“Direct” or “conjugated” bilirubin indicates that a sugar has been attached to it. “Indirect” or “unconjugated” bilirubin indicates the absence of a sugar. The important distinction is that direct bilirubin is water soluble, while indirect bilirubin is not.
What is the difference between bilirubin total and direct?
Total bilirubin: 0.3 to 1.9 mg/dL. Direct bilirubin: 0.0 to 0.3 mg/dL. Indirect bilirubin is the difference between total and direct bilirubin. Common causes of higher indirect bilirubin include: Hemolytic anemia. This means your body is getting rid of too many red blood cells. Bleeding into the skin caused by injury.
What does direct bilirubin indicate?
What does direct bilirubin indicate? Elevated levels may indicate liver damage or disease. Higher than normal levels of direct bilirubin in your blood may indicate your liver isn't clearing bilirubin properly. One common, and harmless, cause of elevated bilirubin is Gilbert's syndrome, a deficiency in an enzyme that helps break down bilirubin.
What could be causing elevated direct bilirubin levels?
If your gallbladder is sick or if you have a bile duct blockage, this can cause elevated levels of bilirubin. Other conditions that can lead to elevated bilirubin include tumors of the gallbladder, pancreas, or bile duct.
What is bilirubin direct in blood test?
“Direct” or “conjugated” bilirubin indicates that a sugar has been attached to it. “Indirect” or “unconjugated” bilirubin indicates the absence of a sugar. The important distinction is that direct bilirubin is water soluble, while indirect bilirubin is not. Blood tests to assess bilirubin will measure total, direct, and indirect.

What does bilirubin direct mean?
Some bilirubin is bound to a certain protein (albumin) in the blood. This type of bilirubin is called unconjugated, or indirect, bilirubin. In the liver, bilirubin is changed into a form that your body can get rid of. This is called conjugated bilirubin or direct bilirubin.
What is the difference between total bilirubin and direct bilirubin?
What is the difference between direct bilirubin and total bilirubin? Total bilirubin is the sum of direct and indirect bilirubin, whereas direct bilirubin is conjugated bilirubin.
How does direct bilirubin become indirect bilirubin?
The microsomal enzyme uridine diphosphate–glucuronyl transferase then conjugates the insoluble unconjugated bilirubin with glucuronic acid to form the water-soluble conjugated forms, bilirubin monoglucuronide (15%) and bilirubin diglucuronide (85%).
Why direct bilirubin is higher than total bilirubin?
Direct bilirubin is a component of total bilirubin and therefore should always be smaller in value. The presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin (2220 mg/dL) falsely increased the direct, but not the total, bilirubin measurement. Hemolysis and lipemia can also interfere at high concentrations (2).
Which is more important direct or total bilirubin?
Direct Bilirubin Is More Valuable than Total Bilirubin for Predicting Prognosis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Gut Liver.
What causes elevated direct bilirubin?
The conjugated (direct) bilirubin level is often elevated by alcohol, infectious hepatitis, drug reactions, and autoimmune disorders. Posthepatic disorders also can cause conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
Why is indirect bilirubin known as unconjugated bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubin does not react well in this system unless alcohol is added to promote its solubility in water. Conjugated bilirubin also is called direct bilirubin because it reacts directly with the reagent, and unconjugated bilirubin is called indirect because it has to be solubilized first.
Is unconjugated bilirubin direct or indirect?
Unconjugated (“indirect”) bilirubin. This is the bilirubin created from red blood cell breakdown. It travels in the blood to the liver.
How do you differentiate between conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin?
A urine test positive for bilirubin indicates conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Conjugated bilirubin is soluble in water; therefore, it can be excreted via urine but not unconjugated bilirubin due to water insolubility.
What is the ratio of direct and indirect bilirubin?
Indirect bilirubin: 0.2-0.8 mg/dL or 3.4-12.0 μmol/L (SI units) Direct bilirubin: 0.1-0.3 mg/dL or 1.7-5.1 μmol/L (SI units)
Is 0.7 direct bilirubin normal?
Normal Results A normal level is: Direct (also called conjugated) bilirubin: less than 0.3 mg/dL (less than 5.1 µmol/L) Total bilirubin: 0.1 to 1.2 mg/dL (1.71 to 20.5 µmol/L)
How do you reduce direct bilirubin?
However, following these four tips can help you boost overall liver health in addition to medical guidance.Stay hydrated. Staying hydrated helps lower bilirubin levels by facilitating the removal of waste from the body. ... Consume fresh fruits and vegetables. ... Increase your intake of fiber. ... Avoid alcohol.
How do you calculate direct bilirubin from total bilirubin?
Answer: Total bilirubin = 0.3 to 1.0 mg/dL or 5.1 to 17.0 mmol/L. Direct bilirubin (conjugated bilirubin) = 0.1 to 0.3 mg/dL or 1.0 to 5.1 mmol/L. Indirect bilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) = (total bilirubin minus direct bilirubin level) = 0.2 to 0.7 mg/dL or 3.4 to 11.9 mmol/L.
What happens if total bilirubin is high?
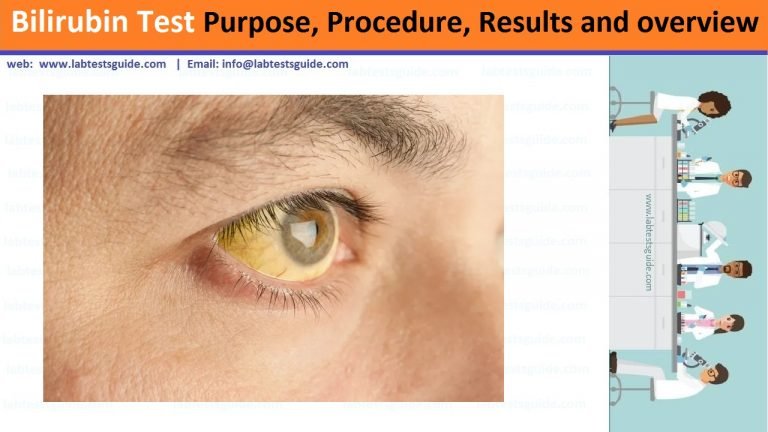
If too much bilirubin is in your bloodstream it can cause jaundice, which can make your skin and eyes turn yellow. The results of the bilirubin test and signs of jaundice can help your doctor check your liver and determine if you have liver disease. A bilirubin test is also used to determine jaundice in newborns.
What does high total bilirubin mean?
If your bilirubin levels are higher than normal, it's a sign that either your red blood cells are breaking down at an unusual rate or that your liver isn't breaking down waste properly and clearing the bilirubin from your blood.
What is normal range of direct bilirubin?
Normal Results A normal level is: Direct (also called conjugated) bilirubin: less than 0.3 mg/dL (less than 5.1 µmol/L) Total bilirubin: 0.1 to 1.2 mg/dL (1.71 to 20.5 µmol/L)
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test?
Your healthcare provider is likely to order this test as part of a liver panel, or group of related liver tests. When your liver is damaged, liver...
What Do My Test Results Mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean...
Does This Test Pose Any Risks?
Having a blood test with a needle carries some risks. These include bleeding, infection, bruising, and feeling lightheaded. When the needle pricks...
What Might Affect My Test Results?
Strenuous exercise and pregnancy can affect your results. Vitamin C, androgen hormones, and certain medicines, such as phenazopyridine and rifampin...
How Do I Get Ready For This Test?
You don't need to prepare for this test. Be sure your healthcare provider knows about all medicines, herbs, vitamins, and supplements you are takin...
What does it mean if your Bilirubin Direct result is too high?
In adults, an elevated level of direct bilirubin typically points to a blockage or disease of the liver, bile ducts, or gallbladder. Possible diseases include: viral hepatitis, cancer of the liver, and alcoholic liver disease. Blockages are usually caused by gallstones, tumors, or scarring.
What is the difference between bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin?
All of the bilirubin in our body together is called “total” bilirubin. “Direct” or “conjugated” bilirubin indicates that a sugar has been attached to it . “Indirect” or “unconjugated” bilirubin indicates the absence of a sugar.
Why is my baby's skin yellow?
In newborn babies, infant jaundice (yellow discoloration of the skin caused by an excess of bilirubin) isn’t unusual and typically resolves within a few days or weeks; however, a bilirubin level that remains elevated in an infant can indicate a variety of physiological issues, including: blood type incompatibility with the mother, an infection of the blood, viral or bacterial infection, and liver disease.
Is bilirubin low in blood?
A low level of direct bilirubin in the blood is not a cause for concern. There are some medicines (like vitamin C) that can cause bilirubin levels to drop, but there are no detrimental effects associated with this.
Is bilirubin water soluble?
The important distinction is that direct bilirubin is water soluble, while indirect bilirubin is not. Blood tests to assess bilirubin will measure total, direct, and indirect. Comparing the three results will provide information regarding any conditions that may be present, including: damage to the liver, liver disease, ...
What is Bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a yellow compound produced during the normal breakdown of hemoglobin, the compound in red blood cells that allows them to carry oxygen. As red blood cells are broken down, the iron -containing part of hemoglobin (heme) is converted to bilirubin [ 1 ].
Why do you need bilirubin test?
Bilirubin tests are usually ordered to monitor liver health. Indirect bilirubin is the unconjugated form of bilirubin in the blood. It is carried from the blood to the liver where it is conjugated to its direct form and excreted into the intestines. Indirect and direct bilirubin together make up total bilirubin. Indirect bilirubin may be too high when the liver is unable to adequately process (conjugated) bilirubin or when there is abnormal destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis). Meanwhile, direct bilirubin may be too high if the liver is unable to pass on the bilirubin after it has been conjugated.
What enzyme converts bilirubin into bilirubin?
The UGT1A1 enzyme, which converts indirect bilirubin into direct bilirubin, is well-developed in the adult liver, but not in the livers of newborns. This is why jaundice with high indirect bilirubin is common in babies [ 2 ].
What does it mean when your bilirubin is high?
High Direct Bilirubin Levels. A high direct bilirubin often means that your body has a harder time removing bilirubin, either due to a liver problem, or blocked bile ducts. However, a result that’s higher than normal, doesn’t necessarily mean that you have a health condition needing treatment.
Why is my skin yellow?
This is a yellow discoloration of skin and eyes due to excess bilirubin building up in these tissues. Jaundice can occur in adults when bilirubin is higher than 2.3 mg/dL [ 37 ].
How is bilirubin measured?
Bilirubin is normally measured with a blood test. A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from your vein and send it to a lab for analysis. The test determines your total and direct bilirubin levels. Indirect bilirubin is what is left after subtracting direct bilirubin from the total [ 11 ]. The bilirubin test is normally included in ...
Why does bilirubin increase?
Indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin levels can increase due to: Gilbert’s syndrome. This benign syndrome is due to an inherited gene mutation that mildly increases bilirubin levels. Up to 16 % of all people have this syndrome. Bilirubin levels may spike when exposed to stress [ 15, 16] Strenuous exercise.
What is bilirubin bound to?
Bilirubin that is bound to a certain protein is called unconjugated, or indirect, bilirubin. Conjugated, or direct, bilirubin travels freely through your bloodstream to your liver. Most of this bilirubin passes into the small intestine. A very small amount passes into your kidneys and is excreted in your urine. This bilirubin also gives urine its distinctive yellow color.
What causes bilirubin to rise?
Gallstones. The bile duct is a tube that carries bile to the small intestine. Bilirubin or cholesterol can form stones that block the duct. This causes bilirubin—mostly direct bilirubin—to rise in your bloodstream.
What enzymes are tested for in the liver?
Your healthcare provider is likely to order this test as part of a liver panel, or group of related liver tests. When your liver is damaged, liver enzymes may leak into your blood. Your provider may order blood tests for these enzymes, such as: 1 Alkaline phosphatase, or ALP 2 Aspartate transaminase, or AST 3 Alanine transaminase, or ALT
What is the term for an infection in the bloodstream?
Septicemia, an infection in the bloodstream commonly known as blood poisoning
Does bilirubin show up in urine?
If your results on the blood test are higher, bilirubin may also show up in your urine. Urine in adults normally contains only 0.02 mg/dL. Most urine tests will not detect this amount.
What is the process of bilirubin being released into the intestine?
Indirect bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of hemoglobin in the red blood cells. The liver converts this bilirubin into direct bilirubin, which can then be released into the intestine by the gallbladder for elimination. Total bilirubin levels are therefore indicative of both the destruction of red blood cells and the proper functioning of the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
What is the indicator of liver dysfunction?
Raised Bilirubin is the indicator of liver dysfunction.
What does it mean when your bilirubin is high?
Occasionally, higher bilirubin levels may indicate an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis).
When is bilirubin test ordered?
Tests for bilirubin may also be ordered when someone is suspected of having (or known to have) hemolytic anemia as a cause of anemia. In this case, it is often ordered along with other tests used to evaluate hemolysis, such as complete blood count , reticulocyte count, haptoglobin, and LDH.
What to do if there is a delay in a test?
If there is a delay in the test then keep the sample away from the light and refrigerate it.
Where is the sex test done?
This test is done in the serum of the patient.
How is bilirubin formed?
Bilirubin consists of an open chain tetrapyrrole. It is formed by oxidative cleavage of a porphyrin in heme, which affords biliverdin. Biliverdin is reduced to bilirubin. After conjugation with glucuronic acid, bilirubin is excreted.
What is total bilirubin?
Total bilirubin = direct bilirubin + indirect bilirubin. Elevation of both alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin is more indicative of serious liver injury than is elevation in ALT alone, as postulated in Hy's law that elucidates the relation between the lab test results and drug-induced liver injury.
Why is urobilinogen in urine dark?
If the liver's function is impaired or when biliary drainage is blocked, some of the conjugated bilirubin leaks out of the hepatocytes and appears in the urine, turning it dark amber. However, in disorders involving hemolytic anemia, an increased number of red blood cells are broken down, causing an increase in the amount of unconjugated bilirubin in the blood. Because the unconjugated bilirubin is not water-soluble, one will not see an increase in bilirubin in the urine. Because there is no problem with the liver or bile systems, this excess unconjugated bilirubin will go through all of the normal processing mechanisms that occur (e.g., conjugation, excretion in bile, metabolism to urobilinogen, reabsorption) and will show up as an increase of urobilinogen in the urine. This difference between increased urine bilirubin and increased urine urobilinogen helps to distinguish between various disorders in those systems.
How long does bilirubin last?
The half-life of delta bilirubin is equivalent to that of albumin since the former is bound to the latter, yields 2–3 weeks. A free-of-bound bilirubin has a half-life of 2 to 4 hours. Further information: Bilirubin glucuronide.
What is the first step in the catabolic pathway?
For example, the molecules excreted in the urine differ from those in the feces. The production of biliverdin from heme is the first major step in the catabolic pathway, after which the enzyme biliverdin reductase performs the second step, producing bilirubin from biliverdin.
How does hemoglobin transport oxygen?
Hemoglobin acts to transport oxygen your body receives to all body tissue via blood vessels. Over time, when red blood cells need to be replenished, the hemoglobin is broken down in the spleen; it breaks down into two parts: heme group consisting of iron and bile and protein fraction. While protein and iron are utilized to renew red blood cells, pigments that make up the red color in blood are deposited into the bile to form bilirubin. Jaundice leads to raised bilirubin levels that in turn negatively remove elastin-rich tissues. Jaundice may be noticeable in the sclera of the eyes at levels of about 2 to 3 mg/dl (34 to 51 μmol/l), and in the skin at higher levels. For conversion, 1 mg/dl = 17.1 μmol/l.
What causes yellow bilirubin?
It is responsible for the yellow color of bruises and the yellow discoloration in jaundice. Its breakdown products, such as stercobilin, cause the brown color of feces.
What is bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood. It forms after red blood cells break down, and it travels through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before being excreted.
What causes high bilirubin?
Having high bilirubin can be a sign of several conditions. Your doctor will take your symptoms, as well as any other test results, into account to help narrow down a diagnosis.
Should I be concerned?
In many cases, high bilirubin isn’t a sign of anything that needs immediate treatment.
What happens if bile ducts are blocked?
If these ducts become inflamed or blocked, bile can’t be properly drained. This can lead to an increased level of bilirubin.
How do you know if you have gallstones?
Symptoms of gallstones include: pain in your upper right abdomen or right below your chest. back pain between your shoulders or in your right shoulder. feeling sick. throwing up. Gallstones may form if your body is already producing too much bilirubin due to a liver condition or if your liver’s creating too much cholesterol.
What is the duct that connects the liver to the gallbladder?
Your bile ducts connect your liver to your gallbladder the opening of your small intestine, called the duodenum. They help to move bile, which contains bilirubin, from your liver and gallbladder into your intestines.
What is the cause of gallstones?
Gallstones happen when substances like cholesterol or bilirubin harden in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is responsible for making bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats before they enter your intestines.
Why is unconjugated bilirubin called indirect?
Conjugated bilirubin also is called direct bilirubin because it reacts directly with the reagent, and unconjugated bilirubin is called indirect because it has to be solubilized first.
What is delta bilirubin?
Delta bilirubin is albumin-bound conjugated bilirubin. The level of delta bilirubin is a calculated value ( [delta bilirubin = total bilirubin – (unconjugated bilirubin + conjugated bilirubin)]. Delta bilirubin is metabolically inactive and is cleared slowly from the body. Its level is increased in biliary obstruction and some liver disease.
What is the best bilirubin level for jaundice?
A patient is generally visibly jaundiced if the bilirubin level is higher than 2 mg/dL.
Where is conjugated bilirubin excreted?
Conjugated bilirubin is excreted into canalicular bile by way of the canalicular multispecific organic anion transport (C-MOAT) system located in the canalicular membrane within the apical region of the hepatocyte. 39 The C-MOAT system shows genetic and structural homology with the multidrug resistance (MDR) family of proteins, 40 and with glutathione S -transferase, 41 but incorporates a different glutathione S -transferase isozyme from that involved in basolateral intracellular ligandin transport of unconjugated bilirubin.
Where does heme breakdown occur?
Bilirubin mono- and diglucuronides are the final breakdown products of heme. Degradation of heme starts in the macrophages of spleen where macrophages scavenge senescent erythrocytes. Bilirubin, the end product of the macrophage stage of heme catabolism, is carried to the liver bound to albumin. Hepatic uptake of free bilirubin likely occurs by passive diffusion. In the hepatocyte, bilirubin is converted to mono- and diclucuroniodes by uridin-diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronide transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) and either transported into the bile by MRP2 or BCRP, or effluxed back to the plasma by MRP3 ( Iusuf et al., 2012). Plasma bilirubin glucuronides are reuptaken into the hepatocytes via OATP1B1 and OATP1B3.
Where is bilirubin excreted?
Bilirubin Glucuronide. Bilirubin glucuronides are excreted into the bile canaliculus primarily via MRP2, which also plays a role in the transport of glucuroniductal bile salts and a wide spectrum of organic anions, including the antibiotic ceftriaxone. From: Blumgart's Surgery of the Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas, 2-Volume Set (Sixth Edition), ...
What are the proteins that are absorbed by the gallbladder?
The protein composition and content change during gallbladder storage. In humans, haptoglobin, IgM, and IgA, as well as α1-glycoprotein, are reported to be absorbed by the gallbladder. At the same time, mucin, albumin, and IgG are secreted into bile. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
