Is it important?
- Is the "first word" the start of language?
- Before words, other forms of communication
- Infant's responsiveness to language, variety of vocalizations, nonword vocalizations and gestures: so language is already forming!
- This "pre-linguistic" communication sets the foundation for later language
What are paralinguistic features in communication?
Paralinguistics are the aspects of spoken communication that do not involve words. These may add emphasis or shades of meaning to what people say. Body language, gestures, facial expressions, tone and pitch of voice are all examples of paralinguistic features.
What is limited receptive communication skills?
When a person is having difficulty understanding or receiving the message, he has limited receptive communication skills. He may have difficulty understanding individual words, phrases, information from the sentence, a question, instructions or descriptions.
What are the problems with communication?
Communications Issues In The Workplace. Communication problems in organizations can stem from internal and external factors. Internal factors include one’s prejudice, preconceived ideas and other distortions while listening to someone. External factors could be disturbances in the environment or problems in the medium being used to communicate.
What is important in English communication?
The importance of English Communication is to communicate effectively and no communication is possible if one doesn’t get a chance to communicate. It is natural that the demand for communication is high in this ever changing world.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1449117-article-gifted-children-and-language-development-01-5aa81c37ba61770037a70b26.png)
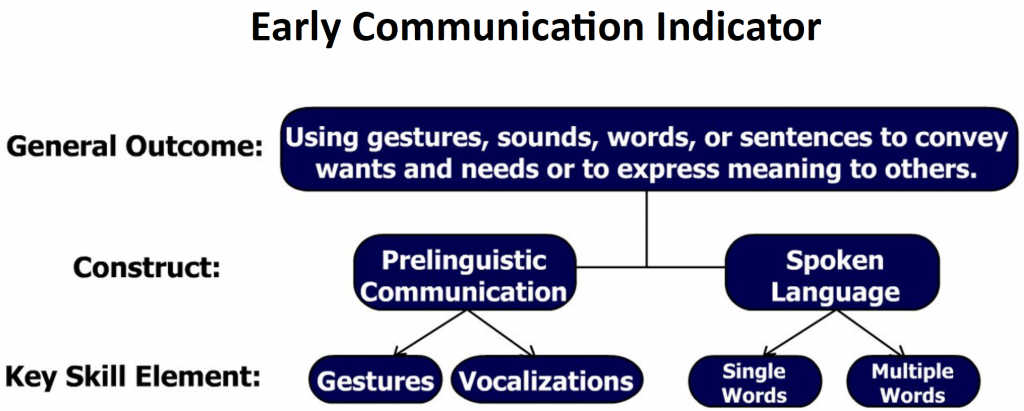
What is the purpose of Prelinguistic communication?
Prelinguistic communication describes behaviors children display, both intentional and unintentional, to communicate their wants and needs.
What is the Prelinguistic stage of language development?
The prelinguistic stage ranges from birth to approximately 6 months. Noises in this stage include crying, whimpering, and cooing. These sounds are not considered language because they are involuntary responses to stimuli. Linguists consider human language creative – as free from internal or external stimuli.
What is an example of Prelinguistic vocalization?
crying, cooing, and babbling.
How do you develop Prelinguistic skills?
Spend quality time with the child playing, interacting and let the child be involved in everyday chores. Encourage eye contact by being at their eye level while talking and by holding the toys of interest at your eye level while playing. Sing action rhymes and play fun games to encourage imitation.
What is Prelinguistic speech?
Prelinguistic communication includes: gestures, eye contact, facial expressions, non-word vocalizations, imitation, and joint attention. Development of these skills set children up to be successful verbal communicators.
What are the Prelinguistic skills?
What are pre-linguistic skills?Eye Contact.Joint Attention.Anticipation.Pointing/Reaching.Facial Expression/Body Language.Social Gestures/Signs.Turn-Taking /Social Routines and Sequences.Babbling/Symbolic Noises.More items...•
What is a Prelinguistic event?
denoting or relating to the period of an infant's life before he or she has acquired the power of speech. The prelinguistic period includes the earliest infant vocalizations as well as the babbling stage typical of the second half of the first year.
What is Prelinguistic milieu teaching?
Prelinguistic Milieu Teaching (PMT) is an intervention for children with language delays and facilitates the child's development of non-verbal communication as a foundation for later spoken word production.
What is the baby first word?
So when do babies usually say their first word? Around 12 months, according to experts. Common first words may be greetings ("hi" or "bye-bye") or they might be very concrete: people ("mama" or "dada"), pets ("doggy" or "kitty"), or food ("cookie," "juice," or "milk").
Is turn taking a Prelinguistic skill?
Many times, speech-language pathologists think about turn-taking as a verbal skill, but like every other prelinguistic skill we're discussing, turn taking begins as a nonverbal activity.
Why are preverbal skills important?
A child usually starts to learn preverbal skill from birth until three years old. This skill is very important for further speech and language development. Early preverbal skill acquisition marks good speech andlanguage skills at later age. Eye contact happens when a child looks at the parents or other person's eyes.
What activities help language development?
Fun activities that help develop language learning in childrenWord games. Expand your children's vocabulary with word games. ... Jokes. Telling age-appropriate puns will also help foster good humour and creativity in children. ... Riddles. ... Rhymes. ... Homonyms. ... Storytelling. ... Songs. ... Tongue twisters.
What are some examples of symbolic thought?
Symbolic thought is common for children to engage in through the process of pretend or make believe. Young children express symbolic thoughts by reenacting actions of parents or care givers by using various objects that represent what they pretend them to be. An example is children playing in the dirt to make food.
What is paralinguistic and examples?
Body language, gestures, facial expressions, tone and pitch of voice are all examples of paralinguistic features. Paralinguistic features of language are extremely important as they can change message completely.
What is Holophrastic speech?
: expressing a complex of ideas in a single word or in a fixed phrase.
What is meant by Para linguistic communication?
“Paralinguistic communication” has been defined as “not WHAT you say, but THE WAY you say it.” Paralanguage, sometimes known as nonverbal communication, is communication by means other than words, although (usually) operating alongside language.
When do babies start smiling?
Babies begin smiling around six weeks of age. When babies smile, it fosters increased interactions between babies and their caregivers. Adults are more likely to continue interacting with babies when they are rewarded with a response like a smile. When babies are responsive to adult interactions, adults initiate communication more often.
Is Your Child Having Difficulty with Prelinguistic Skills?
If your child is having difficulty developing prelinguistic skills you may notice these things:
What is prelinguistic communication? You might be wondering
Before getting started with tips and activities, let’s define prelinguistic communication.
Tip 2 - Say the name of the thing you are offering
Next, you can use this as an opportunity to help your child identify the object with language. When you offer an item to your child (after making sure they don’t grab it from you), be sure to say the name of the item you’re offering. For example, “Car.
Tip 3 - Wait and watch for signs of requesting
When you practice these skills, take time to observe your child closely and see if they display signs of requesting. Oftentimes, you are able to anticipate your child’s wants or needs. Anticipating your child’s needs is great; knowing when they need a diaper change or nourishment is important.
Why are prelinguistic skills important?
These prelinguistic skills are necessary to establish the neural responses and neural connections for sensory stimuli, i.e., sound, light, and touch. As a result, the sensory information transmission is taking place via these established neural connections. Hence, these neural connections develop during the first two years of life. Therefore, these initial years are a critical period in the development of communication skills. And provide the foundation of more language-based communication such as reading, writing, and theory of mind.
How many prelinguistic skills are there?
There are 11 prelinguistic skills. These skills revolve around above mentioned three developmental domains. A child starts learning these skills after birth till his first meaningful word appears. In other words, we can say a child unable to utter an expressive word until he gets mastery in prelinguistic skills. Let’s have a look at these prelinguistic skills:
What is massage communication?
Communication is a way to deliver a message from one person to another. That massage could be about a need, an experience, an idea, knowledge, or a desire. Moreover, it can be verbal or non-verbal. A child learns prelinguistic or non-verbal communication before uttering a word in a meaningful contest. A baby by birth is communicating via lots of means without any verbal response. For instance, s/he uses a different kind of cry to convey a message. Therefore, we can say prelinguistic skills are a non-verbal way of communication. There are various non-verbal means of communication, such as babbling, pointing, and making eye contact.
What is the utmost important skill?
Respond to the sensory stimulus p resent in the surroundings is the utmost important skill. These sensory stimuli could be sound, light, or touch. It is a cognition domain-based skill. Sensory information transmission passage is created when a child responds to the sensory stimuli present in his surroundings. That builds the neural connection within our brain and establishes the auditory and visual perceptual modalities. That’s why if a child is hard of hearing, he must be amplified with hearing aids or cochlear implants on an emergency basis to save the auditory neural connection pathways.
When do neurotypical children master prelinguistic skills?
A neurotypical growing child achieves that mastery level by the age of 9-18 months. However, if a child struggles to mastery prelinguistic skills henceforth, he will be a victim of expressive language delay or learning disability. These prelinguistic skills roam around three main domains.
Why is play important in language development?
The play provides opportunities to think and plan, and it creates a platform for working memories. That’s why play and toys have an essential role in speech and language development.
What is the response to people present in the surrounding?
Response to people present in the surrounding comes under the social domain. For instance, a 1-2 months old baby realizes that he can grab his mom’s attention when he cries. Later, he learns who his mom is.
What is pre-linguistic communication?
Infant's responsiveness to language, variety of vocalizations, nonword vocalizations and gestures: so language is already forming! This "pre-linguistic" communication sets the foundation for later language.
Why do babies use their communication?
Thus, this social development may be the reason babies learn to use their communication intentionally , as it provides environmental support to the babies
What does a baby's pleasant cooing sound do?
Infant's pleasant cooing sounds also draw adults into having conversations who then respond back vocally, thus engaging the infant to produce more speechlike sounds in turn
Why is direct speech important for language development?
The more the parents talk to babies (as opposed to each other ), the faster the rate of language learning, thus direct adult-to-child speech quantity is important for language development
What does a child do when he is in contact with his partner?
The child makes eye contact with the partner while gesturing or vocalizing, often alternating his or her gaze between an object and the partner
How long does it take to start pointing?
Between 6-10 months, begin pointing at objects or pictures
How long does it take for speech perception to change?
In the first year speech perception gets shaped by the language heard, and the ability to hear the differences among those sounds that are not used is lost by 1 year of age
How do children with developmental disabilities learn to communicate?from link.springer.com
While most typically developing children learn to communicate without formal teaching, children with developmental disabilities are often delayed in the use of first words and may need guidance to learn how to communicate . Because prelinguistic communication (e.g., facial expressions, natural gestures, and vocalizations.) is seen as a foundation for spoken word production, helping children to develop their prelinguistic communication may facilitate acquisition of spoken language. This chapter explores Prelinguistic Milieu Teaching (PMT), an intervention designed to teach children to initiate nonverbal communication during social routines in their natural environment as a foundation for later spoken word production. First, the theoretical background of PMT, which is typically viewed as a transactional model is discussed. Then, the implementation of PMT is described and the available research reviewed. Finally, suggestions for further research and implications for practitioners are provided.
Why is the primary caretaker capable of using these PMT strategies to promote the child’s intentional communication?from prezi.com
Their primary caretaker is capable of using these PMT strategies to promote the child’s intentional communication because they have the greatest impact on them.
Why is it important to remind parents of their schedule?from prezi.com
It's important to remind the parent (s) that it's not just another thing to add on top of their schedule, but that they can incorporate it in their daily activities they are already involved in.
What are the four stages of pre-linguistic language development?
Pre-linguistic language development can be divided into four categories: vegetative sounds, cooing and laughter, vocal play and babbling. Linguistic language development is the stage of language development signaled by the emergence of words and symbolic communication.
What is linguistic development?
Linguistic language development is the stage of language development signaled by the emergence of words and symbolic communication. Prior to this stage, most of the sounds a child produces are no more than the practice of sound manipulation and sound sequencing in order to gain the motor skills necessary to create words. There are six periods of linguistic language development.
What is receptive language?
There's also the development of receptive language to consider. Receptive language refers to speech comprehension or the ability to understand what is being said. Receptive and expressive language develops separately of one another, but there is some parallel development of note between them.
When do kids start to express past and future time?
It begins around the ages of 48-60 months. At this time, a child regularly produces phrases longer than six words in length, and they begin to express concepts of past and future time. Examples are: 'Daddy comes home from the trip tomorrow' and 'I saw a dog at the park yesterday.'.
What are the stages of language development?
The stages of language development explores the process of children learning syntax. Discover the pre-linguistic language stage, symbolic/linguistic language stage, and expressive vs. receptive language in this lesson. Lastly, the four categories of pre-linguistic language development and the six categories of linguistic language development are detailed. Updated: 09/21/2021