
What is the difference between intradermal and intramuscular?
What is the difference between intradermal and intramuscular vaccination? Intramuscular vaccination is given deep into the deltoid (upper arm) muscle in adults and into the anterolateral area of the thigh in infants. Intradermal vaccination is given into the upper skin area over the deltoid muscle in adults or lateral thigh area of infants.
What is the purpose of intradermal injection?
Intradermal injections are most commonly used for sensitivity tests, including tuberculin skin tests and allergy tests, as well as sensitivity tests to medications a person has never had before. The reactions caused by tests which use intradermal injection are more easily seen due to the location of the injection, and when positive will present as a red or swollen area.
How to administer intramuscular (IM) injections?
You will need:
- One alcohol wipe
- One sterile 2 x 2 gauze pad
- A new needle and syringe -- the needle needs to be long enough to get deep into the muscle
- A cotton ball
How to administer intramuscular?
To minimize possible discomfort before your injection:
- Apply ice or an over-the-counter topical numbing cream to the injection site before cleaning it with the alcohol pad.
- Allow the alcohol to dry completely before the injection. ...
- Warm the vial of medication by rubbing it between your hands prior to drawing the medication into the syringe.
- Have someone you trust give you the injection. ...
Why do we use intradermal injection?
Intradermal injection provides a local and very little systemic effect. It is commonly used for tuberculin skin testing but can also be used for allergy testing and local anesthetics. To give an intradermal injection, a 25-gauge or smaller needle is inserted just under the epidermis at an angle of approximately 10°.
What is the most common reason the intradermal route is used?
Intradermal (ID) injections have the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes because there are fewer blood vessels and no muscle tissue. These types of injections are used for sensitivity testing because the patient's reaction is easy to visualize and the degree of reaction can be assessed.
What injections are given intradermal?
Intradermal injections (ID) are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB (see Figure 7.13), allergy, and local anesthesia tests.
Is intradermal faster than subcutaneous?
Intradermal insulin infusion achieves faster insulin action than subcutaneous infusion for 3-day wear. Drug Deliv Transl Res.
When is an intradermal injection administered?
Place the needle almost flat against the patient's skin, bevel side up, and insert needle into the skin. Insert the needle only about 1/4 in., with the entire bevel under the skin. Keeping the bevel side up allows for smooth piercing of the skin and induction of the medication into the dermis.
What is the most commonly used site for intradermal injection?
The most common sites used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. Choose an injection site that is free from lesions, rashes, moles, or scars, which may alter the visual inspection of the test results (Lynn, 2011).
What are the advantages of intradermal route?
Intradermal injection used for vaccination. Vaccination through intradermal injection holds many advantages compared to other types of vaccination, such as an improved immune response to vaccine, a potential reduction of the antigen dose (9), and decreased anxiety and pain (1-3;5;6).
Why is intradermal injection painful?
However, because the pH of lidocaine solution is about 6, it is weakly acidic and inevitably causes pain during injection.
Why is BCG given intradermally?
When you are vaccinated with INTRADERMAL BCG Vaccine your body produces a response (called "cell-mediated immunity") against the weakened tuberculosis-causing bacteria. If you later come into contact with TB, this same response will again be produced to protect you so that you do not catch the disease.
How deep is an intradermal injection?
With bevel (opening) side up, the needle is inserted about 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) with the entire bevel inside and injected while watching for a small wheal or blister to appear.
What size needle is used for intradermal injection?
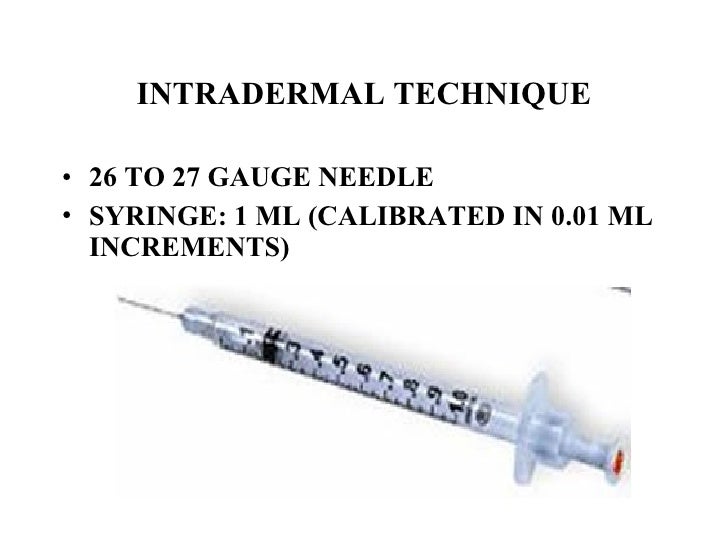
Intradermal injections (ID) are administered into the dermis just below the epidermis. Use a tuberculin syringe, calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter, with a needle length of 1/4 inches to 1/2 inches and a gauge of 25 – 27 Page 2 ID injections may be given on the inner aspect of the forearm.
How do intradermal vaccines work?
With intradermal administration, the vaccine is injected into an outer layer of skin, called the dermis. The dermis has a high number of cells that stimulate the immune response compared to fatty subcutaneous tissue, which means a smaller dose of vaccine can be given to get similar protection.
At what angle are intradermal injections given quizlet?
Using nondominant hand, stretch skin over site with forefinger. 5. Insert needle at a 5- to 15-degree angle into the skin until resistance is felt.
What is a subcutaneous injection quizlet?
Subcutaneous Injection. Involves depositing medication into the loose connective tissue underlying the dermis.
Which of the following are appropriate locations for a subcutaneous injection?
The best areas on your body to give yourself a SQ injection are:Upper arms. At least 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) below your shoulder and 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) above your elbow, on the side or back.Outer side of upper thighs.Belly area.
When should a patients medication list be updated?
Make sure you change your list any time you are prescribed a new medicine or stop taking one.
Where are intradermal injections administered?
Intradermal injections (ID) are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB (see Figure 7.13), allergy, and local anesthesia tests. The advantage of these tests is that the body reaction is easy to visualize, and the degree of reaction can be assessed. The most common sites used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. Choose an injection site that is free from lesions, rashes, moles, or scars, which may alter the visual inspection of the test results (Lynn, 2011).
What is the needle used for ID injection?
Equipment used for ID injections is a tuberculin syringe calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a millilitre, and a 1/4 to 1/2 in., 26 or 27 gauge needle. The dosage of an ID injection is usually under 0.5 ml. The angle of administration for an ID injection is 5 to 15 degrees. Once the ID injection is completed, a bleb (small blister) should appear under the skin. Checklist 56 outlines the steps to administer an intradermal injection.
How to administer SC injections?
To administer an SC injection, a 25 to 30 gauge, 3/8 in. to 5/8 in. needle is used. Some subcutaneous injections come prefilled with the syringe attached. Always confirm that the right-size needle is appropriate for the patient before use. Subcutaneous injections are usually given at a 45- to 90-degree angle. The angle is based on the amount of subcutaneous tissue present. Generally, give shorter needles at a 90-degree angle and longer needles at a 45-degree angle (Lynn, 2011). SC injections do not need to be aspirated as the likelihood of injecting into a blood vessel is small. Usually, no more than 1 ml of medication is given subcutaneously, as larger amounts may cause discomfort to the patient and may not be absorbed appropriately (Lynn, 2011).
Why do you rotate the site of insulin injection?
Typically, a patient will pick one anatomic area (e.g., upper arm) and rotate the injection sites within that region to maintain consistent insulin absorption from day to day. Insulin absorption rates vary from site to site. The abdomen absorbs the fastest, followed by the arms, thighs, and buttocks.
Why is timing important for insulin injection?
The timing of an insulin injection is critical to ensure the patient receives insulin correctly.
Where is the SC injection?
Subcutaneous (SC) injections are administered into the adipose tissue layer just below the epidermis and dermis. This tissue has few blood vessels, so drugs administered by this route have a slow, sustained rate of absorption.
Is insulin a high risk medication?
Insulin is considered a high-risk medication, and special care must be taken to ensure the correct amount of medication and type of insulin is administered at the correct time. As well, safety checks related to a patient receiving SC insulin should be carried out (Ellis & Parush, 2012).
Where to inject intradermal injection?
These areas typically include the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. Additionally, the skin injection site should have no sores, rashes, moles, or scars.
What is intramuscular injection?
Doctors can use intramuscular injections to deliver medication into a person’s muscle tissue. The muscles have a rich blood supply, which helps the body absorb the medication quickly.
Why do people use IV injections?
Because a person directly injects the medication into the bloodstream, it allows for rapid absorption, according to 2015 research. This causes an immediate response, per a 2019 review of the literature.
What is the purpose of injections?
Injections, also known as shots, deliver liquid medications, fluids, or nutrients directly into a person’s body. A healthcare professional can use injections to administer vaccines and other types of medications into a person’s vein, muscle, skin, or bone.
When to reserve intraosseous injections?
Healthcare professionals typically reserve intraosseous injections for emergencies, when intravenous access proves difficult or impossible, according to a 2016 systematic review.
Where do you give subcutaneous injections?
Healthcare professionals administer subcutaneous injections into the fatty tissue just below the skin and above the muscle tissue. They will use a smaller needle to give subcutaneous injections to ensure the medication enters the fatty tissue and not the muscle.
What antibiotics are administered to the body?
administering select antibiotics, such as penicillin and streptomycin

Overview
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. This route of administration is relatively rare compared to injections into the subcutaneous tissue or muscle. Due to the more complex use, ID injections are not the preferred route of administration for injection and therefore used for certain therapies only, such as tuberculosis tests and allergy tests. Specific benefits are a …
Injection sites
Common injection sites include the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the shoulder blade.
Equipment
Equipment include syringes calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter. The dosage given is usually less than 0.5 mL, less than given subcutaneously or intramuscularly. A 1⁄4-to-1⁄2-inch-long (6 to 13 mm) and 26 or 27 gauge thick needle is used.
Mantoux procedure
The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the Mantoux test) involves injecting at angle of administration of 5 to 15 degrees angle, almost against the skin. With bevel (opening) side up, the needle is inserted about 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) with the entire bevel inside and injected while watching for a small wheal or blister to appear.
Intradermic needles
Traditionally hypodermic needles are used for intradermal injections, instead of intradermic needles. Various microneedle technology researchers worldwide develop new devices and therapies to overcome typical usability issues associated with the traditional Mantoux procedure. Most intradermic needles require a change in injection technique or instruction to use, for example a perpendicular intradermal injection.
See also
• Subcutaneous injection
• Intramuscular injection
• Intravenous injection