
What is the role of carbon(C) in soil?
It is the “glue and sponge” of the soil as it sticks together soil aggregates, adsorbs and desorbs nutrients, retains water, and gives habitat and energy to soil micro-organisms. Crops do not take up carbon from the soil (they absorb carbon from the atmosphere) and as such carbon (C) is not an essential nutrient.
What is the importance of soil organic matter?
Organic matter contributes to nutrient retention and turnover, soil structure, moisture retention and availability, degradation of pollutants, and carbon sequestration. How is soil organic carbon different to soil organic matter?
What is soil organic carbon (SOC)?
Qiang Chai, in Advances in Agronomy, 2013 Soil organic carbon (SOC) affects the chemical and physical properties of the soil, such as water infiltration ability, moisture holding capacity, nutrient availability, and the biological activity of microorganisms.
Why choose organic?
What the Soil Association organic symbol really means 1. Is better for the planet Designed to respect nature and to enhance the health of soils, water and air, organic farming is leading the way on sustainability.
What is a good organic carbon in soil?
Topsoil ranges from 0.5% to 3.0% organic carbon for most upland soils. Soils with less than 0.5% organic C are mostly limited to desert areas. Soils containing greater than 12–18% organic carbon are generally classified as organic soils.
What is organic carbon used for?
The role of organic carbon By providing a food source for micro-organisms, organic carbon can help improve soil stability by micro-organisms binding soil particles together into aggregates or 'peds'. Bacteria excretions, root exudates, fungal hyphae and plant roots can all contribute to better soil structure.
Why is total organic carbon important?
TOC is the first chemical analysis to be carried out on potential petroleum source rock in oil exploration. It is very important in detecting contaminants in drinking water, cooling water, water used in semiconductor manufacturing, and water for pharmaceutical use.
What is the effect on soil with less organic carbon?
Loss of soil organic carbon content can limit the soil's ability to provide nutrients for sustainable plant production. This may lead to lower yields and affect food security. Less organic carbon also means less food for the living organisms present in the soil, thus reducing soil biodiversity.
What are examples of organic carbon?
organic carbon compounds produced in living things; examples include carbohydrates, lipids (fat, soils, waxes), and DNA.
What is a source of organic carbon?
Organic carbon can be allochthonous, or sourced from outside the system (e.g. by atmospheric deposition or transported long distances via stream flow) or it can be autochthonous, or sourced from the immediate surroundings of the system (e.g. plant and microbial matter and sediments/soils within the catchment).
Where is organic carbon found?
soilsOrganic forms of carbon in the lithosphere include litter, organic matter, and humus (organic matter) found in soils.
What is meant by organic carbon?
Page last updated: Tuesday, 28 June 2022 - 10:09am. Soil organic carbon is a measureable component of soil organic matter. Organic matter makes up just 2–10% of most soil's mass and has an important role in the physical, chemical and biological function of agricultural soils.
Why is organic carbon important for agriculture?
Farmers are interested in retaining and increasing soil organic carbon for individual fields in order to improve soil health and yield. One of the main reasons behind this is the ability of soil organic carbon in maintaining the soil fertility.
Why is soil carbon storage important?
Soil carbon storage is a vital ecosystem service. In an agricultural land soil carbon loss takes place as a result of improper methods of soil managements such as excessive tillage, increased rate of irrigation, increased use of chemical fertilizers etc.
How to restore soil health?
Replacing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers and manures will help to restore the soil health. Erosion of top soil which brings down the amount of carbon present in soil can be controlled by maintaining the ground cover. Growing cover crops like eucalyptus can reduce the wash away of top soil. Excessive irrigation can deteriorate soil ...
What is the carbon in soil?
Soil organic carbon is the carbon that remains in the soil after partial decomposition of any material produced by living organisms. It is present as a main component of soil organic matter and is. believed to play crucial role for many soil functions and ecological properties.
How does SOC affect soil?
SOC improves soil aeration, water retention capacity, drainage, and enhances microbial growth. As carbon stored in the soil is increased carbon is “sequestered” (long -term storage) and risk of loss of nutrients through leaching and erosion is reduced. When the amount of carbon in the soil is increased it reduces the amount ...
How to monitor soil organic carbon?
This can be done using the technology of remote sensing. Quantitative and qualitative estimation of soil using the conventional method is difficult since soil show variability from site to site even within the same field. The method of remote sensing is cost-effective and rapid. FARMONAUT app uses remote sensing technology to create a SOC image that provides color map of percentage of organic matter present in the selected field. If the content of SOC is more than 5% the area appears dark green in the color map and it appears red if the SOC content is less than 1%.Change in SOC content with time is also noted with the help of remote sensing in FARMONAUT. This provides precise information to the farmers which help them to take the right measures, in the right time, and in the right place hence ensuring productivity and soil health.
What can farmers do with less SOC?
Once Farmonaut data has identified some locations to be having less SOC levels, farmers can get the soil testing done on those regions and add required nutrients to those regions to rejuvenate the soil organic matter levels. This will ultimately lead to better yields.
How is soil organic carbon different to soil organic matter?
Soil organic carbon (SOC) refers only to the carbon component of organic compounds. Soil organic matter (SOM) is difficult to measure directly , so laboratories tend to measure and report SOC.
What is organic carbon?
Soil organic carbon is a measureable component of soil organic matter. Organic matter makes up just 2–10% of most soil's mass and has an important role in the physical, chemical and biological function of agricultural soils. Organic matter contributes to nutrient retention and turnover, soil structure, moisture retention and availability, ...
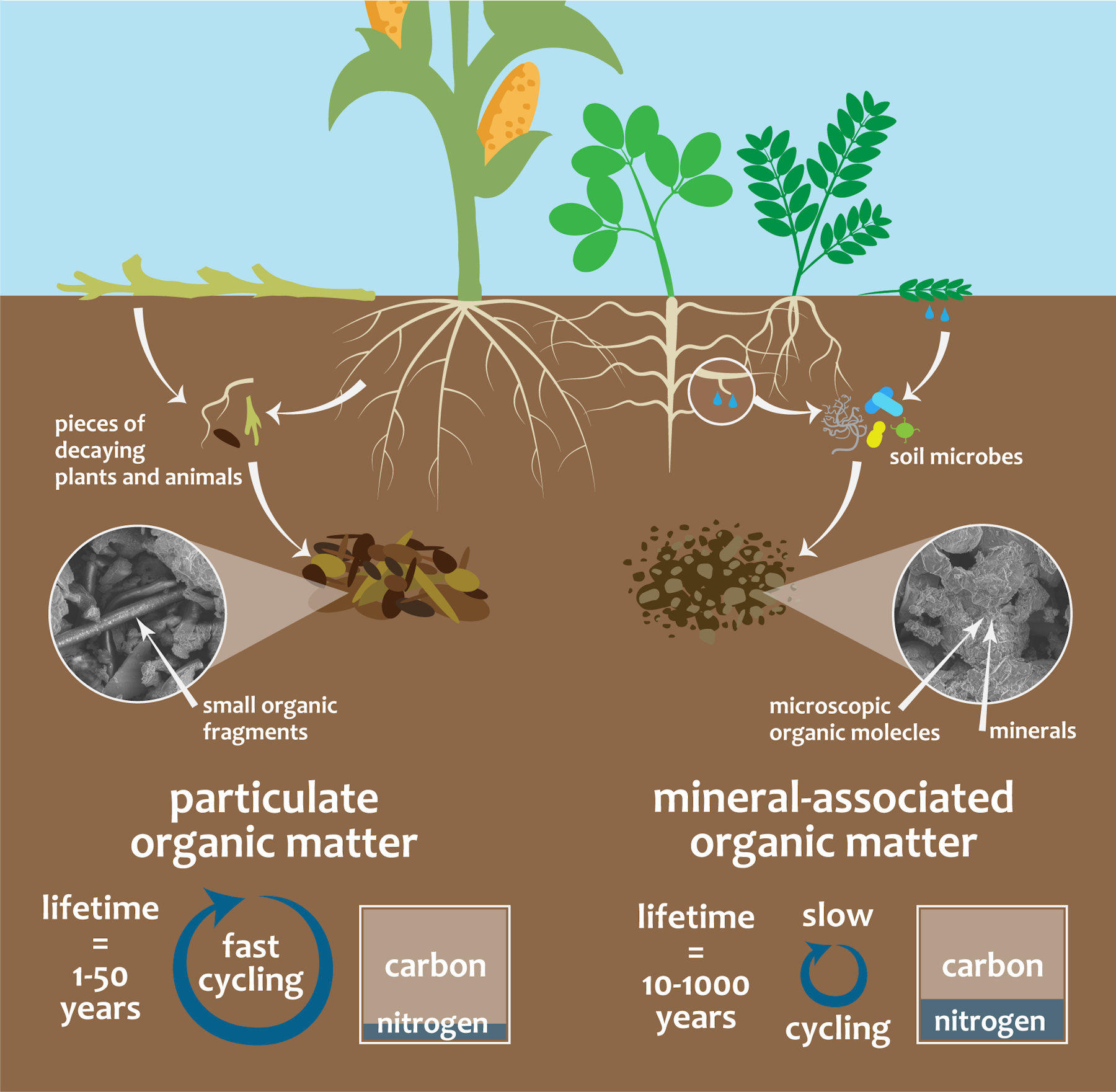
What is soil organic matter?
SOM is composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and has small amounts of other elements, such as nitrogen, phosphorous, sulfur, potassium, calcium and magnesium contained in organic residues. It is divided into ‘living’ and ‘dead’ components and can range from very recent inputs, such as stubble, to largely decayed materials that are thousands of years old. About 10% of below-ground SOM, such as roots, fauna and microorganisms, is ‘living’ (Figure 1).
How much of the soil organic carbon that enters soil stays there?
Microorganisms digest up to 90% of the organic carbon that enters a soil in organic residues. In doing so, they respire the carbon back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. While up to 30% of organic inputs can eventually be converted to humus, depending on soil type and climate, in Australian agricultural soils this value is often significantly less. There are 3 main factors influencing the ability of a given soil type to retain SOC (Figure 5). Soils naturally higher in clay content generally retain more organic matter – and hence can retain more organic carbon – than sandy soils.
How do I measure or interpret soil organic carbon results?
Changes in stable SOC generally occur very slowly (over decades), and it is often hard to measure small changes against a relatively large background of soil carbon. Changes in SOC are largely determined by how much biomass is grown and retained above and below ground.
What percentage of organic matter is carbon?
About 58% of the mass of organic matter exists as carbon. We can estimate the percentage of SOM from the SOC% using the conversion factor 1.72 (derived from 100/58).
What is the role of rain in soil?
Rainfall is a major driver of plant growth (biomass) and biological activity which results in the decomposition of organic matter that enters soil.
What is Soil Organic Carbon?
Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) is part of the soil organic matter. Soil organic matter is built up with additions of organic fertilizers such as animal manure and compost, and also via the crop residues left in the field (roots, stems and leaves). SOC has multiple benefits on soil quality and agricultural production, and it is crucial for climate change mitigation.
Why is soil water holding capacity important?
The capacity of soils to hold water is crucial for plant growth at the field level and can be decisive for flood control at the landscape level. Moreover, an increase in SOC content in soils most often results in an increase in soil water holding capacity.
What is the glue and sponge of soil?
It is the “glue and sponge” of the soil as it sticks together soil aggregates, adsorbs and desorbs nutrients, retains water, and gives habitat and energy to soil micro-organisms. Crops do not take up carbon from the soil (they absorb carbon from the atmosphere) and as such carbon (C) is not an essential nutrient.
What does a low SOC level do to your soil?
Correcting a low SOC content will improve the capacity of your soil to retain water for your crops.
Is soil a part of climate?
Climate change is often seen as something that only involves the atmosphere. Not so many people know that soil is a vital element of the climate system. Yet, the soil is the second-largest carbon store, or ‘sink’, after the oceans. Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO 2) from the atmosphere and transform it into plant tissue (leaves, stems, roots and fruits).
How does organic farming help the soil?
Organic farming creates healthy, living soils by nourishing them with compost, nitrogen-fixing crops, and crop rotations. As a result, organic farmland stores (or ‘sequesters’) more carbon – on average 3.5 tonnes extra for every hectare), and organic soils are around 25% more effective at storing carbon in the long-term.
How does organic farming contribute to sustainability?
Designed to respect nature and to enhance the health of soils, water and air, organic farming is leading the way on sustainability. In fact, if Europe’s farmland all followed organic principles, agricultural emissions could drop by 40-50% by 2050, with plenty to feed the growing population healthy diets.
Why are organic farms important?
Because organic farmers rely on healthy ecosystems to control pests and protect their soils, they tend to farm in a way that encourages wildlife, like planting trees, ‘beetle banks’ and wildflower margins, and digging ponds around their fields. This means organic farms are more ecologically diverse.
What are the differences between organic and non-organic farming?
The hard work organic farmers put into caring for their crops and animals pays off in the quality of the food they produce. Research has found significant nutritional differences between organic and non-organic farming: 1 A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition in 2014 showed that organic milk and meat contain around 50% more beneficial omega-3 fatty acids than non-organic. These nutritional differences also apply to organic dairy like butter, cream, cheese and yoghurt. 2 The difference in Omega 3 is because organic animals eat a more natural, grass-based diet, containing high levels of clover, which is used to fix nitrogen on organic farms, replacing chemical fertiliser. 3 Organic meat had slightly lower concentrations of two saturated fats, and organic milk and dairy were found to contain slightly higher concentrations of iron, Vitamin E and some carotenoids. 4 What's more, organically produced crops (cereals, fruit and vegetables) were found with up to 68% more antioxidants than non-organic, whilst organic fruit and veg contained lower concentrations of pesticides and the toxic heavy metal cadmium.
What is organic farming?
Organic farming has the highest animal welfare standards of any international farming system; this means truly-free range animals, encouraged to forage, graze and roam, with plenty of space, fresh air, and conditions that allow them to express their natural behaviours.
Why is grazing important in organic farming?
Grazing animals have an important role to play in the ‘closed loop’ approach of organic farming; making use of what’s to hand and limiting the use of imported resources: 1. They reduce the need for chemical fertilisers: As they graze, animals fertilise the soil by spreading their manure.
How to reduce pesticide exposure?
Food that contains fewer pesticides The best way to reduce your exposure to pesticides in food is to buy organic. Certified organic food, including fruit and vegetables, processed food and meat and dairy products will, overall, contain less pesticides.

How Is Soil Organic Carbon Different to Soil Organic Matter?
Soil Organic Carbon and Carbon Sequestration
- Sequestering carbon in SOC is seen as one way to mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide. The argument is that small increases of SOC over very large areas in agricultural and pastoral lands will significantly reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide. For the reduction to be long-lasting, organic matter would have to be in the more ...
What Is Soil Organic Matter?
- SOM is composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and has small amounts of other elements, such as nitrogen, phosphorous, sulfur, potassium, calcium and magnesium contained in organic residues. It is divided into ‘living’ and ‘dead’ components and can range from very recent inputs, such as stubble, to largely decayed materials that are thousands of years old. About 10% …
How Much Soil Organic Carbon Is in WA Soils?
- Most WA soils are low in SOC (Viscarra Rossel et al. 2014). Low rainfall, warm conditions for much of the year, and sandy soils limit the build-up of stable SOC. Typically, the organic carbon content of WA dryland agricultural soils is between 0.7% and 4% (Figure 2), although SOC can be as low as 0.3% for desert soils and as high as 14% for intensive dairy soils. Most organic matter …
Estimating Soil Organic Matter Stock from Soil Organic Carbon
- 1 Start with the measured total organic carbon % About 58% of the mass of organic matter exists as carbon. We can estimate the percentage of SOM from the SOC% using the conversion factor 1.72 (derived from 100/58). Organic matter (%) = total organic carbon (%) x 1.72 This conversion factor can vary in different soils, but 1.72 provides a reasonable estimate of SOM fo…
Soil Organic Matter Cycling
- Soil type, climate and management influence organic matter inputs to soil and its turnover or decomposition. Rainfall is a major driver of plant growth (biomass) and biological activity which results in the decomposition of organic matter that enters soil. The different fractions of SOM (dissolved, particulate, humus and resistant) turn over at vastly different rates (Figure 3). Further…
How Much of The Soil Organic Carbon That Enters Soil Stays there?
- Microorganisms digest up to 90% of the organic carbon that enters a soil in organic residues. In doing so, they respire the carbon back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. While up to 30% of organic inputs can eventually be converted to humus, depending on soil type and climate, in Australian agricultural soils this value is often significantly less. There are 3 main factors influen…
How Do I Measure Or Interpret Soil Organic Carbon Results?
- Changes in stable SOC generally occur very slowly (over decades), and it is often hard to measure small changes against a relatively large background of soil carbon. Changes in SOC are largely determined by how much biomass is grown and retained above and below ground. About 45% of organic matter is carbon and lighter textured soils retain less than 30% of this. For example, WA …
References
- Griffin, E, Hoyle, FC & Murphy, DV 2013, 'Soil organic carbon', in Report card on sustainable natural resource use in Agriculture, Department of Agriculture and Food, Western Australia, viewed 16 November 2016, https://www.agric.wa.gov.au/sites/gateway/files/2.4%20Soil%20organic%20carbon.pdf Hoyle, F…