Why is the carbon cycle is important?
The carbon cycle is vital to life on Earth. Nature tends to keep carbon levels balanced, meaning that the amount of carbon naturally released from reservoirs is equal to the amount that is naturally absorbed by reservoirs. Maintaining this carbon balance allows the planet to remain hospitable for life.
Is the biosphere necessary for the carbon cycle?
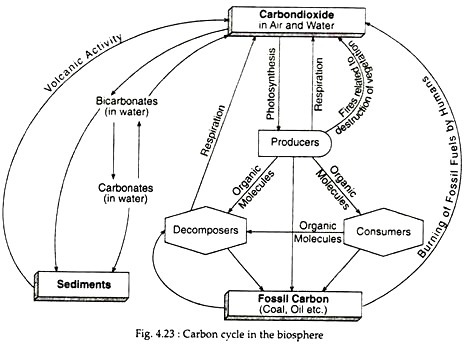
Life is built on the conversion of carbon dioxide into the carbon-based organic compounds of living organisms. The carbon cycle illustrates the central importance of carbon in the biosphere. Different paths of the carbon cycle recycle the element at varying rates.
What processes does carbon cycle through the biosphere?
Carbon cycles through the atmosphere, biosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere via processes that include photosynthesis, fire, the burning of fossil fuels, weathering, and volcanism.
How does carbon dioxide affect the biosphere?
Carbon dioxide increases temperatures, extending the growing season and increasing humidity. Both factors have led to some additional plant growth. However, warmer temperatures also stress plants.
How much carbon is in the biosphere?
About 500 gigatons of carbon are stored above ground in plants and other living organisms, while soil holds approximately 1,500 gigatons of carbon....Terrestrial biosphere.PoolQuantity (gigatons)Living biomass600 – 1,000Dead biomass1,200Aquatic biosphere1 – 2Fossil fuels (total)4,13014 more rows
How is carbon stored in biosphere?
Carbon is stored on our planet in the following major sinks (1) as organic molecules in living and dead organisms found in the biosphere; (2) as the gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere; (3) as organic matter in soils; (4) in the lithosphere as fossil fuels and sedimentary rock deposits such as limestone, dolomite and ...
What happens in the biosphere?
The remains of dead plants and animals release nutrients into the soil and ocean. These nutrients are reabsorbed by growing plants. This exchange of food and energy makes the biosphere a self-supporting and self-regulating system.
How does carbon get from the biosphere to the atmosphere?
When plants and animals die, their bodies, wood and leaves decays bringing the carbon into the ground. Some is buried and will become fossil fuels in millions and millions of years. Carbon moves from living things to the atmosphere. Each time you exhale, you are releasing carbon dioxide gas (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Why is the cycle important to the ecosystem?
Why is the hydrologic cycle important? The hydrologic cycle is important because it is how water reaches plants, animals and us! Besides providing people, animals and plants with water, it also moves things like nutrients, pathogens and sediment in and out of aquatic ecosystems.
What is the relationship between carbon and the three parts of the biosphere?
Carbon is found in the biosphere stored in plants and trees. Plants use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to make the building blocks of food during photosynthesis. Carbon is found in the hydrosphere dissolved in ocean water and lakes. Carbon is used by many organisms to produce shells.
How does the carbon cycle interact with the 4 spheres?
The cycle can be thought of in terms of reservoirs (places where carbon is stored) and flows (the movement between reservoirs). The atmosphere, the biosphere, the hydrosphere, and the lithosphere are the reservoirs and the processes by which carbon moves from one reservoir to another are the flows.
How is the biosphere being impacted?
Destruction of trees not only removes these “carbon sinks,” but tree burning and decomposition pump into the atmosphere even more carbon dioxide, along with methane, another major greenhouse gas. Burning any fossil fuel produces carbon dioxide, which contributes to the greenhouse effect warming Earth.
What if there were no biosphere?
Earth would not be the planet that it is without its biosphere, the sum of its life. But life is not a constant thing, as illustrated in this series of images. The images show the distribution of chlorophyll over the Earth's ocean surface averaged over a year. On land, the images represent the density of plant growth.
How does carbon get from the biosphere to the atmosphere?
When plants and animals die, their bodies, wood and leaves decays bringing the carbon into the ground. Some is buried and will become fossil fuels in millions and millions of years. Carbon moves from living things to the atmosphere. Each time you exhale, you are releasing carbon dioxide gas (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Does carbon cycle through the biosphere in transpiration?
What is the difference between evaporation & transpiration? Carbon cycles through the biosphere in all of the following processes EXCEPT: photosynthesis, transpiration, burning of fossil fuels, or decomposition of plants & animals?
How is the biosphere involved in the nitrogen cycle?
Four processes participate in the cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere: (1) nitrogen fixation, (2) decay, (3) nitrification, and (4) denitrification. Microorganisms play major roles in all four of these.
How long has carbon been stored in the Earth's geosphere?from nasa.gov
We tap into carbon that has been stored in Earth's geosphere for millions of years when we heat our homes with coal and natural gas. We even find the cycle mentioned in the Bible, commonly quoted as saying, "from dust to dust.".
Where is carbon stored on Earth?from oceanservice.noaa.gov
Where the carbon is located — in the atmosphere or on Earth — is constantly in flux. On Earth, most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments, while the rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms.
How much carbon dioxide is in the Northern Hemisphere?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
Current research estimates that permafrost in the Northern Hemisphere holds 1,672 billion tons (Petagrams) of organic carbon. If just 10 percent of this permafrost were to thaw, it could release enough extra carbon dioxide to the atmosphere to raise temperatures an additional 0.7 degrees Celsius (1.3 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100.
What is the carbon dioxide effect?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
Carbon dioxide causes about 20 percent of Earth’s greenhouse effect ; water vapor accounts for about 50 percent; and clouds account for 25 percent. The rest is caused by small particles (aerosols) and minor greenhouse gases like methane. Water vapor concentrations in the air are controlled by Earth’s temperature.
What happens when you dissolve carbon dioxide in the ocean?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
Dissolving carbon dioxide in the ocean creates carbonic acid, which increases the acidity of the water. Or rather, a slightly alkaline ocean becomes a little less alkaline. Since 1750, the pH of the ocean’s surface has dropped by 0.1, a 30 percent change in acidity.
How much carbon dioxide did humans release in 2009?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
In 2009, humans released about 8.4 billion tons of carbon into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuel. Emissions of carbon dioxide by humanity (primarily from the burning of fossil fuels, with a contribution from cement production) have been growing steadily since the onset of the industrial revolution.
How will the Earth's orbit change in 30,000 years?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
In about 30,000 years, Earth’s orbit will have changed enough to reduce sunlight in the Northern Hemisphere to the levels that led to the last ice age. Today, changes in the carbon cycle are happening because of people. We perturb the carbon cycle by burning fossil fuels and clearing land. When we clear forests, we remove a dense growth ...

Quotes
Resources
Geology
Environment
Formation
Chemistry
Mechanism
Results
Biology
- Carbon plays an essential role in biology because of its ability to form many bondsup to four per atomin a seemingly endless variety of complex organic molecules. Many organic molecules contain carbon atoms that have formed strong bonds to other carbon atoms, combining into long chains and rings. Such carbon chains and rings are the basis of living...
Benefits
Timeline
Evolution
Example
Significance
Cause
Climate
Advantages
Introduction