Because radioactive decay is a first-order process, the time required for half of the nuclei in any sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is a constant, called the half-life of the isotope. The half-life tells us how radioactive an isotope is (the number of decays per unit time); thus it is the most commonly cited property of any radioisotope.
What is the formula for calculating half life?
log 1 / 2 ( N ( t) N 0) = t t 1 / 2 {displaystyle log _ {1/2}left ( {frac {N (t)} {N_ {0}}}right)= {frac {t} {t_ {1/2}}}} Multiply both sides by. t 1 / 2 {displaystyle t_ {1/2}} and divide both sides by the entire left side to solve for half-life.
What is the formula for first order half life?
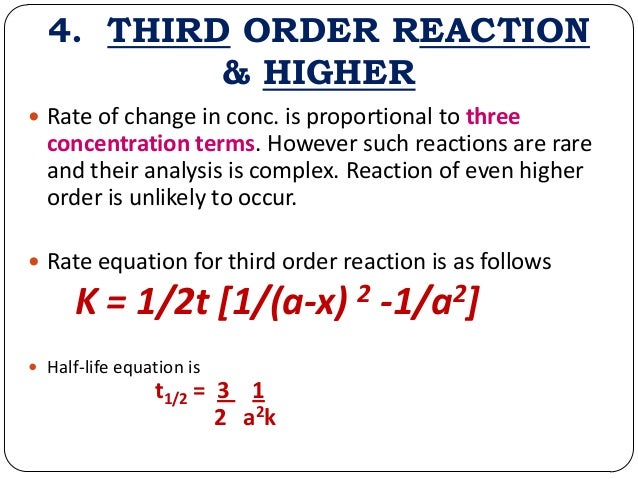
- The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is, t1/2 = R 0/2k
- For the first-order reaction, the half-life is defined as t1/2 = 0.693/k
- And, for the second-order reaction, the formula for the half-life of the reaction is given by, 1/k R 0
How to solve half life problem?
half-life. Definition: Half Life The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for half the substance to decay. Given the basic exponential growth/decay equation (h(t)=ab^{t}), half-life can be found by solving for when half the original amount remains; by solving (dfrac{1}{2} a=a(b)^{t}), or more simply (dfrac{1}{2} =b^{t}).
What is the formula for half lives?
Half life formula is: Half-life (t 1 / 2) = t log 2 log (N o N t) 2. Where. N o = Initial mass of the substance . N t = Quantity os the substance remaining. t = Time elapsed . t 1 2 = Half life of the substance . Example 1

Is half-life of first order constant?
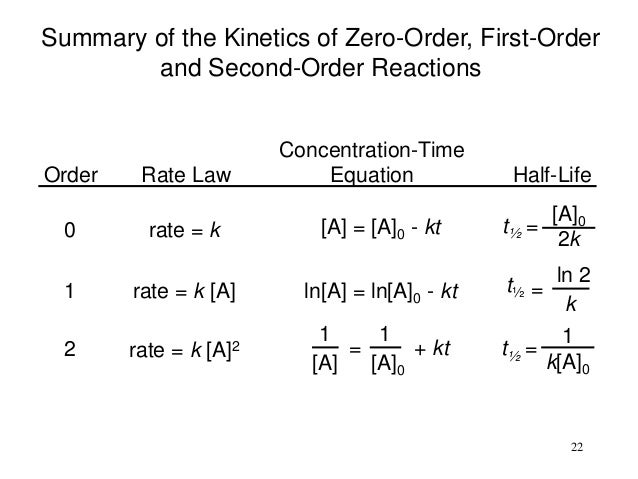
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for a reactant to reach one-half its initial concentration or pressure. For a first-order reaction, the half-life is independent of concentration and constant over time.
Is a first order reaction constant?
Half-lives of first order reactions. The half-life (t1/2) is a timescale on which the initial population is decreased by half of its original value, represented by the following equation. This indicates that the half-life of a first-order reaction is a constant.
What is the half-life of reaction in first order reaction?
0.693/kDerivation of Half-Life Formula for First-Order Reactions Thus, the half-life of a first-order reaction is given by 0.693/k.
Does half-life depend on rate constant?
The half-life of a reaction is defined as the time required for the initial concentration of a reactant to be decreased by 50%. This is not the time for half of the reaction to occur! The half-life is related to the rate constant; thus, if we know the half-life we can also find the rate constant.
What does a first order rate constant mean?
The elimination rate constant (usually a first-order rate constant) represents the fraction of xenobiotics that is eliminated from the body during a given period of time.
For which order the rate of reaction is constant?
Integrated Rate Equation for Zero-Order Reactions k is the rate constant.
How do you find half-life of first order?
0:002:59Half-Life of a First-Order Reaction (Derivation) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHow do you find the half-life for a first-order reaction. Well at the half-life or the the half-lifeMoreHow do you find the half-life for a first-order reaction. Well at the half-life or the the half-life is the amount of time that it takes for the actual concentration to reach the initial concentration
What is half-life of first order reaction if time is required to decrease?
What is half life of first order reaction if time required to decrease concentration of reactants from 0.8M to 0.2M is 12 hrs.
What is half-life derive the relationship between half-life and rate constant for the first order reaction?
The relation between half-life and rate constant for first-order reaction: The integrated rate law for the first-order reaction is k = t A A t 2.303 t log 10 [ A ] 0 [ A ] t where, [A]0 is the initial concentration of reactant at t = 0. It falls to [A]t at time t after the start of the reaction.
Is half-life of first order reaction depends on temperature?
With increase in the temperature, the value of the rate constant increases and the value of the half life period decreases. For the first order reaction the half-life period \[{t_{1/2}}\] , is independent of the initial concentration of reactants.
Is the half-life of first order reaction dependent on temperature?
As temperature increases, rate constant also increases and half life decreases. (half-life is inversely proportional to rate constant).
Is half-life of first order reaction is independent of temperature?
Although the first-order half-life depends on the rate constant k and not the initial concentration [A]0 , k is a function of temperature, and increases with increasing temperature.
What are the characteristics of first order reaction?
A first-order reaction can be defined as a chemical reaction in which the reaction rate is linearly dependent on the concentration of only one reactant. In other words, a first-order reaction is a chemical reaction in which the rate varies based on the changes in the concentration of only one of the reactants.
How do you find the rate constant of a first order reaction?
Because this equation has the form y = mx + b, a plot of the natural log of [A] as a function of time yields a straight line. The rate constant for the reaction can be determined from the slope of the line, which is equal to -k.
What is 1st order reaction?
Definition of first-order reaction : a chemical reaction in which the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reacting substance — compare order of a reaction.
What is the unit of rate constant for 1st order reaction?
reciprocal secondsBecause the units of the reaction rate are always moles per liter per second, the units of a first-order rate constant are reciprocal seconds (s−1).
1. Explain half-life.
The half-life definition of chemistry is the time it takes for half an initial amount to disintegrate. The time that is required for half of a reac...
2. What is the Half-life of First-order Reaction?
The half-life of first-order reaction is defined, in which time the concentration of the reactants becomes half in a chemical reaction. Then it is...
3. What is Rapid Half Life?
Rapid is not usually tagged to Half-life. The Half life phrase refers to the time it takes for a product from ranging from drugs to radioactive ele...
4. What does a nuclear half-life refer to?
It is given as the time needed for one-half the atoms of a given amount of a radioactive substance, which is to disintegrate. Biologically, Half-li...
5. Where can I find a video resource to learn and understand the concept of half life for the first-...
Videos are a great way to understand and learn a new concept. Vedantu offers world-class teaching on its YouTube channels which can be accessed for...
What is the half life of a zero order reaction?
The mathematical expression can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is, t1/2 = R 0/2k
What is the unit of the rate constant for a half life of a zero order reaction?
For the half-life of zero-order reaction, the units of the rate constant are mol.L-1.s-1. And, an expression for a half-life of zero-order reaction's rate constant is given by,
What is the half life of a reaction?
The half-life chemistry or a half-life of a reaction, t1/2, is defined as the specific amount of time required for a reactant concentration to decrease by half when compared to its initial concentration. The half-life application is used in chemistry and in medicine to predict the concentration of a substance over time.
What is half life in radioactive atoms?
For example, if there is only one radioactive atom, and its half-life is just one second, there will not be "half of the atom" left after that one second. Instead, the half-life definition is defined in terms of probability as "Half-life is the required time exactly for half of the entities to decay on average".
What is the t1/2 of a reaction?
For a given half-life reaction, the t1/2 of a reactant is the time required for its concentration to reach a value, the arithmetic mean of its initial and final (or equilibrium) value. For an entirely consumed reactant, it is the time taken for the reactant concentration to fall to one half of its initial value.
What does the number at the top mean in chemistry?
The number at the top is that of how many half-lives have elapsed. Note the consequences of the law of large numbers - with more atoms; the overall decay is more regular and predictable. Usually, Half-life chemistry describes the decay of discrete entities, such as radioactive atoms.
What is the rate constant of a reaction?
k is the rate constant of the reaction (unit - M(1-n)s-1, where ‘n’ is the order of reaction)
What is the half life of a reaction?
Explanation: The half-life of a chemical reaction, regardless of its order, is simply the time needed for half of an initial concentration of a reactant to be consumed by the reaction. Now, a first-order reaction is characterized by the fact that the rate of the reaction depends linearly on the concentration of one reactant.
Does the initial concentration of the reactant have an effect on the half life of the reaction?
In other words, the initial concentration of the reactant has no influence on the half-life of the reaction, i.e. the half-life is constant regardless of the concentration of the reactant. Answer link.
What is the formula for half life of a first order reaction?
As you have studied that half life of a first order reaction is constant at a given temperature because the formula of half life of a first order reaction is ln2/rate constant…and as you know that as the temperature increases the rate constant increases according to the Arrhenius equation so as the denominator increases the whole value decreases so half life of a first order reaction decreases on increasing temperature.
What is the half life of a reaction?
Thus the half-life of a reaction is the time required for the reactant concentration to decrease from [A]0 to [A]0/2. If two reactions have the same order, the faster reaction will have a shorter half-life, and the slower reaction will have a longer half-life.
Why does resistance increase with temperature?
The electrical resistance in a metal is due to a sea of electrons, the electron sea doesn’t have an intrinsic temperature dependence, however if you make apiece of metal longer, the resistance increases, because basically the electrons have to go further. All “pieces of metal” get longer as temperature increases this is known as the linear temperature coefficient of expansion or just CTE for short. All metals have a positive CTE on average. Some alloys can have nearly zero CTE, like Invar - Wikipedia (and some Invar alloys can have a small negative CTE over some temperature range, hence a nega
What is the first order reaction?
First order reactions are reactions in which the rate of the reaction at any given time is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant left at that time, or the active mass. These reactions take forever to finally get completed. The rate of the reaction decreases exponentially as the time slows down.
How does the rate of a reaction decrease exponentially?
The rate of the reaction decreases exponentially as the time slows down. The half life of the sample is just a constant value. After every half life, the amount of reactant gets halved. The rate constant and the half life are inversely proportional, none of which depends on the initial concentration of the sample.
What happens to the half life of a reaction if it is chemical?
If the system is chemical then the half -life will decrease as a function of the temperature. The precise change will be determined by the size of the activation energy for the reaction. But, if the first order reaction is nuclear (nuclear decay) then there will be no effect.
How is rate constant related to temperature?
Rate constant {k} is related to temperature as the above relation. As temperature increases , rate constant also increases and half life decreases. {half life is inversely proportional to rate constant}
Steps for Identifying Half-Life Given the Rate Constant
Step 1: Substitute the given rate constant into the half-life formula and calculate the half-life.
Formulas and Definitions for Identifying Half-Life Given the Rate Constant
First Order Reactions: A first-order reaction is a decomposition of a single reactant whose reaction rate is proportional to the concentration of that reactant to the first power. Thus, for the generalized decomposition of substance {eq}A {/eq}
Example Problem 1 - Identifying Half-Life Given the Rate Constant
Hydrogen peroxide solutions are stored in dark bottles to slow their decomposition. Outside the dark and at room temperature, this first-order reaction occurs with a rate constant of {eq}3.5\times10^ {-4} s^ {-1} {/eq}.
Example Problem 2 - Identifying Half-Life Given the Rate Constant
Sulfuryl chloride is a foul-smelling liquid. Its decomposition products are sulfur dioxide and chlorine, which do not make it more pleasant. The rate constant for the reaction is {eq}0.045 s^ {-1} {/eq}. What is its half-life?
Example Problem 3 - Identifying Half-Life Given the Rate Constant
0.0480 mol of dinitrogen pentoxide is placed in a 1.00 L container at 343 K. The {eq}N_2O_5 {/eq} decomposes at that temperature under first-order kinetics according to the reaction
What is the half life of a first order reaction?
Thus, the half-life of a first-order reaction is given by 0.693/k.
What is Reaction Half-Life?
The half-life of a chemical reaction can be defined as the time taken for the concentration of a given reactant to reach 50% of its initial concentration (i.e. the time taken for the reactant concentration to reach half of its initial value). It is denoted by the symbol ‘t 1/2 ’ and is usually expressed in seconds.
What is the rate constant of a reaction?
k is the rate constant of the reaction (unit: M (1-n) s -1 where ‘n’ is the reaction order)