
Because of its potential use in amphetamine manufacture, it is controlled by the Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act of 2005. It is still available for veterinary use in dogs, however, as a treatment for urinary incontinence.
Is phenylpropanolamine banned by the FDA?
Phenylpropanolamine is a sympathomimetic that was previously used in nasal decongestants and weight loss products, but has been withdrawn by the FDA due to safety risks and lack of efficacy. Phenylpropanolamine is a sympathomimetic agent that acts as a nonselective adrenergic receptor agonist and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.
Is oxaprozin a controlled dangerous substance?
Oxaprozin may also cause stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal. Oxaprozin can increase your risk of fatal heart attack or stroke, even if you don't have any risk factors. Do not use this medicine just before or after heart bypass surgery (coronary artery bypass graft, or CABG).
Will propofol become a controlled substance?
Propofol is not currently controlled by either the Federal Government or State governments, and may not be a target or priority of law enforcement; therefore, information on reported seizures and cases from Federal, State and local law enforcement agencies is very limited.
Is Fycompa considered controlled substance?
Fycompa is a controlled substance (CIII) because it can be abused or lead to drug dependence. Keep your Fycompa in a safe place to protect it from theft. Never give your Fycompa to anyone else because it may harm them.
Is phenylpropanolamine a controlled substance?
While PPA is not a controlled substance, it is a listed chemical, and subject to federal regulation under the Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act of 2005.
Why was phenylpropanolamine taken off the market?
Phenylpropanolamine has been voluntarily removed from the market in the United States by its manufactures because of concerns raised about its ability to precipitate a stroke when used, or perhaps abused, as an appetite suppressant Kernan et al (2000).
What class of drug is phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine is a sympathomimetic agent that acts as a nonselective adrenergic receptor agonist and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It has been used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant.
Is proin controlled substance?
What is Proin? Proin is an aid in the management of urinary incontinence in dogs. Proin requires a prescription from your veterinarian, and is considered a controlled substance in some states.
Can you still buy phenylpropanolamine?
It is available in nonprescription products alone and in combination with other nonprescription drugs, to treat symptoms of allergy , colds, and upper respiratory infections.
Why did the US and Canada ban the use of phenylpropanolamine?
Health Canada has officially withdrawn many cough, cold and sinus drugs containing phenylpropanolamine, or PPA, because they can cause bleeding in the brain, resulting in a stroke.
What OTC drugs contain phenylpropanolamine?
Although most of these products have been taken off the market, the ones that contain phenylpropanolamine include Tavist-D, Dimetapp, Robitussin, Vicks, and Alka Seltzer Plus. Any cold and cough medicines purchased over the counter should be inspected for phenylpropanolamine, or a pharmacist may be consulted.
Is it safe to take phenylpropanolamine?
That review included phenylpropanolamine. In 1976, one expert panel recommended that phenylpropanolamine be generally recognized as safe and effective as a nasal decongestant, and in 1982 another expert panel recommended that phenylpropanolamine be generally recognized as safe and effective for weight control.
What is another name for phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine (brand names: Proin®, Propalin®, Cystolamine®, Uricon®, Uriflex-PT®) is a sympathomimetic medication used to treat urinary incontinence due to poor muscle tone in the urethral sphincter.
In what states is Proin a controlled substance?
Description: We cannot ship this medicine to AR, IA, LA, OR, and WV. It is deemed a controlled substance in these states. Proin is a supplement used to treat urinary incontinence in dogs.
Who should not take phenylpropanolamine?
Who should not take phenylpropanolamine? Do not take phenylpropanolamine if you have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), or tranylcypromine (Parnate) in the last 14 days. A very dangerous drug interaction could occur, leading to serious side effects.
Which medication is a Schedule V controlled substance?
Schedule V Controlled Substances Examples of Schedule V substances include: cough preparations containing not more than 200 milligrams of codeine per 100 milliliters or per 100 grams (Robitussin AC®, Phenergan with Codeine®), and ezogabine.
Is it safe to take phenylpropanolamine?
That review included phenylpropanolamine. In 1976, one expert panel recommended that phenylpropanolamine be generally recognized as safe and effective as a nasal decongestant, and in 1982 another expert panel recommended that phenylpropanolamine be generally recognized as safe and effective for weight control.
Who should not take phenylpropanolamine?
Who should not take phenylpropanolamine? Do not take phenylpropanolamine if you have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), or tranylcypromine (Parnate) in the last 14 days. A very dangerous drug interaction could occur, leading to serious side effects.
What are the side effects of phenylpropanolamine?
Are there any potential side effects? The most common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, lack of appetite, increased thirst, restlessness, irritability, and difficulty urinating. Serious side effects include seizures, collapse, or stroke-like signs (for example, not being able to walk).
What are the contraindications of phenylpropanolamine?
The following conditions are contraindicated with this drug....Conditions:overactive thyroid gland.increased pressure in the eye.closed angle glaucoma.high blood pressure.stenosing peptic ulcer.blockage of the urinary bladder.enlarged prostate.an inability to completely empty the bladder.More items...
What Is Phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine is a decongestant. It works by constricting (shrinking) blood vessels (veins and arteries) in your body. Constriction of blood...
What Is The Most Important Information I Should Know About Phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine has been associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into the brain or into tissue surrounding the brain)...
Who Should Not Take Phenylpropanolamine?
Do not take phenylpropanolamine if you have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), or tra...
How Should I Take Phenylpropanolamine?
Take phenylpropanolamine exactly as directed by your doctor, or follow the instructions that accompany the package. If you do not understand these...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take only your next regula...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention.Symptoms of a phenylpropanolamine overdose include extreme tiredness, sweating, dizziness, a slow heart beat, and...
What Should I Avoid While Taking Phenylpropanolamine?
Use caution when driving, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous activities. Phenylpropanolamine may cause dizziness or drowsiness. If...
Phenylpropanolamine Side Effects
If you experience any of the following serious side effects from this medication, stop taking phenylpropanolamine and seek emergency medical attent...
Phenylpropanolamine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Nasal Congestion:25 mg orally every 4 hours.-or-75 mg orally extended release every 12 hours.Not to exceed 150 mg/day.Usual Ad...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Phenylpropanolamine?
Do not take phenylpropanolamine if you have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), or tra...
What is the simplest unsubstituted phenylisopropylamine?
The simplest unsubstituted phenylisopropylamine, 1-phenyl-2-aminopropane, or amphetamine , serves as a common structural template for hallucinogens and psychostimulants. Amphetamine produces central stimulant, anorectic, and sympathomimetic actions, and it is the prototype member of this class (39). ...
What is the compound of d-norephedrine?
The compound exists as four stereoisomers, which include d - and l -norephedrine and d - and l -norpseudoephedrine. d -Norpseudoephedrine is also known as cathine, and is found naturally in Catha edulis ( khat ).
What is PPA used for?
It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.
What is a Category 1 PPA?
A European Category 1 Licence is required to purchase PPA for academic use. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a public health advisory against the use of the drug in November 2000.
What is the parent compound of a sympathomimetic amine?
β-Phenylethylamine (Table 12–1) can be viewed as the parent compound of the sympathomimetic amines, consisting of a benzene ring and an ethylamine side chain. The structure permits substitutions to be made on the aromatic ring, the α- and β-carbon atoms, and the terminal amino group to yield a variety of compounds with sympathomimetic activity. ...N-methylation increases the potency of primary amines ...
What is the phase 1 metabolism of amphetamines?
The phase 1 metabolism of amphetamine analogs is catalyzed by two systems: cytochrome P450 and flavin monooxygenase. ... Amphetamine can also undergo aromatic hydroxylation to p-hydroxyamphetamine. ... Subsequent oxidation at the benzylic position by DA β-hydroxylase affords p-hydroxynorephedrine.
When was PPA banned in India?
Drugs containing PPA were banned in India on 27 January 2011.
What is phenylpropanolamine used for?
Phenylpropanolamine is an ingredient used in many over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription cough and cold medications as a decongestant and in OTC weight loss products.
Is phenylpropanolamine removed from all drugs?
FDA, today, is taking steps to remove phenylprop anolamine from all drug products and has requested that all drug companies discontinue marketing products containing phenylpropanolamine.
Does phenylpropanolamine cause stroke?
Scientists at Yale University School of Medicine conducted the study in which the researchers found an association between phenylpropanolamine use and stroke in women. The increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke was detected among women using the drug for weight control, and for nasal decongestion, in the 3 days after starting use of the medication. Men may also be at risk.
What is phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine is a decongestant. It works by constricting (shrinking) blood vessels (veins and arteries) in your body. Constriction of blood vessels in your sinuses, nose, and chest allows drainage of those areas, which decreases congestion.
What is the most important information I should know about phenylpropanolamine?
Phenylpropanolamine has been associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into the brain or into tissue surrounding the brain) in women. Men may also be at risk. Although the risk of hemorrhagic stroke is low, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends that consumers not use any products that contain phenylpropanolamine.
What should I avoid while taking phenylpropanolamine?
Use caution when driving, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous activities. Phenylpropanolamine may cause dizziness or drowsiness. If you experience dizziness or drowsiness, avoid these activities.
What are some other medications that interact with phenothiazines?
other commonly used phenothiazines, including fluphenazine (Prolixin), perphenazine (Trilafon), mesoridazine (Serentil), and trifluoperazine (Stelazine). Drugs other than those listed here may also interact with phenylpropanolamine.
Is it safe to take phenylpropanolamine at 60?
You may require a lower dose of this medication. Using a short-acting formulation of phenylpropanolamine ( not a long-acting or a controlled-release formulation) may be safer if you are over 60 years of age.
Can you use phenylpropanolamine for a stroke?
Although the risk of hemorrhagic stroke is low, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends that consumers not use any products that contain phenylpropanolamine. Phenylpropanolamine may also be used for purposes other than those listed in this medication guide.
Does phenylpropanolamine cause a stroke?
Phenylpropanolamine also causes a decrease in appetite and is used in some over-the-counter diet aids. Phenylpropanolamine has been associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into the brain or into tissu e surrounding the brain) in women . Men may also be at risk.
What is phenylpropanolamine used for?
NOTICE - Phenylpropanolamine can be used in Illicit Amphetamine Manufacture. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is issuing this notice to inform individuals and businesses handling phenylpropanolamine that this chemical is used in the illicit manufacture of amphetamine.
Why do phenylpropanolamine handlers need to know their customers?
Handlers of phenylpropanolamine need to know their customers so as not to become an unwitting supplier to a clandestine amphetamine laboratory.
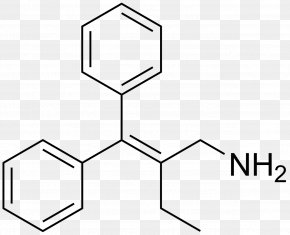
Overview
Society and culture
In Sweden, PPA is still available in prescription decongestants, PPA is also still available in Germany. It is used in some polypill medications like Wick DayMed capsules.
In the United Kingdom, PPA was available in many 'all in one' cough and cold medications which usually also feature paracetamol or another analgesic and caffeine and could also be purchased on its own; however, it is no longer approved for human use. A European Category 1 Licence is requ…
Chemistry
PPA is also known as β-hydroxyamphetamine, and is a member of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is closely related to the cathinones (β-ketoamphetamines). The compound exists as four stereoisomers, which include d- and l-norephedrine and d- and l-norpseudoephedrine. d-Norpseudoephedrine is also known as cathine, and is found naturally in Catha edulis (khat). Pharmaceutical drug preparations of PPA have varied in their stereoisomer co…
History
Phenylpropanolamine was patented in 1938. In the United States, PPA is no longer sold due to an increased risk of haemorrhagic stroke. In a few countries in Europe, however, it is still available either by prescription or sometimes over-the-counter. In Canada, it was withdrawn from the market on 31 May 2001. It was voluntarily withdrawn from the Australian market by July 2001. In India, human use of PPA and its formulations was banned on 10 February 2011, but the ban was overt…
Pharmacology
Although originally thought to act as a direct agonist of adrenergic receptors, PPA was subsequently found to show only weak or negligible affinity for these receptors, and has been instead characterized as an indirect sympathomimetic which acts by inducing norepinephrine release and thereby activating adrenergic receptors.
PPA acts primarily as a selective norepinephrine releasing agent. It also acts as a dopamine relea…
Drug interactions
Certain drugs increase the chances of déjà vu occurring in the user, resulting in a strong sensation that an event or experience currently being experienced has already been experienced in the past. Some pharmaceutical drugs, when taken together, have also been implicated in the cause of déjà vu. Taiminen and Jääskeläinen (2001) reported the case of an otherwise healthy male who started experiencing intense and recurrent sensations of déjà vu upon taking the drugs amantadine and …
External links
• Phenylpropanolamine Information Page at FDA.gov (update, includes earlier reports)
• U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Phenylpropanolamine