Why is the Grignard reaction so synthetically useful?
Grignard reagents are used synthetically to form new carbon–carbon bonds. A Grignard reagent has a very polar carbon–magnesium bond in which the carbon atom has a partial negative charge and the metal a partial positive charge.
What are Grignard reactions used for in the real world?
Grignard reagents are commonly used to manufacture chemo-catalyst for its application in pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Due to the development of eco-friendly products with soil enriching properties, the market for Grignard reagents is making a leeway in the agrochemical industry.Jan 11, 2017
Is the Grignard reaction environmentally friendly?
A critical chemical reaction that uses the volatile metal magnesium and flammable solvents such as ether to create new carbon bonds, each company depends on the Grignard reaction for production of many of their pharmaceuticals. Each agrees it's an unsafe and non-environmentally friendly process.Aug 30, 2011
How do you synthesize Grignard reagent?
0:049:14Organic Chemistry: Synthesis of a Grignard Reagent - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOur grignard reagent is used to make carbon-carbon double bonds grignard reagents are made up of anMoreOur grignard reagent is used to make carbon-carbon double bonds grignard reagents are made up of an alkyl group a magnesium atom and an halogen.
Where are Grignard reagents used?
Grignard reagents can be used for determining the number of halogen atoms present in a halogen compound. Grignard degradation is used for the chemical analysis of certain triacylglycerols as well as many cross-coupling reactions for the formation of several carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds.
Does using iodine as an additive improve the Grignard reaction?
Addition of iodine is to help remove any MgO on the surface of the Mg. Removing MgO allows for Mg and the aryl/alkyl halide to come in contact and react. Sonication or addition of methyl iodide or 1,2-dibromoethane can also help with initiation.
How many types of chemical reactions are there?
5The 5 primary types of chemical reactions are: Combination reaction. Decomposition reaction....Combination Reaction. A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is known as a combination reaction. ... Decomposition Reaction. ... Displacement Reaction. ... Double Displacement Reaction. ... Precipitation Reaction.
Why can't Grignard reagents react with water?
Water or alcohols would protonate and thus destroy the Grignard reagent, because the Grignard carbon is highly nucleophilic. This would form a hydrocarbon.
Which substrate would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent?
The most reactive alkyl halide is an iodide, followed by bromide and chloride. Fluoride is unreactive, so the alkyl fluoride will not generate a Grignard reagent.
Which of following can be used as solvent for Grignard reagent?
Dry etherDry ether is used as a solvent in the preparation of Grignard reagent.Mar 12, 2022
What is an example of a solvent?
One such example is the Grignard reagent, represented as R—Mg—X, which can be prepared from haloalkanes as well as from aryl halides.
What is the reaction between aryl and vinyl halides?
Haloalkanes and aryl and vinyl halides react with magnesium metal to yield organomagnesium halides called Grignard reagents. An ether solvent, usually diethyl ether, is required for preparation of Grignard reagents. The French chemist Victor Grignard discovered this reaction over a century ago in 1900.
What is the polarity of Grignard reagent?
Grignard reagents are used synthetically to form new carbon–carbon bonds. A Grignard reagent has a very polar carbon–magnesium bond in which the carbon atom has a partial negative charge and the metal a partial positive charge. The polarity of the carbon–magnesium bond is opposite that of the carbon–halogen bond of haloalkanes.
Why is Grignard a reactive reactant?
Because the carbon atom in a Grignard reagent has a partial negative charge, it resembles a carbanion, and it reacts with electrophiles. Grignard reagents are very reactive reactants that are used synthetically to form new carbon-carbon bonds. We will discuss these reactions in Section 10.6.
How do alkynides react with carbonyl groups?
Alkynide ions react with carbonyl groups in much the same way as Grignard reagents do. We recall that these ions are effective nucleophiles that will displace a halide ion from an alkyl halide to give an alkylated alkyne. The alkynides are prepared in an acid–base reaction with acetylene or a terminal alkyne using sodium amide in ammonia. If a carbonyl compound is then added to the reagent, an alcohol forms after acid work-up. If the alkynide is derived from acetylene, an acetylenic alcohol forms.
What is the name of the compound that reacts with magnesium metal?
Haloalkanes and other compounds with the halogen atom bonded to either sp 3 -hybridized or sp 2 -hybridized carbon atoms (aryl and vinyl halides) react with magnesium metal to yield organomagnesium halides called Grignard reagents. Grignard reagents are usually prepared in diethyl ether (CH 3 CH 2 O─CH 2 CH 3 ). An ether solvent is essential for the reaction. The French chemist Victor Grignard discovered this reaction in 1900, and it has been studied and used extensively ever since.
Why is the boiling point of cyclic ether higher than the rate of the reaction?
The higher boiling point of the cyclic ether provides more vigorous reaction conditions, but the rate of the reaction is also increased because THF solvates the Grignard reagent better than diethyl ether. The solvent, either diethyl ether or THF, is an essential component of the reaction.
What is the Grignard reaction?
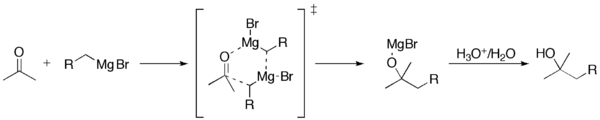
The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide (Grignard reagent) to a ketone or aldehyde, to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol, respectively . The reaction with formaldehyde leads to a primary alcohol. Grignard Reagents are also used in the following important reactions: The addition of an excess of a Grignard reagent ...
What happens after work up?
After work up, the starting ketone is recovered. A reduction can also take place, in which a hydride is delivered from the β-carbon of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl carbon via a cyclic six-membered transition state.
Is carboxylic acid chloride reactive?
With carboxylic acid chlorides: Esters are less reactive than the intermediate ketones, therefore the reaction is only suitable for synthesis of tertiary alcohols using an excess of Grignard Reagent: With nitriles: With CO 2 (by adding dry ice to the reaction mixture): With oxiranes: