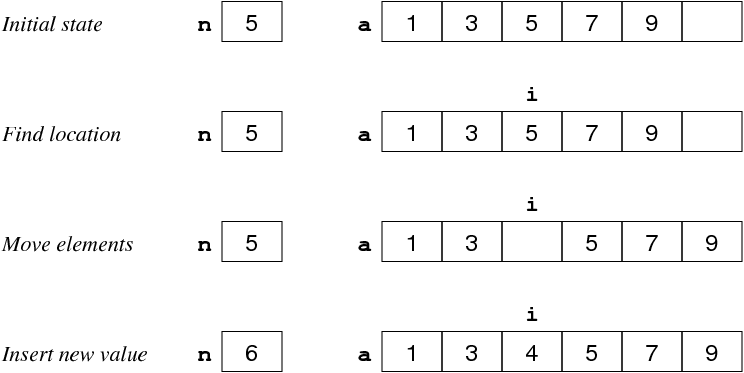
Why does indexing in an array start with 0?
An array arr[i] is interpreted as *(arr+i). Here, arr denotes the address of the first array element or the 0 index element. So *(arr+i) means the element at i distance from the first element of the array. So array index starts from 0 as initially i is 0 which means the first element of the array.
Is the first number in an array 0?
Zero-based array indexing is a way of numbering the items in an array such that the first item of it has an index of 0, whereas a one-based array indexed array has its first item indexed as 1.
What is the starting index of an array?
0Note: In most programming languages, the first array index is 0 or 1, and indexes continue through the natural numbers. The upper bound of an array is generally language and possibly system specific.
Why do JavaScript arrays start at 0?
Arrays in JavaScript are zero-based. This means that JavaScript starts counting from zero when it indexes an array. In other words, the index value of the first element in the array is “0” and the index value of the second element is “1”, the third element's index value is “2”, and so on.
Do arrays start at 0 or 1 java?
The indexes of elements in a Java array always start with 0 and continue to the number 1 below the size of the array. Thus, in the example above with an array with 10 elements the indexes go from 0 to 9.
Is it possible to change the starting index of an array from 0 to 1?
Explanation: No. You can not change the C Basic rules of Zero Starting Index of an Array.
What is the first index in an array in C?
0Arrays in C are indexed starting at 0, as opposed to starting at 1. The first element of the array above is point[0]. The index to the last value in the array is the array size minus one. In the example above the subscripts run from 0 through 5.
Why do programming languages count from 0?
Counting from zero encourages us to use asymmetric ranges to express intervals. [0, rows) instead of [1, rows] and that's easier to use because [m, n) has n-m elements, while [m, n] has n-m+1.
Why does Python use zero indexing?
The first element of the array is exactly contained in the memory location that array refers (0 elements away), so it should be denoted as array[0]. Most programming languages have been designed this way, so indexing from 0 is pretty much inherent to the language as most of the languages (not all) follow C standards.
Why does an array start at 0 and not 1?
It's all about Pointers! A pointer (array) is a memory direction and index is an offset of that memory direction, so the first element of the pointer (array) is the one who offset is equal to 0. @drhirsch because when we count a set of objects, we begin by pointing at an object and saying "one".
Is JavaScript 0 indexed?
JavaScript arrays are zero-indexed: the first element of an array is at index 0 , the second is at index 1 , and so on — and the last element is at the value of the array's length property minus 1 .
What is the need of index in an array?
The index indicates the position of the element within the array (starting from 1) and is either a number or a field containing a number.
What is the starting index of an array in C?
0Arrays in C are indexed starting at 0, as opposed to starting at 1. The first element of the array above is point[0]. The index to the last value in the array is the array size minus one.
Is Java 0 based?
Java uses zero-based indexing because c uses zero-based indexing. C uses zero-based indexing because an array index is nothing more than a memory offset, so the first element of an array is at the memory it's already pointing to, *(array+0) .
Why do programming languages count from 0?
Counting from zero encourages us to use asymmetric ranges to express intervals. [0, rows) instead of [1, rows] and that's easier to use because [m, n) has n-m elements, while [m, n] has n-m+1.
What is the memory address of the first element of an array called?
The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical concept of a matrix can be represented as a two-dimensional grid, two-dimensional arrays are also sometimes called matrices.