Jacques Cartier (December 31, 1491 – September 1, 1557) was the first French Explorer to explore the New World. He explored what it now Canada and set the stage for the great explorer and navigator Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain was a French colonist, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean, and founded Quebec, and New France, on July 3, 1608. An important fi…
What bad things did Jacques Cartier do?
What are some bad things that Jacques Cartier did? C artier had ended up making a overall bad impact on the trade between the French and the Iroquois. This lowered his reputation with the tribe and induced hate between the two. It wasn’t for a couple of decades before they would attempt to associate with natives of the new world.
Why did Jaques Cartier use an astrolabe?
Jaques cartier use many types of tools.Jaques cartier used a map to see were he is navigating or were he is going.Jaques cartier also use a telescope to see if theres any lands. Jacques cartier also use a magnetic compass and a "astrolabe" a very popular navigation tool,that allowed him to find the location, each day.Jacques cartier also used a ...
Why did Jacques Cartier trade with the Indians?
The Micmac held up furs showing that they wanted to trade and indicating that they had encountered Europeans before and knew what they wanted. Cartier sent two men ashore with knives and other iron goods and a brisk trade occurred. In some instances, the Indians literally traded the clothes they were wearing.
What was the way Jacques Cartier affect history?
On the return voyage to France, Cartier took two Indian boys and a supply of maize, probably the first of that crop to reach Europe. Jacques Cartier’s first voyage helped to change the French conception of North America. It had been widely believed that the area’s only value lay in its fisheries.

Why is Jacques Cartier famous?
French mariner Jacques Cartier was the first European to navigate the St. Lawrence River, and his explorations of the river and the Atlantic coast...
What were Jacques Cartier’s goals?
Cartier was commissioned (initially in 1534) by King Francis I of France to lead an expedition westward across the Atlantic Ocean to explore the no...
What was Jacques Cartier’s legacy?
Although Jacques Cartier helped France lay claim to North America by journeying far up the St. Lawrence River, he did not proceed beyond the Lachin...
Where is Jacques Cartier buried?
Little is known of Jacques Cartier’s personal life. He was born (1491) in Saint-Malo on the Brittany coast in France, sailed from there on his firs...
Why is Jacques Cartier so famous?
Why is Jacques Cartier famous? French mariner Jacques Cartier was the first European to navigate the St. Lawrence River, and his explorations of the river and the Atlantic coast of Canada, on three expeditions from 1534 to 1542, laid the basis for later French claims to North America. Cartier is also credited with naming Canada.
Where did Cartier travel?
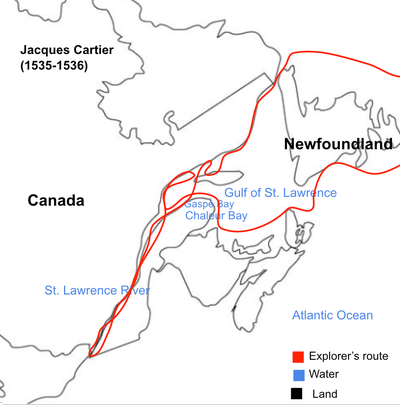
Reaching North America a few weeks later, Cartier traveled along the west coast of Newfoundland, discovered Prince Edward Island, and explored the Gulf of St. Lawrence as far as Anticosti Island.
What prevented Francis I from sending another expedition?
War in Europe prevented Francis I from sending another expedition until 1541. This time, to secure French title against the counterclaims of Spain, he commissioned a nobleman, Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, to establish a colony in the lands discovered by Cartier, who was appointed Roberval’s subaltern. Cartier sailed first, arriving at Quebec on August 23; Roberval was delayed until the following year. Cartier again visited Montreal, but as before he remained only a few hours and failed to go even the few miles necessary to get beyond the rapids. The subsequent maps based on the knowledge he provided fail to indicate that he had reached a large island at the confluence of the Ottawa and St. Lawrence rivers.
Where did Cartier abandon the base?
In the spring, not waiting for Roberval to arrive with the main body of colonists, Cartier abandoned the base and sailed for France. En route he stopped at Newfoundland, where he encountered Roberval, who ordered him back to Quebec.
What was the name of the French colony in North America?
New France, (1534–1763), the French colonies of continental North America, initially embracing the shores of the St. Lawrence River, Newfoundland, and Acadia (Nova Scotia) but gradually expanding to include much of the Great Lakes region and parts of the trans-Appalachian West. The…
Where is Jacques Cartier buried?
He is entombed in St. Vincent’s Cathedral in Saint-Malo.
Where did Cartier steal his mineral specimens?
Cartier, however, stole away during the night and continued back to France. There, his mineral specimens were found to be valueless. Roberval enjoyed no better success.
Why did Francis order Jacques Cartier to return to Canada?
On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a Huguenot courtier and friend of the king named as the first lieutenant general of French Canada. Roberval was to lead the expedition, with Cartier as his chief navigator. While Roberval waited for artillery and supplies, he gave permission to Cartier to sail on ahead with his ships.
How did Cartier die?
He died at age 65 on September 1, 1557, during an epidemic, possibly of typhus, though many sources list his cause of death as unknown. Cartier is interred in Saint-Malo Cathedral .
How many men did Jacques Cartier have on his second voyage?
Jacques Cartier set sail for a second voyage on May 19 of the following year with three ships, 110 men, and his two Iroquoian captives. Reaching the St. Lawrence, he sailed upriver for the first time, and reached the Iroquoian capital of Stadacona, where Chief Donnacona ruled.
What did Le Veneur say about the voyages of the Veneur?
Le Veneur cited voyages to Newfoundland and Brazil as proof of Cartier's ability to "lead ships to the discovery of new lands in the New World". On April 20, 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of Asia.
What river did Cartier go to?
Having reached Hochelaga, he was prevented by bad weather and the numerous rapids from continuing up to the Ottawa River . Returning to Charlesbourg-Royal, Cartier found the situation ominous.
Why was Canada named Canada?
Cartier was the first to document the name Canada to designate the territory on the shores of the St-Lawrence River. The name is derived from the Huron - Iroquois word kanata, or village, which was incorrectly interpreted as the native term for the newly discovered land. Cartier used the name to describe Stadacona, the surrounding land and the river itself. And Cartier named Canadiens the inhabitants ( Iroquoians) he had seen there. Thereafter the name Canada was used to designate the small French colony on these shores, and the French colonists were called Canadiens until the mid-nineteenth century, when the name started to be applied to the loyalist colonies on the Great Lakes and later to all of British North America. In this way Cartier is not strictly the European discoverer of Canada as this country is understood today, a vast federation stretching a mari usque ad mare (from sea to sea). Eastern parts had previously been visited by the Norse, as well as Basque, Galician and Breton fishermen, and perhaps the Corte-Real brothers and John Cabot (in addition of course to the natives who first inhabited the territory). Cartier's particular contribution to the discovery of Canada is as the first European to penetrate the continent, and more precisely the interior eastern region along the St. Lawrence River. His explorations consolidated France's claim of the territory that would later be colonized as New France, and his third voyage produced the first documented European attempt at settling North America since that of Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón in 1526–27.
What was Cartier's goal in 1541?
The goals were now to find the "Kingdom of Saguenay" and its riches, and to establish a permanent settlement along the St. Lawrence River.
What did Jacques Cartier do to the colony?
He had filled a dozen barrels with what he believed were precious stones and metal. At a stop in St. John’s, Newfoundland, however, Cartier met Roberval’s fleet and was given the order to return to Cap Rouge. Refusing to obey, Cartier sailed toward France under the cover of darkness. The stones and metal that he brought back turned out to be worthless and Cartier was never reimbursed by the king for the money he had borrowed from the Breton merchants. After this misadventure, he returned to business. Cartier died about 15 years later at his estate at Limoilou near Saint-Malo. He kept his reputation as the first European to have explored and mapped this part of the Americas, which later became the French axis of power in North America.
What did Cartier explore?
From 1534 to 1542, Cartier led three maritime expeditions to the interior of the Gulf of the St. Lawrence River. During these expeditions, he explored, but more importantly accurately mapped for the first time the interior of the river, from the Gulf to Montreal ( see also History of Cartography in Canada ).
What was the first voyage of Jacques Cartier?
Jacques Cartier’s orders for his first expedition were to search for a passage to the Pacific Ocean in the area around Newfoundland and possibly find precious metals. He left Saint-Malo on 20 April 1534 with two ships and 61 men. They reached the coast of Newfoundland 20 days later. During his journey, Cartier passed several sites known to European fishers. He renamed these places or noted them on his maps. After skirting the north shore of Newfoundland, Cartier and his ships entered the Gulf of St. Lawrence by the Strait of Belle Isle and travelled south, hugging the coast of the Magdalen Islands on 26 June. Three days later, they reached what are now the provinces of Prince Edward Island and New Brunswick. He then navigated towards the west, crossing Chaleur Bay and reaching Gaspé, where he encountered Iroquoian lndigenous people from the region of Quebec. They had come to the area for their annual seal hunt. After planting a cross and engaging in some trading and negotiations, Cartier’s ships left on 25 July. Before leaving, Cartier abducted two of Iroquoian chief Donnacona’s sons. They returned to France by following the coast of Anticosti Island and re-crossing the Strait of Belle Isle.
Where did Jacques Cartier sail?
Like his countrymen, Cartier probably sailed along the coast of France, Newfoundland and South America (Brazil), first as a sailor and then as an officer.
Which river did Jacques Cartier use to occupy North America?
At the time, however, this term described only the region immediately surrounding Quebec. Cartier’s upstream navigation of the St. Lawrence River in the 16th century ultimately led to France occupying this part of North America. Jacques Cartier.
When did Jacques Cartier reach Hochelaga?
Cartier reached Hochelaga on 2 October 1535. There he met other Iroquoian people, who tantalized Cartier with the prospect of a sea in the middle of the country.
Why is Jacques Cartier considered an invader?
This is due to his actions, motives, and adaptations to the bumps along his journey in hopes to find a new passage to Asia. Cartier’s motivation surrounded around profit, opposed to an Explorer, whose focus would be directed further towards finding new land and discovering new things. These were some of the results following Cartier’s travels, but they were not intended. He harmed First Nations he encountered, and was a kidnapper, taking advantage of the people around him. Cartier was a brave captain, who discovered many new lands and established new colonies, but was an invader nonetheless. With the King of France’s payment, Jacques Cartier set sail on his first major voyage during the 1530s with hopes of finding a new passage to Asia. This would gain access to the trading, markets, and gold found there. The motivation behind Cartier's work is one of the major defining points on whether he should be considered as an explorer or an invader, as this gives a look into his character, and what is going through his mind. An explorer travels with the intent on learning new things, finding new places, or better understanding something/where. Money may factor in a little bit, as you need money to continue, but it would never be the reason for…show more content…
What were the motives of the French colonists?
The French Entered race late, 1608. Their motives were Profit, national glory, spreading faith, Northwest passage to the Orient, Piracy of Spanish treasure ships. The settlements were fishermen, fur traders, trappers, did business with natives and intermarried. The colonists were primarily soldiers, traders, trappers, and priests. The motives of Exploration were English Interest for profit, national glory, spreading Protestant faith, Northwest passage, piracy, religious sanctuary.
What does Kipling say about the British Empire?
Kipling remarks, “But the Empires and the Kings continue to divert themselves as selfishly as before.” His word choice of “selfishly” discloses his feelings toward the British Empire as he believes it is self- indulgent and only has interest in benefiting itself. Kipling does not believe the Empire is colonizing other countries to help those people, but forcing their culture and beliefs onto other areas for more power and control. Additionally,
What did European explorers discover?
Many of us know that without European exploration, we would not be living here today. However, we forget the other side of the picture. Yes, he discovered new trade-worthy items such as gold, silver, and spices .
Why did the British want to expand their empire?
The desire for expansion within the British empire arose due to a culmination of heavy losses in terms of warfare, particularly with France at the end of the hundred years’ war, great envy toward their rivals, a longing for exotic commodities, but also a crippling debt in the monarchy was a key factor. In the 16th century, however, the state neglected to fully commit itself to help fund voyages of exploration, settlement, and colonisation, due to a lack of resources. T. O. Lloyd, in his book ‘The British Empire 1558-1983’, explains “The government certainly had no money to spare to help the colonies, and this introduced the general rule that English colonies had to cover their own costs.” Therefore, much of the conquest and discovery was left in the hands of privateers and private enterprises “whose concern for immediate gain was detrimental to long-term planning needed to promote colonisation.” The first real expedition
Was Jacques Cartier an explorer?
This however, does not make him an explorer. Cartier, over his years, has done many things that an Explorer would not think of doing. He has kidnapped Iroquois, claimed and changed territories, and taken advantage of people to make a profit. The impact Cartier has had on Canada today is immeasurable, and I am not sure where I would be right now if it was not for that greed that drove Cartier to try and find Asia. I strongly believe that Jacques Cartier was an invader, but our country was built on invaders, which we need to realize if we want to continue to make positive impacts on the world around
Who Was Jacques Cartier?
French navigator Jacques Cartier was sent by King Francis I to the New World in search of riches and a new route to Asia in 1534. His exploration of the St. Lawrence River allowed France to lay claim to lands that would become Canada. He died in Saint-Malo in 1557.
What was Cartier's main goal in his voyage?
On a voyage that would add him to the list of famous explorers, Cartier was to search for gold and other riches, spices, and a passage to Asia. Cartier sailed on April 20, 1534, with two ships and 61 men, and arrived 20 days later.
Why did Cartier wait until spring to capture the Iroquois?
Because of his hasty escape, Cartier was only able to report to the king that untold riches lay farther west and that a great river, said to be about 2,000 miles long, possibly led to Asia.
What did Cartier do instead of heading to Quebec?
Cartier, however, had other plans; instead of heading to Quebec, he sneaked away during the night and returned to France. There, his "gold" and "diamonds" were found to be worthless, and the colonists abandoned plans to found a settlement, returning to France after experiencing their first bitter winter.
When did Cartier leave France?
In May 1541, Cartier departed on his third voyage with five ships. He had by now abandoned the idea of finding a passage to the Orient and was sent to establish a permanent settlement along the St. Lawrence River on behalf of France. A group of colonists was a few months behind him this time.
Where did Cartier explore?
Born in Saint-Malo, France on December 31, 1491, Cartier reportedly explored the Americas, particularly Brazil, before making three major North American voyages. In 1534, King Francis I of France sent Cartier — likely because of his previous expeditions — on a new trip to the eastern coast of North America, then called the "northern lands." On a voyage that would add him to the list of famous explorers, Cartier was to search for gold and other riches, spices, and a passage to Asia.
When did Cartier die?
Cartier died on September 1, 1557, in Saint-Malo, France.
What is Jacques Cartier best remembered for?
Jacques Cartier is best remembered for his exploration of parts of Canada. We even credit him with giving the country its name. Although Cartier named the land he traveled to “Canada,” the word actually comes from the Iroquois-Huron language. These natives referred to their village of Stacona as a kanata – which simply means “village” ...
What was Jacques Cartier's legacy?
Legacy. Jacques Cartier is credited with not only claiming and discovering land for France. However, his treatment of the natives was not always great. Throughout his three voyages, Cartier became the first European to explore the St. Lawrence Gulf and St. Lawrence River.
What did Cartier find in Hochelaga?
They began exploring the area. Soon, Cartier and his men believed found stones that looked like diamonds and gold. However, it turned out that the diamonds were actually pieces of quartz, and the gold was iron pyrite – better known as “fool’s gold.”11 Cartier and some of his men went back to Hochelaga.
How long did it take Cartier to reach Newfoundland?
After just 20 days of sailing, the expedition reached the area that is now modern day Newfoundland by early May. The fleet sailed north along the coastline for a short while, before turning around and heading south. Cartier continued to explore the western coastline of Newfoundland.
Where did Cartier meet Roberval?
After leaving Charlesbourg-Royal, Cartier’s fleet met Roberval in St. John’s harbour in Newfoundland. He had with him barrels of the “diamonds” and “gold” which he would later find to be worthless. Roberval ordered Cartier and the settlers to turn around and go back to the settlement. But they refused.
What was Cartier's first discovery?
In June of 1534 he made his first major discovery when he came upon an area we know today as Prince Edward Island.6 This is a large island that is still part of modern day Canada. After landing on Prince Edward Island, Cartier’s expedition explored the gulf and various inlets nearby in search of a passage to Asia.
Where did Cartier stop in 1535?
On September 7, 1535, Cartier and his men reached the site of the present day city of Quebec. They stopped at a village called Stadacona, where they were greeted by the Donnaconna, chief of the Huron natives.10 Several Huron natives went with Cartier as guides.
What was Cartier's reputation?
Lawrence region, Cartier's reputation was tarnished by his harsh dealings with the Iroquois and by his abandoning the incoming colonists as he fled the New World. He returned to Saint-Malo but got no new commissions from the king.
Why did Cartier report to the King?
Because of his hasty escape, Cartier could only report to the king that untold riches lay farther west and that a great river, said to be 2,000 miles long, possibly led to Asia. These and other reports, including some from the hostages, were so encouraging that King Francis decided on a huge colonizing expedition. He put military officer Jean-François de la Rocque, Sieur de Roberval, in charge of the colonization plans, although the actual exploration was left to Cartier.
What did Cartier gather in the winter?
After a difficult winter, Cartier gathered drums filled with what he thought were gold, diamonds, and metal and started to sail for home. But his ships met Roberval's fleet with the colonists, who had just arrived in what is now St. John's, Newfoundland .
What was Cartier's cargo?
Roberval ordered Cartier and his men to return to Cap-Rouge, but Cartier ignored the order and sailed for France with his cargo. When he arrived in France, he found that the load was really iron pyrite—also known as fool's gold—and quartz. Roberval's settlement efforts also failed. He and the colonists returned to France after experiencing one bitter winter.
What was Cartier's first discovery?
Cartier explored what became known as Newfoundland, the Magdalen Islands, Prince Edward Island, and the Gaspé Peninsula, and was the first explorer to map the St. Lawrence River. He claimed what is now Canada for France.
How many men did Cartier have on his second voyage?
Second Voyage. Cartier set out on a larger expedition the next year, with 110 men and three ships adapted for river navigation. Donnacona's sons had told Cartier about the St. Lawrence River and the “Kingdom of the Saguenay” in an effort, no doubt, to get a trip home, and those became the objectives of the second voyage.
How many ships did Cartier have?
Francis was hoping the expedition would find precious metals, jewels, spices, and a passage to Asia. Cartier was selected for the commission. With two ships and 61 crewmen, Cartier arrived off the barren shores of Newfoundland just 20 days after setting sail.

Overview
Popular references
The fr:Banque Jacques-Cartier existed, and printed banknotes, between 1861 and 1899 in Lower Canada, then Quebec. It was folded into the fr:Banque provinciale du Canada, and later still the National Bank of Canada.
In 2005, Cartier's Bref récit et succincte narration de la navigation faite en MDXXXV et MDXXXVI was named one of the 100 most important books in Canadian history by the Literary Review of C…
Early life
Jacques Cartier was born in 1491 in Saint-Malo, the port on the north-east coast of Brittany. Cartier, who was a respectable mariner, improved his social status in 1520 by marrying Mary Catherine des Granches, member of a leading aristocratic family. His good name in Saint-Malo is recognized by its frequent appearance in baptismal registers as godfather or witness.
First voyage (1534)
In 1534, two years after the Duchy of Brittany was formally united with France in the Edict of Union, Cartier was introduced to King Francis I by Jean Le Veneur, bishop of Saint-Malo and abbot of Mont Saint-Michel, at the Manoir de Brion. The King had previously invited (although not formally commissioned) the Florentine explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano to explore the eastern coast of North America …
Second voyage (1535–1536)
Jacques Cartier set sail for a second voyage on May 19 of the following year with three ships, 110 men, and his two Iroquoian captives. Reaching the St. Lawrence, he sailed upriver for the first time, and reached the Iroquoian capital of Stadacona, where Chief Donnacona ruled.
Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his small…
Third voyage (1541–1542)
On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a Huguenot courtier and friend of the king named as the first lieutenant general of French Canada. Roberval was to lead the expediti…
Later life
Cartier spent the rest of his life in Saint-Malo and his nearby estate, where he often was useful as an interpreter in Portuguese. He died at age 65 on September 1, 1557, during an epidemic, possibly of typhus, though many sources list his cause of death as unknown. Cartier is interred in Saint-Malo Cathedral.
No permanent European settlements were made in Canada before 1605, when Samuel Champlain
Legacy
Having already located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage, he now opened up the greatest waterway for the European penetration of North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St. Lawrence Iroquoians were di…
Voyages to The Americas
First Voyage
- Jacques Cartier’s orders for his first expedition were to search for a passage to the Pacific Ocean in the area around Newfoundland and possibly find precious metals. He left Saint-Malo on 20 April 1534 with two ships and 61 men. They reached the coast of Newfoundland 20 days later. During his journey, Cartier passed several sites known to European...
Second Voyage
- The expedition of 1535 was more important than the first expedition. It included 110 people and three medium-sized ships. The ships were called the Grande Hermine (the Great Stoat), the Petite Hermine (the Lesser Stoat) and the Émérillon (the Merlin). The Émérillonhad been adapted for river navigation. They left Brittany in mid-May 1535 and reached Newfoundland after a long, 50-d…
Third Voyage
- The war in Europe led to a delay in returning to Canada. In addition, the plans for the voyage were changed. This expedition was to include close to 800 people and involve a major attempt to colonize the region. The explorations were left to Jacques Cartier, but the logistics and colonial management of the expedition were entrusted to Jean-François de La Rocque, sieur de Roberval…
Return to France
- In a state of relative siege during the winter, and not expecting the arrival of Jean-François de La Rocque, sieur de Roberval until spring, Jacques Cartier decided to abandon the colony at the end of May. He had filled a dozen barrels with what he believed were precious stones and metal. At a stop in St. John’s, Newfoundland, however, Cartier met Roberval’s fleet and was given the order t…