Reasons for the Positive Slope of the Labor Supply Curve. An increase in the wage affects the quantity of labor supplied in three ways: An increase in hours worked per worker Occupational choice: a higher wage will attract workers to that occupation Migration: people will move to the city where wages in a given occupation are higher
Why does the supply curve have a positive slope?
The supply curve has a positive slope because of the relationship between a price change and quantity supplied. The Law of Supply tells us that as prices increase quantity supplied will increase as well and vise versa. The relationship between price and quantity supplied is positive or direct.
What is the labor supply curve?
The labor supply curve is the graphical representation of the relationship between the wage rate and the quantity of labor supplied. The wage rate is the price firms pay for employing labor at any point in time.
Why is the supply curve of a perfectly competitive market positive?
As a result, the price that they must receive to produce this output increases, in order to continue to receive a zero profit in a perfectly-competitive market. The explanation provided below describes the supply curve. The supply curve has a positive slope because of the relationship between a price change and quantity supplied.
What is the relationship between the wage rate and labor supply?
The labor supply curve graphically represents labor supply, showing the relationship between the wage rate and the quantity of labor supplied. The wage rate has a positive relationship with the quantity of labor supplied. This is because people are willing to supply more labor if the wage rate is higher.

Why is Labour supply curve positively sloped?
labour supply is the total number of hours that workers to work at a given wage rate. Such a comparison generally means that a higher wage entices people to spend more time working for pay; the substitution effect implies a positively sloped labour supply curve.
Why is supply of labour upwards sloping?
However, supply curves for labor in specific labor markets are generally upward sloping. As wages in one industry rise relative to wages in other industries, workers shift their labor to the relatively high-wage one. An increased quantity of labor is supplied in that industry.
What is the slope of the Labour supply curve?
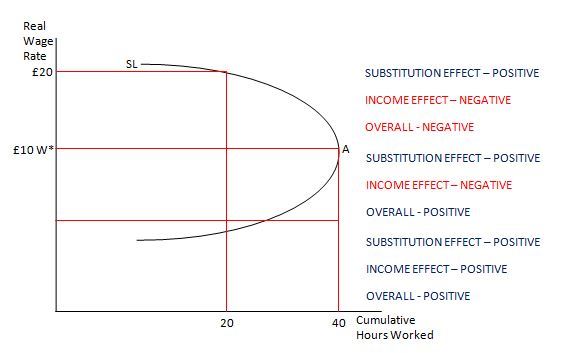
In other words, the supply curve of labour slopes backward, that is, slopes upward from right to left. It should be noted that it is the nature or pattern of indifference curves between income and leisure that yields backward sloping supply curve.
Why does the labor supply curve slope downward?
Labor demand curves slope downward because of the law of diminishing returns. As a firm hires more and more workers, each additional worker contributes less and less additional output—and revenue—to the firm.
What does the labor supply curve show?
An individual's labor supply curve marks out the number of hours they are willing to work at different wages, the same way that a seller's supply curve marks out how much they are willing to sell at different prices.
Can the labor supply curve be downward sloping?
The curve representing the hours of work supply could be downward sloping, especially among the population with lower incomes.
Why does the demand for labor have a downward slope quizlet?
The demand curve for labor is downward sloping because: marginal productivity is falling. A firm will only hire an additional worker if: marginal revenue product is greater than or equal to the additional cost associated with hiring the worker.
How does the supply curve shift?
A change in attitudes toward work and leisure can shift the supply curve for labor. If people decide they value leisure more highly, they will work fewer hours at each wage, and the supply curve for labor will shift to the left. If they decide they want more goods and services , the supply curve is likely to shift to the right.
Why do people supply labor?
People supply labor in order to increase their utility— just as they demand goods and services in order to increase their utility. The supply curve for labor will shift in response to changes in the same set of factors that shift demand curves for goods and services.
What happens to the marginal utility of the remaining leisure time?
As the individual does so, however, the marginal utility of the remaining leisure time rises and the marginal utility of the income earned will fall. The individual will continue to make the substitution until the two sides of the equation are again equal.
What is demand for labor?
The demand for labor is one determinant of the equilibrium wage and equilibrium quantity of labor in a perfectly competitive market. The supply of labor, of course, is the other. Economists think of the supply of labor as a problem in which individuals weigh the opportunity cost of various activities that can fill an available amount ...
Why do labor organizations oppose immigration?
Labor organizations have generally opposed increases in immigration because their leaders fear that the increased number of workers will shift the supply curve for labor to the right and put downward pressure on wages.
What is the effect of higher wages on the price of leisure?
The higher wage increases the price of leisure. We saw in the chapter on consumer choice that consumers substitute more of other goods for a good whose price has risen. The substitution effect of a higher wage causes the consumer to substitute labor for leisure.
What is the opportunity cost of leisure?
Second, the opportunity cost or “price” of leisure is the wage an individual can earn. A worker who can earn $10 per hour gives up $10 in income by consuming an extra hour of leisure. The $10 wage is thus the price of an hour of leisure. A worker who can earn $20 an hour faces a higher price of leisure.
