Why is Heijunka important to understand? As one of the foundational elements of TPS, Heijunka will help stabilize and level your production cycle. Use of takt time to drive your process
Why leveling (Heijunka) is important?
Why Leveling (Heijunka) is important. Production leveling, also known as heijunka ( 平準化) or production smoothing, is one of the hottest topics in lean manufacturing. Successful leveling is considered one of the highest achievements in lean manufacturing. Unfortunately, if the production system is not ready for leveling,...
What is heijunka in production?
Heijunka: The Art of Leveling Production. 7 comments. Heijunka (pronounced hi-JUNE-kuh) is a Japanese word that means “leveling.” When implemented correctly, heijunka elegantly – and without haste – helps organizations meet demand while reducing while reducing wastes in production and interpersonal processes.
What is the fulcrum of heijunka?
Changeover time: Efficiency of changeover is the fulcrum of heijunka; narrowing changeover times helps tighten the value stream between supply and demand.
Is heijunka a “self inflicted choice”?
Dr. Jeffrey Liker explains that implementing heijunka is a “self inflicted choice.” Sounds painful, eh?

Why do we need heijunka?
Heijunka allows you to level your production by the average volume of orders you receive. For example, if your average demand is 20 orders per week, but the number fluctuates by the day (e.g., Mon 3; Tue 10; Wed 5; etc.), it would be wise to implement Heijunka to level the production by volume.
What is the core idea of heijunka?
Heijunka is the process of leveling the type and amount of production over a set period of time. The goal is to iron out issues like overproduction, or batching — which has the added benefit of minimizing waste, reducing labor, maximizing inventory space, and reducing production lead time.
What does heijunka aim to level?
Heijunka (pronounced hey-june-kuh) is a Japanese word that means leveling. In Lean, it refers to the leveling of production, aimed at improving the flow of a process to better match customer demand, reduce waste, and decrease or quit batch processing.
How does a heijunka board help in reducing the waiting time in a project?
Heijunka helps avoid the inefficiencies of manufacturing in large lots by putting the production process closer in line with customer demand. The flexibility that Heijunka instills brings three benefits to manufacturing: Predictability – Happens when demand is level. Flexibility – Achieved by reducing changeover time.
What are the 2 elements of heijunka?
There are at least five elements of HEIJUNKA: the interval in which all products will be produced (1) a fixed sequence of products (2), a predetermined inventory policy (3), variable number of items for each product (4) and the direction for improvement (5).
What are the disadvantages of heijunka?
Drawbacks of HeijunkaHeijunka trades inventory or lead time for stability.Heijunka limits rapid adjustments.Heijunka requires industrial discipline.Heijunka can only handle moderate variations in demand.
Who uses heijunka?
The Toyota Production System uses Heijunka to solve the former by assembling a mix of models within each batch, and ensuring that there is an inventory of product proportional to the variability in demand.
Why is level loading important?
It prevents new orders from being processed until the Work in Progress is completed. Level loading also ensures that a company is able to meet customer demands through either the current inventory or the current production schedule.
Why should you level production?
Leveling Production is a very important Lean Principle in which it smoothens the production process. It enables production to make the material flow at the pull of the customer which will reduce upstream schedule variability and response times to changes in demand.
What is the purpose for reducing setup time?
Setup Reduction is a technique useful for level load balancing, a key strategy for lean deployment. Setup Time is defined as the time to change from the last item of the previous order to the first good item of the next order.
How can we reduce waiting in lean manufacturing?
Steps that Lean Consultants recommend to reduce or eliminate Waiting Waste include:redesigning processes to ensure even production flow or even single piece flow in response to the manufacturing process 'pull'standardizing instructions, training and processes.More items...•
Which tool is used to reduce the time for production?
What Are Lean Tools?Lean ToolsSummaryBottleneck AnalysisStructured way of looking at workflowsJust-in-Time (JIT)On-demand system of productionValue Stream MappingAnalyzing and optimizing a processOverall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)Measure of productive time3 more rows•Jun 30, 2021
What is the core idea of lean manufacturing?
The core idea behind lean is maximizingcustomer valuewhile minimizing waste,” states LEI. “Simply put, lean means creating more value for customers with fewer resources.” A lean organization understands customer value and focuses its key processes to continuously increase it.
What does Yokoten meaning?
Yokoten is a Japanese term that can be roughly translated as “across everywhere.” In the Japanese lean system, it is used to mean “best practice sharing.” In short, Yokoten is used to talk about the transfer of lean manufacturing knowledge and practices from one operation to another.
What is the core of a production system?
Inputs into the technical core include human resources, land, equipment, buildings and technology. Outputs from the technical core include the goods and services that are provided for customers and clients.
What is the main purpose of visual controls?
Visual controls are designed to make the control and management of a company as simple as possible. This entails making problems, abnormalities, or deviations from standards visible to everyone. When these deviations are visible and apparent to all, corrective action can be taken to immediately correct these problems.
What is Heijunka?from safetyculture.com
Heijunka is one of the thirteen pillars of the Toyota Production System and was established to save production costs and reduce the unevenness in a production process. It is a Japanese term for “leveling” which allows organizations to optimize their inventory management system in order to meet customer needs and depend on customer buying rates. It is a lean manufacturing method that helps reduce overproduction by processing orders based on customer demand and avoiding bulk production in batches.
When is Heijunka applicable?from kanbanize.com
Heijunka is applicable when you are managing a portfolio of products as well. It allows you to level production based on the average demand for each product in the portfolio and organize your work around it.
Why use Heijunka Box?from kanbanize.com
However, in this case, you need to use Heijunka to level production even further so you can keep up with the demand for each product. Facing this challenge, Toyota developed a tool called Heijunka Box to visualize the number of vehicles they need to produce for each model.
What is Heijunka method?from kanbanize.com
Heijunka allows you to produce and deliver value to your customer at a steady pace so that you can react to fluctuations according to your average demand. For that purpose, the method has two ways of leveling production:
Why is lean thinking important?from kanbantool.com
But Lean seeks to reduce the lead time, improve quality and value to the customer at all times. Lean thinking takes from the Kanban method, meaning that items are not built to forecast for future demand, but are produced only when customers order them. This way, production teams will never be working on products that won’t sell.
Why should work be sequenced?from kanbantool.com
Work should be sequenced to ensure many small batches as opposed to one large volume and to execute order delivery in the same sequence that it was placed in . At Toyota, the ordering of materials and production of goods is aligned with the principle of Just-In-Time ( JIT) - items are simply delivered to customers when they need it.
Can you order multiple items in a Heijunka box?from kanbanize.com
Depending on your takt time, you may need to place multiple or no orders in each box. In the Toyota Production system, each item in the Heijunka box is a Kanban card that later goes through their manufacturing process steps. Partner with Kanbanize. Learn more.
What is Heijunka?
Heijunka is one of the thirteen pillars of the Toyota Production System and was established to save production costs and reduce the unevenness in a production process. It is a Japanese term for “leveling” which allows organizations to optimize their inventory management system in order to meet customer needs and depend on customer buying rates. It is a lean manufacturing method that helps reduce overproduction by processing orders based on customer demand and avoiding bulk production in batches.
What is Heijunka in manufacturing?
Heijunka in lean manufacturing aims to improve production workflow to better match the customer orders, reduce wastes, and minimize the chance of overburden. It helps the organization to achieve the following:
What is a Heijunka box?
In manufacturing scenarios, it’s been common to use a Heijunka Box - a tool built from table-like cells with room for Kanban cards representing various order types and their amount. The same can be shown on a virtual Kanban board with swimlanes - horizontal rows. A team could use columns for days of the week, and rows for different product types, and place the demanded number of cards in each cell.
Why should work be sequenced?
Work should be sequenced to ensure many small batches as opposed to one large volume and to execute order delivery in the same sequence that it was placed in . At Toyota, the ordering of materials and production of goods is aligned with the principle of Just-In-Time ( JIT) - items are simply delivered to customers when they need it.
Is Heijunka a state?
Heijunka is not an easy state to be achieved and it does need a company to persist on its Lean journey. A leveled production is often associated with a mature Lean implementation and it often comes about together with the following practices: To achieve Heijunka, a company should do the following:
Why is Heijunka important to understand?
As one of the foundational elements of TPS, Heijunka will help stabilize and level your production cycle.
What is the purpose of Heijunka?
The purpose of Heijunka is to meet customer demand through smaller batches, standardized work, and single-minute exchange of dies (SMED). The graphic below shows where Heijunka fits into the TPS model.
What is Heijunka schedule?
The Heijunka schedule is driven by your takt time or takt rate. Use a pull system for your production cycle rather than a push system.
What is heijunka in manufacturing?
Heijunka is a lean manufacturing technique for reducing unevenness in a production cycle. The word itself means leveling in Japanese. It was first used by the Toyota Production System (TPS) to develop production efficiency. It forms the foundation of TPS along with the concepts of standard work and Kaizen.
How does Heijunka achieve production leveling?
Heijunka accomplishes production leveling by the use of two different strategies: leveling by volume or leveling by product. Let’s explore each.
What is a heijunka box?
Definition of Heijunka: A Japanese term that means “leveling.”. When implemented correctly, heijunka provides predictability by leveling demand, flexibility by decreasing changeover time and stability by averaging production volume and type over the long term. The heijunka box helps visualize the optimized production schedule.
What is the concept of Heijunka?
The concept of Heijunka is linked to the concepts of takt time and takt rate. No manufacturing system can be stable if there are uneven levels of production.
Why is Heijunka important?
Before talking about putting heijunka in place, let’s consider how Lean expert Michael Ballé describes the importance of heijunka to Lean organizations: By producing every product during every relevant timeframe, lead time is reduced and the business is closer to meeting “real” demand.
What Is Heijunka?
Here is how Lean Lexicon, 4th Edition defines heijunka: “Leveling the type and quantity of production over a fixed period of time. This enables production to efficiently meet customer demands while avoiding batching and results in minimum inventories, capital costs, manpower, and production lead time through the whole value stream .”
What should the frame of a Heijunka implementation begin with?
The frame of any heijunka implementation should begin with takt time and end with a heijunka box.
What percentage of capacity is needed for Heijunka?
What’s the catch? Changeover time. Heijunka depends significantly upon putting a percentage of capacity (Ballé recommends 10 percent) into changeover flexibility. “If you want to make every product every day, which is kind of the Lean first goal, you need to reduce changeover time accordingly,” Ballé writes. Demand forecasts are often not quite right, and sometimes completely wrong. Increasing changeover flexibility and efficiency protects a production line from demand ambushes set up by the forecasts themselves.
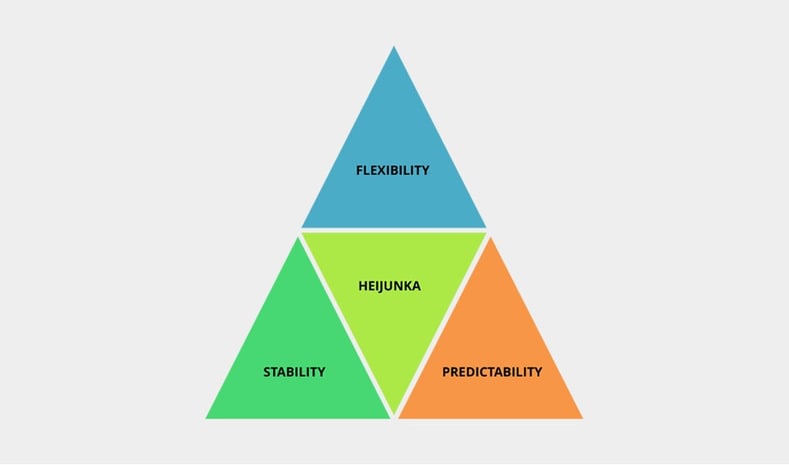
Which relationship is a predictability, flexibility, and stability?
Figure 1: Relationship Among Predictability, Flexibility and Stability Is Heijunka – When implemented correctly, heijunka provides predictability by leveling demand, flexibility by decreasing changeover time and stability by averaging production volume and type over the long term.
What is the essence of Heijunka?
That is the essence of heijunka: pulling production in tight and cozy with demand. If all product types are created (and stored as necessary) throughout a year, flexibility is increased, the hats should all sell (perhaps not immediately, but eventually) and production will be able to meet peak demand periods.
Is Heijunka better than Lean?
According to many Lean experts, heijunka is better achieved as a later-stage implementation in a Lean organization, long after value streams have been identified and solidified and refined, when Lean philosophy and legacy are already deeply embedded into process and materials cycles.
What is Heijunka?
The Toyota House, or the TPS House, is a great metaphor for the Toyota Production System. The TPS House is based on the idea that “A House Divided Cannot Stand”, Citing the great Abraham Lincoln, who is quoting from the Bible. This means that every part of the house has a role and has a specific purpose.
Not Heijunka
Suppose you run an operation where you make small widgets (11 A), medium widgets (9 B), and large widgets (7 C). You follow a production schedule that looks like this:
Why Heijunka is a Foundational Block in Lean
We’ve seen from the non-heijunka example above that there are several wastes that come from a non-level production environment. If what I say is true, then much of continuous improvement will be limited if there is no level production. In fact, in that environment most of the mental and physical energy is trying to figure out what is going on.
The Challenge of Heijunka
One challenge of Heijunka is in its application. Depending on the industry and business you are in, the application will generally need to adjust. But the principle remains the same – to level production, create stability and predictability.
Introduction to Heijunka
Here’s the introduction to Heijunka and How to apply Heijunka in your operation.
Why is Heijunka important?
Heijunka also allows us to schedule resources (equipment , employees, etc.) in a more balanced manner. Instead of having employees stand around in January or February, when demand is lower , and then watching them run around like maniacs and paying “mandatory” overtime in October and November during the peak season we can level the demand producing the same or similar amounts throughout the year. In some cases this may mean overproducing and carrying a small amount of inventory during the slow seasons as we prepare for the peak season. While not the perfect situation this is far better than the alternative.
What about the challenges to Heijunka?
Liker means is that when we implement heijunka, and one piece flow for that matter, we can no longer allow things like long changeovers to exist, or to produce defect after defect, or to basically hide behind the piles of inventory mass producers do. These crutches are gone.
What is the bull whip effect?
The “bullwhip” effect is common in mass production circles. The slight twist of the wrist (i.e. demand) can create a massive strike at the end of the bull whip. This means even small demand variations can wreak havoc throughout our plant and especially with our suppliers. If you don’t believe me just ring up some of Dell’s suppliers and ask them how demand gyrations impact them. Dell doesn’t just flip their wrists… they wind up and pound on their suppliers. When we level production the entire value stream, including our suppliers, can cope much better.

Sources of Fluctuation
- There are different sources of fluctuations that mess up your shop floor. Different tools and methods are used to address these fluctuations. Leveling reduces the negative effect of fluctuations in demand. Hence let’s have a look at the sources of fluctuations.
Realize That These Sources of Fluctuation Are Connected
- With the different sources of fluctuations, it is important to realize that they are connected. You receive the fluctuations from your customer. You also receive fluctuations from your supplier. However, you are the customer of your supplier, and they also receive fluctuations from you!Hence the fluctuations on your shop floor are not only a result of others, but also by itself a …
How Not to Do It – The Bullwhip Effect
- But before we go into how to do it, let’s illustrate it first by describing how NOT to do it. Assume you have a fluctuating demand. You struggle to produce the parts the customer needs. Your production plan is different every day. You expect your suppliers to deliver whenever and whatever you order – after all, you are their customer. Nevertheless, you miss deliveries to your customer …
Again, Why leveling?
- Hence, breaking this vicious cycle of fluctuations can yield great benefits throughout the value chain. Usually, these benefits materialize upstream where your parts come from. However, these can also be within your own system, where your workers can probably work more efficient if production is leveled. The benefit of leveling is probably least downstream, as the customer just …
Overview of Posts in This Series About Leveling
Why Does The Leveling of Production Matter?
Production Leveling by Volume and Type
- Production teams, and most teams in general, tend to think that there is nothing wrong with the way they are working and that customers will simply receive their orders when they are ready. But Lean seeks to reduce the lead time, improve quality and value to the customer at all times. Lean thinking takes from the Kanbanmethod, meaning that items are not built to forecast for future d…
How to Achieve A Heijunka Flow?
- Heijunka is not an easy state to be achieved and it does need a company to persist on its Lean journey. A leveled production is often associated with a mature Lean implementation and it often comes about together with the following practices: 1. Single minute exchange of die 2. Small batch sizes 3. Kanban production system aligned with customer dem...