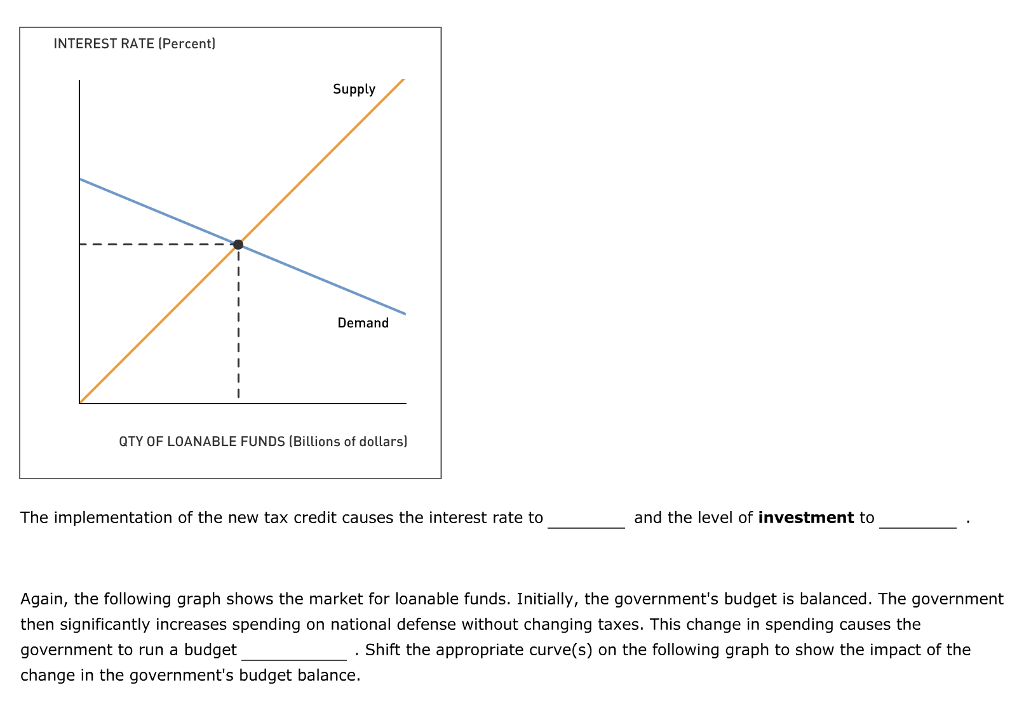
The demand curve for loanable funds is negatively sloped. More loans are demanded at lower real interest rates, and fewer loans are demanded when real interest rates are higher. Businesses, for example, will find more projects worthwhile to invest in at lower rates than at higher rates.
What is the slope of the demand curve for loanable funds?
If we plot it on a graph, the demand curve for loanable funds has a downward slope (negative). For the borrower, the interest rate represents the cost of borrowing funds. The higher the interest rate, the greater the cost of paying it back.
How do interest rates affect the demand for loanable funds?
If we plot it on a graph, the demand curve for loanable funds has a downward slope (negative). For the borrower, the interest rate represents the cost of borrowing funds. The higher the interest rate, the greater the cost of paying it back. So, when interest rates rise, the demand for loanable funds decreases.
What is the relationship between demand and supply and loanable funds?
It is the amount of national savings in a country. Meanwhile, demand represents the total funds available to be borrowed at a certain interest rate. The loanable funds market reaches equilibrium when demand equals supply, determining the amount of loanable funds and the economy’s interest rate.
What causes a shift in the curve in the loan-fund market?
A shift in the curve in the loan-fund market. Movements along the demand and supply curves occur because of changes in interest rates. Meanwhile, both curves will shift only if the non-interest rate factor changes. Meanwhile, two factors that cause the demand for loanable funds to shift are: Change in opportunities perceived by businesses
Why is the supply for loanable funds downward sloping?
It is downward sloping because as price level goes down, quantity demanded of all goods will increase.
Why is the demand for money downward sloping?
Money demand curve is negatively sloped as there is a negative relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate. In other words, the money demand curve is downward sloping because of the interest rate, which represents the opportunity cost of holding money.
What affects demand for loanable funds?
Deficits increase the demand for loanable funds; surpluses decrease the demand for loanable funds. The logic of this point of view is that if the government runs a deficit, it has to borrow money just like everyone else.
What shifts the supply curve for loanable funds?
Increase in public savings. Increase in national savings. Supply curve of loanable funds shifts right. Decrease in public savings.
WHY IS curve is negatively sloped?
The IS curve is negatively sloped because a decrease in the interest rate (i) increases planned investment spending (I) and therefore increases aggregate demand, thus increasing the equilibrium level of income.
Why is the demand for money downward sloping quizlet?
The money demand Curve is: Downward sloping Because as the interest rate increases, people will physically hold less money! Money Supply Curve: The amount of money in the economy, determined by the fed.
What does the slope of the demand for loanable funds curve represent?
Answer and Explanation: The slope of the demand for loanable funds curve represents the D) negative relationship between the real interest rate and D) Investment. The demand curve of loanable funds depicts the negative slope between the real interest rate and investments.
What factors affect the demand for loanable funds quizlet?
Consumption smoothing is another factor that shifts the loanable funds supply. What factors shift the demand for loanable funds? Capital productivity is the main determinant of the demand for loanable funds. Investor confidence also affects the demand for loanable funds.
Why does the supply of loanable funds slope upward?
The supply of loanable funds slopes upward because higher interest rates make it more costly to borrow. savers will make more funds available at lower interest rates.
What are the 4 factors that influence interest rates?
Demand for and supply of money, government borrowing, inflation, Central Bank's monetary policy objectives affect the interest rates.
Which factor brings the supply and demand of loanable funds into balance?
The interest rate adjusts to bring the supply and demand for loanable funds into balance. If the interest rate were below the equilibrium level, the quantity of loanable funds supplied would be less than the quantity demanded. The resulting shortage of loanable funds would push the interest rate upward.
How do you find the demand of a loanable fund?
The loanable funds market is characterized by the following demand function DLF where the demand for loanable funds curve includes only investment demand for loanable funds: r = 10 - (1/2000)Q where r is the real interest rate expressed as a percent (e.g., if r = 10 then the interest rate is 10%) and Q is the quantity ...
How to reduce crowding out effect?
One option to reduce the crowding-out effect is to borrow from the international market. Say, the government finances the increase in the deficit by borrowing from abroad (for example, by issuing global bonds). It doesn’t result in an increase in demand for loanable funds in the domestic market. Hence, domestic interest rates should not increase.
Why does the loanable fund supply curve have a positive slope?
Not only you, but other individuals or businesses will also do the same when interest rates rise. As a result, the loanable funds supply in the economy increases . This is why the loanable fund’s supply curve has a positive slope – showing a positive relationship between the loanable funds’ supply and the interest rate.
How is the demand curve for loanable funds determined?
The loanable funds’ demand is determined by the interest rate. The two have an inverse relationship. If we plot it on a graph, the demand curve for loanable funds has a downward slope (negative). For the borrower, the interest rate represents the cost of borrowing funds.
What is loanable funds market?
What’s it: Loanable funds market is a market where the demand and supply of loanable funds interact in an economy. This term, you will probably often find in macroeconomics books. Basically, this market is a domestic financial market. Transactions involve money, not goods or services.
How does capital outflow affect the supply curve?
That leads the supply curve to shift to the right. Conversely, capital outflows will cause the curve to shift to the left and borrowed funds to decrease.
Why is knowledge of supply demand important?
In general, knowledge of the supply-demand concept is useful for you to understand how the loanable fund market works.
Why are low interest rates good?
On the other hand, low-interest rates tend to attract large numbers of borrowers. This is because the borrowing cost is cheaper. This situation provides an incentive for borrowers to demand more funds.
What is not included in GDP?
A person engages in household production if he or she produces for himself or herself. Doityourself work is household production. Homemaking and child care done by a parent for their own child is household production. This is clearly productive work, but is excluded from the calculation of GDP. Second, GDP does not include the production of the underground economy. This includes activity, work that is unreported to avoid taxes, and work that is unreported to avoid regulation. Again these are all productive activities, yet are not included in GDP.
What is the difference between nominal and real interest rates?
The nominal interest rate is the stated interest rate on a loan, while the real interest rate is the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
What would happen if the unemployment rate increased?
The unemployment rate would increase and the labor force participation rate would stay the same. The number of unemployed would rise, but the labor force would stay the same. The parttime workers who wanted to be fulltime workers would simply go from being employed to unemployed. With no change in the labor force, the labor force participation rate would not change.
How would the unemployment rate and labor force participation rate change?
The unemployment rate would rise because adding the same number to the numerator and the denominator of the fraction that is less than one increases the value of the fraction. The labor force participation rate would rise because the labor force increases with no change in the workingage population.
Why would the labor force participation rate rise?
The labor force participation rate would rise because the labor force increases with no change in the workingage population. Suppose 180,000 people are employed, 20,000 people are unemployed, the workingage population is 250,000, and 50,000 people are out of the labor force. Calculate the unemployment rate.
Is real GDP higher than nominal GDP?
Real GDP would be higher, as long as the base year was before the period of deflation. Nominal GDP would be measured using the lower prices that resulted from the deflation. Real GDP would use the higher prices before the deflation, assuming the base year was before the deflation.
Will unemployment decrease?
a. The unemployment rate will likely decrease, since decreasing the time people are eligible to receive unemployment benefits will increase the opportunity cost of searching for a job.
