (indicating high cellular energy). Additionally, PFK-1 is feedback regulated by the glycolytic product phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP), the presence of which indicating that pyruvate kinase is not fully active (probably because of an abundance of amino acids (alanine) or cellular energy). Finally, cells respond to the hormonal signals of insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine via the presence or absence of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. This molecule is synthesized and degraded by the phosphofructokinase 2/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase bifunctional enzyme. Phosphorylation of this enzyme by protein kinase A. Protein kinase A is activated by the presence of cyclic AMP (cAMP). cAMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylyl cyclase, and adenylyl cyclase is activated through a G-protein/G-protein coupled receptor system that is responsive to either glucagon or epinephrine. Insulin reverses this process. Thus, PFK-1 controls glycolysis in response to the needs of the body as well as the needs of the cell itself.
What is the process that allows an organism to live, grow, reproduce, heal, and adapt to its environment?
Metabolism is a biochemical process that allows an organism to live, grow, reproduce, heal, and adapt to its environment. Anabolism and catabolism are two metabolic processes, or phases. Anabolism refers to the process which builds molecules the body needs; it usually requires energy for completion. Catabolism refers to the process that breaks down complex molecules into smaller molecules; it usually releases energy for the organism to use.
